
The Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) is a Taiwanese nationalist and centre-left political party in Taiwan. Controlling both the Taiwan Presidency and the unicameral Legislative Yuan, it is the majority ruling party and the dominant party in the Pan-Green Coalition.

The Legislative Yuan is the unicameral legislature of the Republic of China now based in Taiwan. It is one of the five branches of government stipulated by the Constitution of the Republic of China, which follows Sun Yat-sen's Three Principles of the People.

The National Assembly were several national parliamentary government organizations of the Republic of China, now commonly known as Taiwan.

During the National Constituent Assembly session on December 25, 1946 in Nanjing, the fifth and current Chinese constitution, known as the Constitution of the Republic of China, was ratified by the Kuomintang and adopted on December 25, 1947. Since 1949, the constitution, along with its Additional Articles, remains effective in ROC-controlled territories.

The Election for the 6th Legislative Yuan (第六屆立法委員選舉) of Taiwan was held on December 11, 2004. All 225 seats of the Legislative Yuan were up for election: 168 elected by popular vote, 41 elected on the basis of the proportion of nationwide votes received by participating political parties, eight elected from overseas Chinese constituencies on the basis of the proportion of nationwide votes received by participating political parties, eight elected by popular vote among the aboriginal populations. Members served three-year terms beginning on February 1, 2005, and ending January 31, 2008. The next term served four years.

This is a timeline of the Republic of China.

The Election for the 5th Legislative Yuan of Taiwan was held on 1 December 2001. All 225 seats of the Legislative Yuan were up for election: 168 elected by popular vote, 41 elected on the basis of the proportion of nationwide votes received by participating political parties, eight elected from overseas Chinese constituencies on the basis of the proportion of nationwide votes received by participating political parties, eight elected by popular vote among the Taiwanese aboriginal populations. Members served three year terms from February 1, 2002 to February 1, 2005.
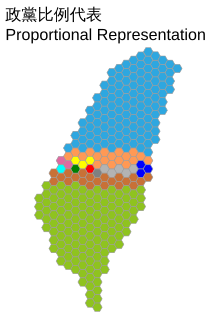
An election for the National Assembly took place in Taiwan on Saturday 14 May 2005, from 07:30 to 16:00 local time. It elected an ad hoc National Assembly whose only function was to serve as a constitutional convention in order to approve or reject amendments to the Constitution of the Republic of China already proposed by the Legislative Yuan. The results indicated that the amendments would be approved, as the parties supporting them won an overwhelming majority, and indeed the amendments were passed on June 7, 2005. The election was carried out using purely the party-list proportional representation system. The official campaign period was 07:00 to 22:00 each day from 4 May 2005 to 13 May 2005. Official election broadcasts by the ad hoc coalitions and (established) parties were provided by the Public Television Service Taiwan on 7 May 2005; several unofficial debates were also arranged. Notably, this election saw the temporary breakdown of the traditional two-coalition system in Taiwanese politics: instead of dividing into the Pan-Green Coalition and Pan-Blue Coalition over the political status of Taiwan, the parties divided themselves into larger and smaller parties, with the larger Democratic Progressive Party and Kuomintang in support of the amendments and the smaller People First Party and Taiwan Solidarity Union against them.

The Election for the 7th Legislative Yuan of Taiwan was held on January 12, 2008. The results gave the Kuomintang (KMT) and the Pan-Blue Coalition a supermajority in the legislature, handing a heavy defeat to then-President Chen Shui-bian's Democratic Progressive Party, which won the remaining 27 seats only. The junior partner in the Pan-Green Coalition, the Taiwan Solidarity Union, won no seats.
The First Legislative Representative Election of the Republic of China, and the preceding 1947 National Assembly Election were the Republic of China's first public direct elections since its founding. At the time most of China's territory was under the control of the Government of the Republic of China, using a direct voting system elected 759 Legislative Representatives. Using the Republic's then 461 million population to calculate, on average 600,000 people elected one representative in the Legislature. The election along with the one held for the National Assembly also made China the largest democracy at the time.

The Election for the 4th Legislative Yuan were held in Taiwan on 5 December 1998. The result was a victory for the Kuomintang, which won 123 of the 225 seats. Voter turnout was 68.1%.

The Government of the Republic of China, commonly known as the Government of Taiwan, is the democratic, constitutional government that exercises control over Taiwan and other islands in the free area. The president is the head of state. The government consists of Presidency and five branches (Yuan), the Executive Yuan, Legislative Yuan, Judicial Yuan, Examination Yuan, and Control Yuan.

The China Democratic Socialist Party was founded in Shanghai on 15 August 1946. It was formed through the merger of the former Chinese National Socialist Party and the Democratic Constitutionalist Party, both of which had survived the years of Japanese aggression by generally supporting the Kuomintang-led national government. The new party's first head was Carsun Chang.
The first supplementary elections took place for the National Assembly and the Legislative Yuan in the Republic of China on 20 December 1969. Voter turnout was 54.7% and 55.0% respectively.
The third supplementary elections for the Legislative Yuan were held in the Republic of China (Taiwan) on 20 December 1975.
The fourth supplementary elections for the National Assembly and Legislative Yuan were held in the Republic of China (Taiwan) on 6 December 1980.
The fifth supplementary elections for the Legislative Yuan were held in the Republic of China (Taiwan) on 3 December 1983.
The sixth supplementary elections for the National Assembly and Legislative Yuan were held in the Republic of China (Taiwan) on 6 December 1986.
The seventh and final supplementary elections for the Legislative Yuan were held in the Republic of China (Taiwan) on 3 December 1989.
General elections will be held in Taiwan, officially the Republic of China, on 11 January 2020 to elect the 15th President and Vice President of the Republic of China, and all 113 members of the 10th Legislative Yuan.











