
2,4-Dinitrophenol (2,4-DNP or simply DNP) is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H3(NO2)2. It has been used in explosives manufacturing and as a pesticide and herbicide.

A defoliant is any herbicidal chemical sprayed or dusted on plants to cause their leaves to fall off. Defoliants are widely used for the selective removal of weeds in managing croplands and lawns. Worldwide use of defoliants, along with the development of other herbicides and pesticides, allowed for the Green Revolution, an increase in agricultural production in mid-20th century. Defoliants have also been used in warfare as a means to deprive an enemy of food crops and/or hiding cover, most notably by the United Kingdom during the Malayan Emergency and the United States in the Vietnam War. Defoliants were also used by Indonesian forces in various internal security operations.

Acetylacetone is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3−C(=O)−CH2−C(=O)−CH3. It is classified as a 1,3-diketone. It exists in equilibrium with a tautomer CH3−C(=O)−CH=C(−OH)−CH3. The mixture is a colorless liquid. These tautomers interconvert so rapidly under most conditions that they are treated as a single compound in most applications. Acetylacetone is a building block for the synthesis of many coordination complexes as well as heterocyclic compounds.

Amitraz is a non-systemic acaricide and insecticide and has also been described as a scabicide. It was first synthesized by the Boots Co. in England in 1969. Amitraz has been found to have an insect repellent effect, works as an insecticide and also as a pesticide synergist. Its effectiveness is traced back on alpha-adrenergic agonist activity, interaction with octopamine receptors of the central nervous system and inhibition of monoamine oxidases and prostaglandin synthesis. Therefore, it leads to overexcitation and consequently paralysis and death in insects. Because amitraz is less harmful to mammals, amitraz is among many other purposes best known as insecticide against mite- or tick-infestation of dogs. It is also widely used in the beekeeping industry as a control for the Varroa destructor mite, although there are recent reports of resistance.

m-Xylene (meta-xylene) is an aromatic hydrocarbon. It is one of the three isomers of dimethylbenzene known collectively as xylenes. The m- stands for meta-, indicating that the two methyl groups in m-xylene occupy positions 1 and 3 on a benzene ring. It is in the positions of the two methyl groups, their arene substitution pattern, that it differs from the other isomers, o-xylene and p-xylene. All have the same chemical formula C6H4(CH3)2. All xylene isomers are colorless and highly flammable.

4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, also known as p-hydroxybenzoic acid (PHBA), is a monohydroxybenzoic acid, a phenolic derivative of benzoic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water and chloroform but more soluble in polar organic solvents such as alcohols and acetone. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is primarily known as the basis for the preparation of its esters, known as parabens, which are used as preservatives in cosmetics and some ophthalmic solutions. It is isomeric with 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, known as salicylic acid, a precursor to aspirin, and with 3-hydroxybenzoic acid.
Xylidine can refer to any of the six isomers of xylene amine, or any mixture of them.

3,5-Xylidine is the organic compound with the formula C6H3(CH3)2NH2. It is one of several isomeric xylidines. It is a colorless viscous liquid. It is used in the production of the dye Pigment Red 149.

2,6-Xylidine is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(CH3)2NH2. It is one of several isomeric xylidines. It is a colorless viscous liquid. Commercially significant derivatives are the anesthetics lidocaine, bupivacaine, mepivacaine, and etidocaine.

2,5-Xylidine is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(CH3)2NH2. It is one of several isomeric xylidines. It is a colorless viscous liquid. Commercially significant derivatives include Solvent Yellow 30, Solvent Red 22, Acid Red 65, and Solvent Red 26.

2,6-Lutidine is a natural heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the formula (CH3)2C5H3N. It is one of several dimethyl-substituted derivative of pyridine, all of which are referred to as lutidines. It is a colorless liquid with mildly basic properties and a pungent, noxious odor.

2,4 Dienoyl-CoA reductase also known as DECR1 is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the DECR1 gene which resides on chromosome 8. This enzyme catalyzes the following reactions

In enzymology, a kynurenine-oxoglutarate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
2,4-Dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP) is a chlorinated derivative of phenol with the molecular formula Cl2C6H3OH. It is a white solid that is mildly acidic (pKa = 7.9). It is produced on a large scale as a precursor to the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D).

NESS-0327 is a drug used in scientific research which acts as an extremely potent and selective antagonist of the cannabinoid receptor CB1. It is much more potent an antagonist, and more selective for the CB1 receptor over CB2, than the more commonly used ligand rimonabant, with a Ki at CB1 of 350fM (i.e. 0.00035nM) and a selectivity of over 60,000x for CB1 over CB2. Independently, two other groups have described only modest nanomolar CB1 affinity for this compound (125nM and 18.4nM). Also unlike rimonabant, NESS-0327 does not appear to act as an inverse agonist at higher doses, instead being a purely neutral antagonist which blocks the CB1 receptor but does not produce any physiological effect of its own.
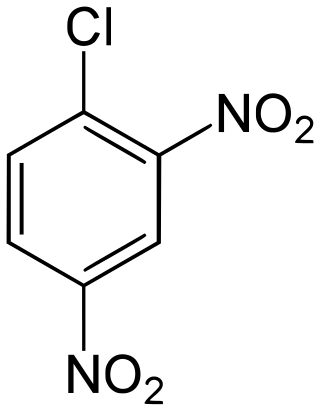
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (O2N)2C6H3Cl. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is an important intermediate for the industrial production of other compounds.

Anthony Joseph Arduengo III is Professor of the Practice at the Georgia Institute of Technology, Saxon Professor Emeritus of Chemistry at the University of Alabama, adjunct professor at the Institute for Inorganic Chemistry of Braunschweig University of Technology in Germany, and co-founder of the StanCE coalition for sustainable chemistry based on woody biomass. He is notable for his work on chemical compounds with unusual valency, especially in the field of stable carbene research.
Metal acetylacetonates are coordination complexes derived from the acetylacetonate anion (CH
3COCHCOCH−
3) and metal ions, usually transition metals. The bidentate ligand acetylacetonate is often abbreviated acac. Typically both oxygen atoms bind to the metal to form a six-membered chelate ring. The simplest complexes have the formula M(acac)3 and M(acac)2. Mixed-ligand complexes, e.g. VO(acac)2, are also numerous. Variations of acetylacetonate have also been developed with myriad substituents in place of methyl (RCOCHCOR′−). Many such complexes are soluble in organic solvents, in contrast to the related metal halides. Because of these properties, acac complexes are sometimes used as catalyst precursors and reagents. Applications include their use as NMR "shift reagents" and as catalysts for organic synthesis, and precursors to industrial hydroformylation catalysts. C
5H
7O−
2 in some cases also binds to metals through the central carbon atom; this bonding mode is more common for the third-row transition metals such as platinum(II) and iridium(III).
Electron-rich is jargon that is used in multiple related meanings with either or both kinetic and thermodynamic implications:

Pelanserin (TR2515) is a chemical compound that acts as an antagonist of the 5-HT2 and α1-adrenergic receptors.




















