
The politics of Guyana takes place in a framework of a representative democratic assembly-independent republic, whereby the President of Guyana is the head of government and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the President, advised by a cabinet. Legislative power is vested in both the President and the National Assembly of Guyana. The judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature.

Elections in Venezuela are held at a national level for the President of Venezuela as head of state and head of government, and for a unicameral legislature. The President of Venezuela is elected for a six-year term by direct election plurality voting, and is eligible for re-election. The National Assembly (Asamblea Nacional) has 165 members (diputados), elected for five-year terms using a mixed-member majoritarian representation system. Elections also take place at state level and local level.

Elections in Angola take place within the framework of a multi-party democracy. The National Assembly is directly elected by voters, while the leader of the party or coalition with the most seats in the National Assembly automatically becomes President.

Elections in Guyana take place within the framework of a multi-party representative democracy and a presidential system. The National Assembly is directly elected, with the nominee of the party or alliance that receives the most votes becoming President.

The People's Progressive Party/Civic (PPP/C) is a major political party in Guyana. As of 2020, the party holds 33 of the 65 seats in the National Assembly and forms the government. It has been the ruling party in the past as well, most recently between 1992 and 2015. In Guyana's ethnically divided political landscape, the PPP/C is a multi-ethnic organization that is supported primarily by Indo-Guyanese people.

The People's National Congress Reform (PNCR) is a social-democratic and democratic socialist political party in Guyana led by Aubrey Norton. The party currently holds 31 of the 65 seats in the National Assembly. In Guyana's ethnically divided political landscape, the PNCR is a multi-ethnic organization.

A parliamentary election was held in the Philippines on April 7, 1978, for the election of the 165 regional representatives to the Interim Batasang Pambansa. The elections were participated in by the leading opposition party, the Lakas ng Bayan (LABAN), which had twenty-one candidates for the Metro Manila area while the leading candidate was the jailed opposition leader Ninoy Aquino, and the Marcos regime's party known as the Kilusang Bagong Lipunan (KBL), which was led by the then-First Lady Imelda Marcos. Ninoy was allowed to run by his fellow partymates under the Liberal Party, who boycotted the election and was not allowed to campaign, and so his family campaigned for him. The night before the election on April 6, 1978, a noise barrage was organized by the supporters of (LABAN) which occurred up to dawn.

General elections were held in Guyana on 15 December 1997. The result was a victory for the People's Progressive Party/Civic, which won 29 of the 53 seats. Voter turnout was 88.4%.
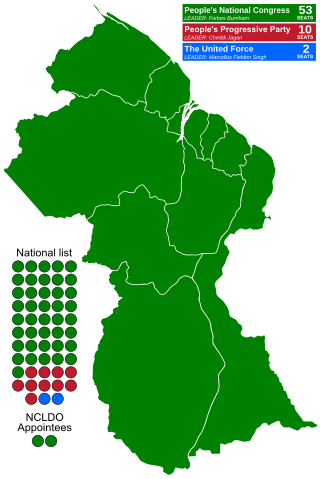
General elections were held in Guyana on 19 March 2001. The result was a victory for the People's Progressive Party/Civic, which won 34 of the 65 seats. Voter turnout was 91.7%.

The Constitution of Guyana is the highest governing document in the Republic of Guyana. It came into effect on October 6, 1980, replacing the constitution enacted in 1966 upon its independence from the United Kingdom. The current Constitution of Guyana contains 12 chapters that are further divided into 232 articles. It also contains a preamble and an oath. Since its 1980 enactment, it has gone through multiple amendments.
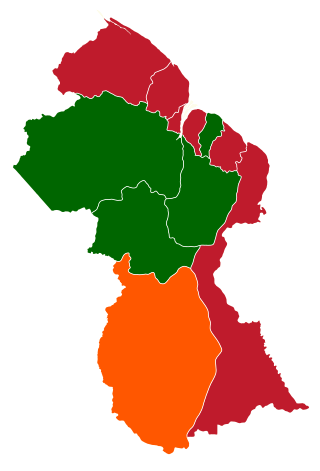
General elections were held in Guyana on 15 December 1980. The result was a victory for the People's National Congress, which won 41 of the 53 directly-elected seats. However, the PNC's victory was the result of fraud as the government had direct control of the elections. Voter turnout was 82.3%.

General elections were held in British Guiana on 27 April 1953. They were the first held under universal suffrage and resulted in a victory for the People's Progressive Party (PPP), which won 18 of the 24 seats in the new House of Assembly. Its leader, Cheddi Jagan, became Prime Minister.

General elections were held in British Guiana on 21 August 1961. The result was a victory for the People's Progressive Party, which won 20 of the 35 seats.

General elections were held in Guyana on 16 December 1968. The result was a victory for the People's National Congress, which won 30 of the 53 seats, although the PNC's victory was the result of fraud as the government had direct control of the elections. Voter turnout was 85.1%.

A constitutional referendum was held in Guyana on 10 July 1978. The proposed change to Article 73 of the constitution would abolish the need for referendums to change the entrenched provisions of the constitution and instead allow them to be changed by a two-thirds majority in parliament. It would also result in the postponement of the elections scheduled for later in the year, and instead the parliament elected in 1973 would be declared a Constituent Assembly.
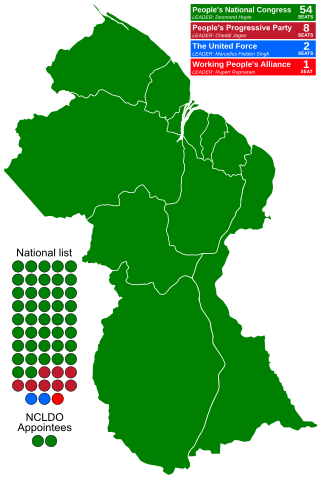
General elections were held in Guyana on 9 December 1985. The result was a victory for the People's National Congress, which won 42 of the 53 directly-elected seats. However, the elections were marred by fraud and the People's Progressive Party and Working People's Alliance withdrew on election day. Voter turnout was 73.8%.

General elections were held in Guyana on 5 October 1992. They were the first free and fair elections since 1964. The newly created People's Progressive Party/Civic alliance ended the People's National Congress' 28-year rule, winning 28 of the 53 seats and 53.5% of the vote following a landslide victory. Voter turnout was 80.4%.

A constitutional referendum was held in Uruguay on 25 November 1917. Amongst the changes to the system of government, the new constitution would create a National Council of Administration alongside the presidency. The National Council of Administration would have nine members; six from the winning party and three from the runner-up party. The proposals were approved by 95.15% of voters. The result was confirmed by the Senate on 18 December, and the new constitution came into force on 1 March 1919.

The House of Assembly was the legislature of British Guiana in the 1950s and 1960s.

The Legislative Assembly was the lower house of the Legislature in British Guiana between 1961 and 1964.















