Norway elects its legislature on a national level. The parliament, the Storting, has 169 members elected for a four-year term by a form of proportional representation in multi-seat constituencies.

The 2004 Hong Kong Legislative Council election was held on 12 September 2004 for members of the Legislative Council of Hong Kong (LegCo). The election returned 30 members from directly elected geographical constituencies and 30 members from functional constituencies, of which 11 were unopposed.
At a national level, Greece holds elections for its legislature, the Hellenic Parliament.

Elections to the Russian Constituent Assembly were held on 25 November 1917. Organized as a result of events in the February Revolution, the elections took place two months after they had been originally meant to occur. They are generally recognised as the first free elections in Russian history, though they did not produce a democratically elected government, as the Bolsheviks subsequently disbanded the Constituent Assembly and proceeded to rule the country as a one-party state with all opposition parties banned.
India has a parliamentary system as defined by its constitution, with power distributed between the union government and the states. India's democracy is the largest democracy in the world.

Since its establishment in 1947, Pakistan has had a non-symmetric federal government and is a federal parliamentary democratic republic. At the national level, the people of Pakistan elect a bicameral legislature, the Parliament of Pakistan. The parliament consists of a lower house called the National Assembly, which is elected directly via first-past-the-post voting, and an upper house called the Senate, whose members are chosen by elected provincial legislators. The head of government, the Prime Minister, is elected by the majority members of the National Assembly and the head of state, the President, is elected by the Electoral College, which consists of both houses of Parliament together with the four provincial assemblies. In addition to the national parliament and the provincial assemblies, Pakistan also has more than five thousand elected local governments.

Parliamentary elections were held in Zimbabwe on 31 March 2005 to elect members to the Zimbabwe House of Assembly. All of the 120 elected seats in the 150-seat House of Assembly were up for election. There were a further 20 members appointed by the President and ten elected by traditional chiefs, who mostly support the government. Electoral colleges for the election of the ten chiefs to the parliament were to be held on 8 April.

The ninth Sarawak state election was held on Saturday, 20 May 2006 with nomination day on Tuesday, 9 May 2006. The election functioned to elect 71 representatives to the Sarawak State Assembly. The eighth state assembly was dissolved by Yang di-Pertua Negeri Sarawak, Tun Abang Muhammad Salahuddin Abang Barieng by the advice of Chief Minister Abdul Taib Mahmud, on 24 April 2006.
Wednesbury was a borough constituency in England's Black Country which returned one Member of Parliament (MP) to the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom from 1868 until it was abolished for the February 1974 general election.

General elections were held in India in five phases between 16 April 2009 and 13 May 2009 to elect the members of the fifteenth Lok Sabha. With a registered electorate of 716 million and a turnout of 417 million voters, it was the largest democratic election in the world until being surpassed by the 2014 general election.

General elections were held in Botswana on 16 October 2009, alongside local elections, with early voting in 26 polling stations abroad taking place 3 October. The result was a tenth successive victory for the Botswana Democratic Party, which won 45 of the 57 elected seats in the National Assembly.
There are five types of elections in the United Kingdom: elections to the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, elections to devolved parliaments and assemblies, local elections, mayoral elections, and Police and Crime Commissioner elections. Within each of those categories, there may also be by-elections. Elections are held on Election Day, which is conventionally a Thursday, and under the provisions of the Dissolution and Calling of Parliament Act 2022 the timing of general elections can be held at the discretion of the prime minister during any five-year period. All other types of elections are held after fixed periods, though early elections to the devolved assemblies and parliaments can occur in certain situations. The five electoral systems used are: the single member plurality system (first-past-the-post), the multi-member plurality, the single transferable vote, the additional member system, and the supplementary vote.

General elections were held in Libya on 17 January 1960 to elect the members of the House of Representatives, the lower house of Parliament.

The 2011 Hong Kong District Council elections were held on 6 November 2011. Elections were held to all 18 District Councils of Hong Kong, returning 412 members from directly elected constituencies, each selecting a council member. After the government's constitutional reform package was passed in 2010, five new seats in the Legislative Council would be created in which the candidates would be nominated by all District Councillors.

Elections for a General National Congress (GNC) were held in Libya on 7 July 2012, having been postponed from 19 June. They were the first elections since the overthrow and death of longtime ruler Muammar Gaddafi a year earlier, the first free national elections since 1952, and only the second free national elections since Libya gained independence in 1951.

The Delhi Legislative Assembly election was held on 4 December 2013, with the result announced on 8 December resulting in formation of the Fifth Legislative Assembly of Delhi.

General elections were held in Singapore on Friday, 10 July 2020 to elect 93 members to the Parliament of Singapore across 31 constituencies. Parliament was dissolved and the general election called by President Halimah Yacob on 23 June, on the advice of Prime Minister Lee Hsien Loong. It elected members of parliament to the 14th Parliament of Singapore since Singapore's independence in 1965, using the first-past-the-post electoral system.

Legislative Assembly elections were held in 2016 for 294 seats of the Vidhan Sabha in the Indian state of West Bengal. The All India Trinamool Congress under Mamata Banerjee won 211 seats, and thus was re-elected with an enhanced majority. Like in the 2011 election, the poll was held in six phases, with the first phase divided into two days. The first phase was held in Naxalite-Maoist affected red corridor areas with two polling dates: 4 April and 11 April. The other phases were held on 17, 21, 25, 30 April and 5 May. The result of the election was declared on 19 May.

The 2018 Karnataka Legislative Assembly election was held on 12 May 2018 in 222 constituencies to the Karnataka Legislative Assembly. The election was postponed in Jayanagar and Rajarajeshwari Nagar, following the death of the MLA B. N. Vijaya Kumar and a voter fraud scandal respectively till 28 May. The election saw a voter turnout of 72.13 per cent, the highest in Karnataka since several decades. The counting of votes took place on 15 May 2018.
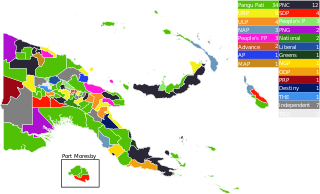
General elections were held in Papua New Guinea from 4 to 22 July 2022 to elect the members of the National Parliament for a new five-year term.















