Presidential elections were held in Croatia for the first time on 2 August 1992 alongside simultaneous parliamentary elections. The result was a victory for incumbent Franjo Tuđman of the Croatian Democratic Union (HDZ), who received 57.8% of the vote, becoming the first popularly elected president of Croatia. Voter turnout was 74.9%.

The current Constitution of France was adopted on 4 October 1958. It is typically called the Constitution of the Fifth Republic(French: Constitution de la Ve République), and it replaced the Constitution of the Fourth Republic of 1946 with the exception of the preamble per a Constitutional Council decision in July 1971. The current Constitution regards the separation of church and state, democracy, social welfare, and indivisibility as core principles of the French state.

The Party of Communists of the Republic of Moldova is a communist party in Moldova led by Vladimir Voronin. It is the only communist party to have held a majority government in the post-Soviet states. It has been variously described as communist, Moldovenist, populist, and Russophile.

The Constitution of the Republic of Lithuania defines the legal foundation for all laws passed in the Republic of Lithuania. It was approved in a referendum on 25 October 1992.

The President of the Republic of Moldova is the head of state of Moldova. The current president is Maia Sandu, who assumed office on 24 December 2020.
A four-part referendum was held in Ukraine on 16 April 2000. The referendum was called by President Leonid Kuchma, and asked voters whether they approved of four amendments to the constitution that would increase the powers of the President and introduce an upper chamber.

A four-part referendum was held in Russia on 25 April 1993. Voters were asked questions on confidence in President Boris Yeltsin, support for the government's socio-economic policies and early elections for both the presidency and parliament. The referendum was initiated by the Congress of People's Deputies, which stipulated that Yeltsin would need to obtain 50% of the electorate, rather than 50% of valid votes. However, the Constitutional Court ruled that the president required only a simple majority on two issues: confidence in him, and economic and social policy; though he would still need the support of more than half the electorate in order to call new parliamentary and presidential elections.

A seven-question referendum was held in Belarus on 24 November 1996. Four questions were put forward by President Alexander Lukashenko on changing the date of the country's independence day, amending the constitution, changing laws on the sale of land and the abolition of the death penalty. The Supreme Council put forward three questions on constitutional amendments by the Communist and Agrarian factions, local elections and the national finances.

A referendum on remaining an independent nation was held in Moldova on 6 March 1994. Initiated by President Mircea Snegur, it was referred to as a "Consultation with the people", and was approved by 97.9% of voters.

A constitutional referendum was held in Russia on 12 December 1993. The new constitution was approved by 58.4% of voters, and came into force on 25 December.

A constitutional referendum was held in France on 5 May 1946. Voters were asked whether they approved of a new draft Constitution proposed by the Constituent Assembly elected in 1945.

A referendum on the method of the election of the president was held in France on 28 October 1962. The question was whether to have the President of the French Republic elected by direct popular vote, rather than by an electoral college. It was approved by 62.3% of voters with a 77.0% turnout. The reform was controversial because it strengthened the executive at the expense of Parliament, and because of the disputed constitutionality of the procedure used.
A constitutional referendum was held in Denmark on 23 May 1939. Voters were asked whether they approved of a new constitution. Although it was approved by 91.9% of those who voted, a turnout of only 48.9% meant that the percentage of eligible voters approving it was only 44.46%, below the 45% required by the existing constitution of 1915.
A constitutional referendum was held in Iceland between 20 and 23 May 1944. The 1 December 1918 Danish–Icelandic Act of Union declared Iceland to be a sovereign state separate from Denmark, but maintained the two countries in a personal union, with the King of Denmark also being the King of Iceland. In the two-part referendum, voters were asked whether the Union with Denmark should be abolished, and whether to adopt a new republican constitution. Both measures were approved, each with more than 98% in favour. Voter turnout was 98.4% overall, and 100% in two constituencies, Seyðisfirði and Vestur-Skaftafjellssýsla.
Presidential elections were held in Moldova on 17 November 1996, with a second round on 1 December. Whilst incumbent President Mircea Snegur received the most votes in the first round, he was defeated in the second by Petru Lucinschi.

A constitutional referendum was held in the Republic of Dahomey on 5 January 1964. The main issues were changing the system of government to a presidential system, scrapping term limits for the president, and having a unicameral parliament. The referendum passed with 99.86% of voters approving the changes. Turnout was 92% of the 1,051,614 registered voters.

A constitutional referendum was held in the Republic of Dahomey on 31 March 1968. As with the 1964 referendum, the main issues were changing the system of government to a presidential system, scrapping term limits for the president, and having a unicameral parliament. The referendum passed with 92.2% of voters approving the changes. Turnout was 81.8% of the 1,126,155 registered voters.

The following is timeline of the History of independent Moldova which started after the independence of Moldova.
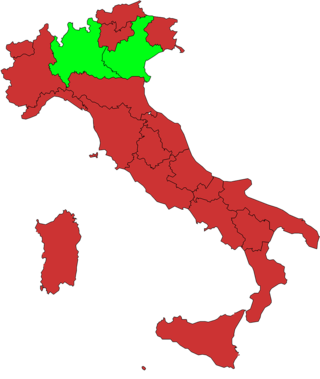
A constitutional referendum was held in Italy on 25 and 26 June 2006. The reforms were proposed and initially approved during Berlusconi II and III cabinet between October 2004 and November 2005. If ultimately approved by referendum, in continuation with the 2001 constitutional enacted modifications, these reforms would have substantially completed the transformation of Italy from a unitary state into a federal republic.
A referendum is a direct vote in which an entire electorate is asked to either accept or reject a particular proposal. This article summarises referendum laws and practice in various countries.












