An earthquake – also called a quake, tremor, or temblor – is the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume.

The epicenter, epicentre, or epicentrum in seismology is the point on the Earth's surface directly above a hypocenter or focus, the point where an earthquake or an underground explosion originates.
The Peru–Chile Trench, also known as the Atacama Trench, is an oceanic trench in the eastern Pacific Ocean, about 160 kilometres (99 mi) off the coast of Peru and Chile. It reaches a maximum depth of 8,065 m (26,460 ft) below sea level in Richards Deep and is approximately 5,900 km (3,666 mi) long; its mean width is 64 km (40 mi) and it covers an expanse of some 590,000 km2 (230,000 sq mi).
Many major earthquakes have occurred in the region of the Kamchatka Peninsula in far eastern Russia. Events in 1737, 1923 and 1952, were megathrust earthquakes and caused tsunamis. There are many more earthquakes and tsunamis originating from the region.
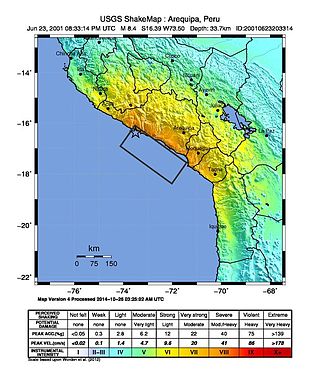
The 2001 southern Peru earthquake occurred at 20:33:15 UTC on June 23 with a moment magnitude of 8.4 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XII (Extreme). The quake affected the Peruvian regions of Arequipa, Moquegua and Tacna. It was the most devastating earthquake in Peru since the catastrophic 1970 Ancash earthquake and globally the largest earthquake since the 1965 Rat Islands earthquake.

The 1950 Assam–Tibet earthquake, also known as the Assam earthquake, occurred on 15 August and had a moment magnitude of 8.7. The epicentre was located in the Mishmi Hills. It is the strongest earthquake ever recorded on land.
The 2006 Kīholo Bay earthquake occurred on October 15 at with a magnitude of 6.7 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). The shock was centered 21 kilometers (13 mi) southwest of Puakō and 21 km (13 mi) north of Kailua-Kona, Hawaiʻi, just offshore of the Kona Airport, at a depth of 38.2 km (23.7 mi). It produced several aftershocks, including one that measured a magnitude of 6.1 seven minutes after the main shock. The Pacific Tsunami Warning Center measured a nondestructive tsunami of 4 in (100 mm) on the coast of the Big Island.

The 2007 Bengkulu earthquakes were a series of megathrust earthquakes that struck the Sunda Trench off the coast of Sumatra, Indonesia, with three of magnitude 7 or greater. A series of tsunami bulletins was issued for the area. The most powerful of the series had a magnitude of 8.4, which makes it in the top 20 of the largest earthquakes ever recorded on a seismograph.
The 2008 Peloponnese earthquake killed two people, injured more than 220 and left at least 2,000 people homeless in north western Peloponnese, Greece, on June 8. The earthquake hit the area at 1525 EET, with a moment magnitude of 6.5, according to the Athens Geodynamic Institute. It was strongly felt as far away as in Athens and in parts of southern Italy. The US Geological Survey reported that the quake had a magnitude of 6.4. The epicenter of the tremor was located about 15 miles (32 km) southwest of the Greek port city of Patras, at a depth of 16 km. Interior Minister Prokopis Pavlopoulos dispatched rescue and recovery teams, the Red Cross and units of the army in order to assess the damage and the needs of survivors in the earthquake affected areas.
The 2013 Okhotsk Sea earthquake occurred with a moment magnitude of 8.3 at 15:44:49 local time on 24 May. It had an epicenter in the Sea of Okhotsk and affected primarily Asian Russia, especially the Kamchatka Peninsula where the shaking lasted for five minutes.
The 1992 Murindó earthquake occurred on October 18 at 15:11 UTC with an epicenter in the Department of Chocó, northern Colombia. The shallow magnitude 7.2 earthquake struck northwest of the town of Murindó, killing ten and injured more than a hundred. Thirty-three municipalities were severely damaged.
An earthquake measuring 8.0 struck Peru and the surrounding areas on 26 May 2019 at 02:41 local time. It had a maximum perceived intensity of VII on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale in the towns of Yurimaguas and Lagunas. Two people died and a further 30 were injured. It was the strongest earthquake in 2019 by magnitude.
The 2018 Fiji earthquakes occurred on August 19, at 00:19:40 UTC and on September 6 15:49 UTC. The epicenters were located close to the Fijian island Lakeba, and around 270 km from the small town of Levuka on Ovalau. The first earthquake registered a magnitude of Mww 8.2, and is the largest earthquake of 2018. It had a focal depth of 600 km, making it the second largest earthquake ever recorded at a depth greater than 300 km; a tie with the 1994 Bolivia earthquake, and behind the 2013 Okhotsk Sea earthquake. The initial earthquake was caused by a normal fault below the South Pacific Ocean. A Mww 7.9 event struck the islands again on September 6 at a depth of 670 km; this earthquake was a mainshock of its own. Both earthquakes may be considered a doublet event.

The 2013 Craig, Alaska earthquake struck on January 5, at 12:58 am (UTC–7) near the city of Craig and Hydaburg, on Prince of Wales Island. The Mw 7.5 earthquake came nearly three months after an Mw 7.8 quake struck Haida Gwaii on October 28, in 2012. The quake prompted a regional tsunami warning to British Columbia and Alaska, but it was later cancelled. Due to the remote location of the quake, there were no reports of casualties or damage.

The 1993 Kushiro–Oki earthquake was one of two large earthquake to strike the Japanese island of Hōkkaido within the same year. The earthquake with a magnitude of 7.6 Mw or 7.8 MJMA struck at 11:06 UTC or 08:06 pm JST on January 15 near the town of Ashoro. Shaking reached a maximum intensity of IX (Violent) on the Mercalli intensity scale, causing considerable damage, and was felt throughout the island, into northern Honshu, Sakhalin, and the Kuril Islands. As a result of the tremors, two people were killed and more than 600 were wounded.
The 1906 Manasi earthquake (玛纳斯地震), also known as the Manas earthquake occurred in the morning of December 23, 1906, at 02:21 UTC+8:00 local time or December 22, 18:21 UTC. It measured 8.0–8.3 on the moment magnitude scale and 8.3 on the surface-wave magnitude scale. The epicenter of this earthquake is located in Manas County, Xinjiang, China. An estimated 280–300 people died and another 1,000 more were injured by the earthquake.
The 2020 Kashgar earthquake, also known as the Jiashi earthquake occurred on 19 January 2020 at 21:27:56 China Standard Time in Xinjiang Province, China. According to the United States Geological Survey, the earthquake had a moment magnitude of 6.0 and a surface-wave magnitude of 6.4 according to the China Earthquake Network Center. It struck at a shallow depth of 5.6 km according to the USGS while the CENC has the figure at 16 km. Local emergency management agencies said the earthquake damaged more than 1,000 homes and businesses in the nearby populated towns and villages. One person is known to have died while two other children were injured.
The 1889 Chilik earthquake occurred on July 11 on the Gregorian calendar, or June 30 on the Julian calendar at 15:14 local time in the Tien Shan mountains. The earthquake measured an estimated Mw 7.9–8.0 on the moment magnitude scale and was assigned a maximum intensity of X (Devastating) on the MSK 64 and Rossi-Forel scales. Over 92 people across Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and China were killed.
The 1947 Satipo earthquake was the largest earthquake in the sub-Andean region of Peru. It occurred on November 1 at 09:58:57 local time with an epicenter in the Department of Junín. The earthquake had an estimated moment magnitude (Mw ) of 7.7 and focal depth of 20 km (12 mi). Damage was severe in the towns of Satipo and La Merced, and at least 233 people died.
The 2016 Alboran Sea earthquake struck offshore, north northeast of Al Hoceïma, Morocco in the Strait of Gibraltar on 25 January at 04:22:02 UTC, or roughly 05:22:02 West Africa Time. At its strongest in the Alboran Sea, the earthquake measured 6.3–6.4 on the moment magnitude scale (Mw ) at a shallow hypocenter depth of 12 km (7.5 mi). Assigned a maximum Modified Mercalli scale intensity of VI (Strong), the earthquake caused one fatality, injuries to at least 30 persons, and moderate damage in Morocco and Spain.