
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction ; it has low resistance in one direction, and high resistance in the other. A diode vacuum tube or thermionic diode is a vacuum tube with two electrodes, a heated cathode and a plate, in which electrons can flow in only one direction, from cathode to plate. A semiconductor diode, the most commonly used type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of asymmetric electrical conduction across the contact between a crystalline mineral and a metal was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconducting materials such as gallium arsenide and germanium are also used.
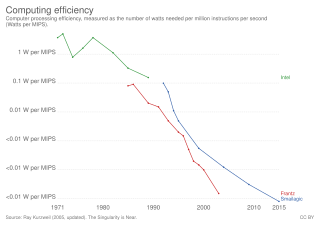
Instructions per second (IPS) is a measure of a computer's processor speed. For CISC computers different instructions take different amounts of time, so the value measured depends on the instruction mix; even for comparing processors in the same family the IPS measurement can be problematic. Many reported IPS values have represented "peak" execution rates on artificial instruction sequences with few branches and no cache contention, whereas realistic workloads typically lead to significantly lower IPS values. Memory hierarchy also greatly affects processor performance, an issue barely considered in IPS calculations. Because of these problems, synthetic benchmarks such as Dhrystone are now generally used to estimate computer performance in commonly used applications, and raw IPS has fallen into disuse.

The Intel 4004 is a 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) released by Intel Corporation in 1971. It was the first commercially produced microprocessor, and the first in a long line of Intel CPUs.

The JEDEC Solid State Technology Association is an independent semiconductor engineering trade organization and standardization body headquartered in Arlington, Virginia, United States.

The Schottky diode, also known as Schottky barrier diode or hot-carrier diode, is a semiconductor diode formed by the junction of a semiconductor with a metal. It has a low forward voltage drop and a very fast switching action. The cat's-whisker detectors used in the early days of wireless and metal rectifiers used in early power applications can be considered primitive Schottky diodes.

In electronics, a varicap diode, varactor diode, variable capacitance diode, variable reactance diode or tuning diode is a type of diode designed to exploit the voltage-dependent capacitance of a reverse-biased p–n junction. VariCap Diodes are also called Varactor Diodes and are defined as whose internal capacitance changes with applied reverse bias voltage and Possess Variable Reactance

The 7400 series of integrated circuits (ICs) were one of the most popular logic families of transistor–transistor logic (TTL) logic chips. In 1964, Texas Instruments introduced the first members of their ceramic semiconductor package series, the SN5400s. A low-cost plastic package SN7400 series was introduced in 1966 which quickly gained over 50% of the logic chip market, and eventually becoming de facto standardized electronic components. Over the decades, many generations of pin-compatible descendant families evolved to include support for low power CMOS technology, lower supply voltages, and surface mount packages.
Pro Electron or EECA is the European type designation and registration system for active components.

The 555 timer IC is an integrated circuit (chip) used in a variety of timer, delay, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. Derivatives provide two (556) or four (558) timing circuits in one package. It was commercialized in 1972 by Signetics and it was reported to still be in wide use as of 2013. Numerous companies have made the original bipolar timers and similar low-power CMOS timers too. In 2017, it was said over a billion 555 timers are produced annually by some estimates, and "probably the most popular integrated circuit ever made."
A power semiconductor device is a semiconductor device used as a switch or rectifier in power electronics. Such a device is also called a power device or, when used in an integrated circuit, a power IC.
In computer engineering, a logic family may refer to one of two related concepts. A logic family of monolithic digital integrated circuit devices is a group of electronic logic gates constructed using one of several different designs, usually with compatible logic levels and power supply characteristics within a family. Many logic families were produced as individual components, each containing one or a few related basic logical functions, which could be used as "building-blocks" to create systems or as so-called "glue" to interconnect more complex integrated circuits. A "logic family" may also refer to a set of techniques used to implement logic within VLSI integrated circuits such as central processors, memories, or other complex functions. Some such logic families use static techniques to minimize design complexity. Other such logic families, such as domino logic, use clocked dynamic techniques to minimize size, power consumption and delay.

ON Semiconductor is a former Fortune 500 semiconductors supplier company, dropping into the Fortune 1000 in 2020. Products include power and signal management, logic, discrete, and custom devices for automotive, communications, computing, consumer, industrial, LED lighting, medical, military/aerospace and power applications. ON Semiconductor runs a network of manufacturing facilities, sales offices and design centers in North America, Europe, and the Asia Pacific regions. Headquartered in Phoenix, Arizona, ON Semiconductor has revenues of $3.907 billion (2016), which puts it among the worldwide top 20 semiconductor sales leaders.

The 2N3904 is a common NPN bipolar junction transistor used for general-purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. It is designed for low current and power, medium voltage, and can operate at moderately high speeds.

The 2N2222 is a common NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) used for general purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. It is designed for low to medium current, low power, medium voltage, and can operate at moderately high speeds. It was originally made in the TO-18 metal can as shown in the picture.

The 2N3906 is a commonly used PNP bipolar junction transistor intended for general purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. It is designed for low electric current and power and medium voltage, and can operate at moderately high speeds.

The 1N4148 is a standard silicon switching signal diode. It is one of the most popular and long-lived switching diodes because of its dependable specifications and low cost. Its name follows the JEDEC nomenclature. The 1N4148 is useful in switching applications up to about 100 MHz with a reverse-recovery time of no more than 4 ns.

DO-204 is a family of diode semiconductor packages defined by JEDEC. This family comprises lead-mounted axial devices with round leads. Generally a diode will have a line painted near the cathode end.

The 1N58xx is a series of medium power, fast, low voltage Schottky diodes, which consists of part number numbers 1N5817 through 1N5825.
The stabistor is the technical term used to designate a special type of semiconductor silicon diode featuring extremely stable forward voltage characteristics. These devices are specially designed for low-voltage stabilization applications requiring a guaranteed voltage over a wide current range and highly stable over temperature. In these applications, stabistors offer improved dynamic impedance than low voltage zener diodes where tunneling instead of avalanche current is dominant. Other typical applications include bias stabilization in class-AB output stages, clipping, clamping, meter protection, etc.



















