
The Marshall Islands, officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands, is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the International Date Line. Geographically, the country is part of the larger island group of Micronesia. The country's population of 58,413 people is spread out over five islands and 29 coral atolls, comprising 1,156 individual islands and islets. The capital and largest city is Majuro. It has the largest portion of its territory composed of water of any sovereign state, at 97.87%. The islands share maritime boundaries with Wake Island to the north, Kiribati to the southeast, Nauru to the south, and Federated States of Micronesia to the west. About 52.3% of Marshall Islanders live on Majuro. In 2016, 73.3% of the population were defined as being "urban". The UN also indicates a population density of 760 inhabitants per square mile (295/km2), and its projected 2020 population is 59,190.

Palau, officially the Republic of Palau and historically Belau, Palaos or Pelew, is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the Caroline Islands with parts of the Federated States of Micronesia. It has a total area of 466 square kilometers (180 sq mi). The most populous island is Koror, home to the country's most populous city of the same name. The capital Ngerulmud is located on the nearby island of Babeldaob, in Melekeok State. Palau shares maritime boundaries with international waters to the north, the Federated States of Micronesia to the east, Indonesia to the south, and the Philippines to the northwest.

The Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI) was a United Nations trust territory in Micronesia administered by the United States from 1947 to 1994.
An associated state is the minor partner in a formal, free relationship between a political territory and a major party—usually a larger nation.
Commonwealth is a term used by two unincorporated territories of the United States in their full official names, which are the Northern Mariana Islands, whose full name is Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, and Puerto Rico, which is named Commonwealth of Puerto Rico in English and Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico in Spanish, translating to "Free Associated State of Puerto Rico." The term was also used by the Philippines during most of its period under U.S. sovereignty, when it was officially called the Commonwealth of the Philippines.

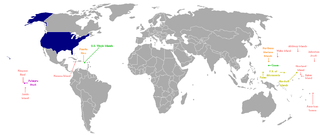
The Compact of Free Association (COFA) is an international agreement establishing and governing the relationships of free association between the United States and the three Pacific Island sovereign states of the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM), the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI), and the Republic of Palau. As a result, these countries are sometimes known as the Freely Associated States.

Throughout the history of Puerto Rico, its inhabitants have initiated several movements to obtain independence for the island, first from the Spanish Empire from 1493 to 1898 and since then from the United States.

Marshall Islands–United States relations are bilateral relations between Marshall Islands and the United States.
United Nations Security Council resolution 683, adopted on 22 December 1990, after recalling Resolution 21 (1947) which approved the Trusteeship Territory of the Japanese Mandated Islands as well as Chapter XII of the United Nations Charter which established the United Nations Trusteeship system, the council determined that, in the light of entry into force of new status agreements for Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands and the Northern Mariana Islands, the objectives of the Trusteeship Agreement had been completed and therefore ended the Trusteeship Agreement with those entities.

The political status of Puerto Rico is that of an unincorporated territory of the United States. As such, the island of Puerto Rico is neither a sovereign nation nor a U.S. state. Because of that ambiguity, the territory, as a polity, lacks certain rights but enjoys certain benefits that other polities have or lack. For instance, in contrast to U.S. states, Puerto Rico residents cannot vote in U.S. presidential elections nor can they elect their own senators and representatives to the U.S. Congress. On the other hand, in contrast to U.S. states, only some residents of Puerto Rico are subject to federal income taxes. The political status of the island thus stems from how different Puerto Rico is politically from sovereign nations and from U.S. states.

A referendum on the Compact of Free Association was held in Palau on 10 February 1983. Voters were asked three questions:
- Whether they approved of the Compact of Free Association between Palau and the United States
- Whether they approved of an agreement which placed restrictions on the USA with regard to storing and using radioactive, chemical and biological materials in Palau
- What their preference for a future political status was if the Free Association was rejected. They were offered the choice of either "a relationship with the United States closer than Free Association" or independence.

A second referendum on the Compact of Free Association was held in Palau on 4 September 1984, after the previous referendum had failed to achieve the 75% in favour necessary. Voters were asked two questions:
- Whether they approved of the proposed Compact of Free Association between Palau and the United States
- What their preference for a future political status was if the Free Association was rejected. They were offered the choice of a closer relationship than Trusteeship, or independence.

A referendum on the islands' status was held in the Federated States of Micronesia on 21 June 1983. Voters were asked two questions. The first was on whether they approved of the Compact of Free Association between the FSM and the United States. The second was what their preference was if Free Association was rejected. Voters were presented with the option of independence or an alternative which they had to fill in on the ballot form.
A referendum on the political status of Puerto Rico was held on December 13, 1998. Voters were given the choice between statehood, independence, free association, being a territorial commonwealth, or none of the given options. A majority voted for the latter, with a turnout of 71.3%.
The proposed political status for Puerto Rico encompasses the different schools of thought on whether Puerto Rico, currently an unincorporated territory of the United States in the form of a commonwealth, should change its current political status. Although there are many differing points of view, there are four that emerge in principle: that Puerto Rico maintains its current status, becomes a state of the United States, becomes fully independent, or becomes a freely associated state.

An independence referendum for Chuuk State to secede from the Federated States of Micronesia was originally scheduled to take place in March 2015. However, it has been delayed three times and it is uncertain if it will take place. The most populous of the four states within the FSM, Chuuk has high levels of unemployment and there are long-standing tensions over the distribution of funding within the FSM. Other concerns include political power within the federation and the preservation of cultural identity.
A referendum on the political status of Puerto Rico was held in Puerto Rico on June 11, 2017. The referendum had three options: becoming a state of the United States, independence/free association, or maintaining the current territorial status. Those who voted overwhelmingly chose statehood by 97%. This figure is attributed to a boycott led by the pro-status quo PPD party, which resulted in a 22.93% turnout.
Marshall Islands Nuclear Claims Tribunal is an international arbitral tribunal established pursuant to the Agreement Between the Government of the United States and the Government of the Marshall Islands for the Implementation of Section 177 of the Compact of Free Association. The Claims Tribunal has the "jurisdiction to render final determination upon all claims past, present and future, of the Government, citizens and nationals of the Marshall Islands which are based on, arise out of, or are in any way related to the [American] Nuclear Testing Program."
Marshallese nationality law is regulated by the Marshallese Constitution of 1979, as amended; the 1984 Citizenship Act of the Marshall Islands, and its revisions; and international agreements entered into by the Marshallese government. These laws determine who is, or is eligible to be, a national of the Marshall Islands. The legal means to acquire nationality, formal membership in a nation, differ from the domestic relationship of rights and obligations between a national and the nation, known as citizenship. Marshallese nationality is typically obtained either on the principle of jus soli, i.e. by birth in the Marshall Islands or under the rules of jus sanguinis, i.e. by birth abroad to parents with Marshallese nationality. It can be granted to persons with an affiliation to the country, or to a permanent resident who has lived in the country for a given period of time through naturalization.
Palauan nationality law is regulated by the 1980 Constitution of Palau, as amended; the 1994 Palau Citizenship Act, and its revisions; and international agreements entered into by the Palauan government. These laws determine who is, or is eligible to be, a national of Palau. The legal means to acquire nationality, formal legal membership in a nation, differ from the domestic relationship of rights and obligations between a national and the nation, known as citizenship. Palauan nationality is typically obtained either on the principle of jus soli, i.e. by birth in Palau or under the rules of jus sanguinis, i.e. by birth abroad to parents with Palauan nationality. It can be granted to persons with an affiliation to the country through naturalization.










