The Rassemblement Démocratique Africain, commonly known as the RDA and variously translated as African Democratic Assembly and African Democratic Rally, was a political party in French West Africa and French Equatorial Africa which was important in the decolonization of the French empire. The RDA was composed of different political parties throughout the French colonies in Africa and lasted from 1946 until 1958. At certain points, the RDA was the largest political party in the colonies in Africa and played a key role in the French government headed by the Democratic and Socialist Union of the Resistance (UDSR). Although the regional party largely dissolved in 1958 with the independence votes for the colonies, many of the national parties retained the RDA in their name and some continue to do so. The political ideology of the party did not endorse outright secession of colonies from France, but it was anti-colonial and pan-Africanist in its political stances.

Elections in Benin take place within the framework of a multi-party democracy and a presidential system. Both the President and the National Assembly are directly elected by voters, with elections organised by the Autonomous National Electoral Commission (CENA).

Elections in Guinea-Bissau take place within the framework of a multi-party democracy and a semi-presidential system. Both the President and the National People's Assembly are directly elected by voters.

Elections in Gabon take place within the framework of a presidential multi-party democracy with the Gabonese Democratic Party, in power since independence, as the dominant party. The President and National Assembly are directly elected, whilst the Senate is indirectly elected.
Elections in the Philippines are of several types. The president, vice-president, and the senators are elected for a six-year term, while the members of the House of Representatives, governors, vice-governors, members of the Sangguniang Panlalawigan, mayors, vice-mayors, members of the Sangguniang Panlungsod/members of the Sangguniang Bayan, barangay officials, and the members of the Sangguniang Kabataan are elected to serve for a three-year term.

Elections in Niger take place within the framework of a semi-presidential system. The President and National Assembly are elected by the public, with elections organised by the Independent National Electoral Commission (CENI).

Guinea elects on the national level a head of state—the president—and a legislature. The president is elected for a five-year term by the people through a two-round system. The National Assembly has 114 members, elected for five-year terms, 38 members in single-seat constituencies and 76 members by proportional representation.

Elections in Togo take place within the framework of a presidential system. Both the President and the National Assembly are directly elected by voters. Togo is a one party dominant state with the Union for the Republic in power.

Elections in Zambia take place within the framework of a multi-party democracy and a presidential system. The President and National Assembly are simultaneously elected for five-year terms.
The 1951 Ontario general election was held on November 22, 1951, to elect the 90 members of the 24th Legislative Assembly of Ontario of the Province of Ontario.

Elections in Southern Rhodesia were used from 1899 to 1923 to elect part of the Legislative Council and from 1924 to elect the whole of the Legislative Assembly which governed the colony. Since the granting of self-government in 1923, Southern Rhodesia used the Westminster parliamentary system as its basis of government. The Political party that had most of the seats in the Legislative Assembly became the government. The person in charge of this bloc was the Premier, later renamed Prime Minister, who then chose his cabinet from his elected colleagues.

The National Assembly is the unicameral legislative house of the Parliament of Mauritania. The legislature currently has 176 members, elected for five-year terms in electoral districts or nationwide proportional lists.

General elections were held in South Africa on 16 April 1958. The result was a victory for the National Party, now under the leadership of J.G. Strijdom after the retirement of Daniel Malan in 1954. The opposition United Party campaigned for the first time under De Villiers Graaff, who would remain party leader for two decades.
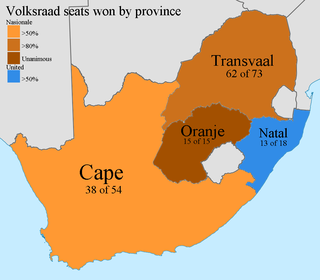
General elections were held in South Africa on 30 March 1966. The result was another comprehensive victory for the National Party under Hendrik Frensch Verwoerd.
Elections were held in the state of Western Australia on 24 April 1901 to elect 50 members to the Western Australian Legislative Assembly. It was the first election to take place since responsible government without the towering presence of Premier Sir John Forrest, who had left state politics two months earlier to enter the first Federal parliament representing the Division of Swan, and the first state parliamentary election to follow the enactment of women's suffrage in 1899.

The House of Assembly was the lower house of the Parliament of South Africa from 1910 to 1981, the sole parliamentary chamber between 1981 and 1984, and latterly the white representative house of the Tricameral Parliament from 1984 to 1994, when it was replaced by the current National Assembly. Throughout its history, it was exclusively constituted of white members who were elected to office predominantly by white citizens, though until 1960 and 1970, respectively, some Black Africans and Coloureds in the Cape Province voted under a restricted form of suffrage.

The first legislative assembly Election to the Madras state based on universal adult suffrage was held in 27 March 1952. This was the first election held in Madras state after the Indian Independence. This election was officially known as the 1951 Madras State Election, even though through delays, actual voting didn't take place until early 1952.

The Tamil Nadu Legislative Assembly is the unicameral legislature of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It has a strength of 234 members, all of whom are democratically elected using the first-past-the-post system. The presiding officer of the Assembly is the Speaker. The term of the Assembly is five years, unless dissolved earlier.
Legislative elections were held in New Caledonia on 8 February 1953.

General elections were held in the Territory of Papua and New Guinea between 15 February and 15 March 1964. They were the first elections in the territory held under universal suffrage. Voter turnout among enrolled voters was 65%.















