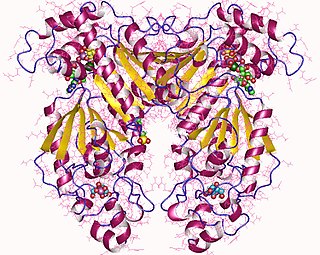
Phosphofructokinase-2 (6-phosphofructo-2-kinase, PFK-2) or fructose bisphosphatase-2 (FBPase-2), is an enzyme indirectly responsible for regulating the rates of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in cells. It catalyzes formation and degradation of a significant allosteric regulator, fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (Fru-2,6-P2) from substrate fructose-6-phosphate. Fru-2,6-P2 contributes to the rate-determining step of glycolysis as it activates enzyme phosphofructokinase 1 in the glycolysis pathway, and inhibits fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 in gluconeogenesis. Since Fru-2,6-P2 differentially regulates glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, it can act as a key signal to switch between the opposing pathways. Because PFK-2 produces Fru-2,6-P2 in response to hormonal signaling, metabolism can be more sensitively and efficiently controlled to align with the organism's glycolytic needs. This enzyme participates in fructose and mannose metabolism. The enzyme is important in the regulation of hepatic carbohydrate metabolism and is found in greatest quantities in the liver, kidney and heart. In mammals, several genes often encode different isoforms, each of which differs in its tissue distribution and enzymatic activity. The family described here bears a resemblance to the ATP-driven phospho-fructokinases, however, they share little sequence similarity, although a few residues seem key to their interaction with fructose 6-phosphate.

URB597 (KDS-4103) is a relatively selective and irreversible inhibitor of the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). FAAH is the primary degradatory enzyme for the endocannabinoid anandamide and, as such, inhibition of FAAH leads to an accumulation of anandamide in the CNS and periphery where it activates cannabinoid receptors. URB597 has been found to elevate anandamide levels and have activity against neuropathic pain in a mouse model.
Paenarthrobacter ureafaciens KI72, popularly known as nylon-eating bacteria, is a strain of Paenarthrobacter ureafaciens that can digest certain by-products of nylon 6 manufacture. It uses a set of enzymes to digest nylon, popularly known as nylonase.
In enzymology, a (R)-6-hydroxynicotine oxidase (EC 1.5.3.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a (S)-6-hydroxynicotine oxidase (EC 1.5.3.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an imidazolonepropionase (EC 3.5.2.7) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a succinyl-diaminopimelate desuccinylase (EC 3.5.1.18) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The alpha-4 beta-2 nicotinic receptor, also known as the α4β2 receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor implicated in learning, consisting of α4 and β2 subunits. It is located in the brain, where activation yields post- and presynaptic excitation, mainly by increased Na+ and K+ permeability.
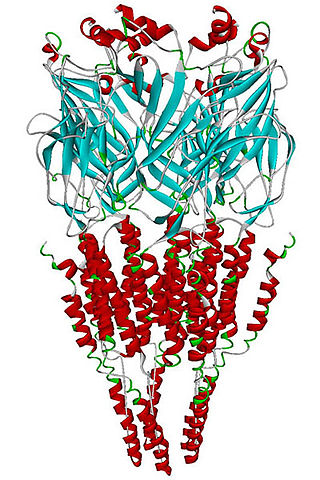
The alpha-7 nicotinic receptor, also known as the α7 receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor implicated in long-term memory, consisting entirely of α7 subunits. As with other nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, functional α7 receptors are pentameric [i.e., (α7)5 stoichiometry].

2,6-Dihydroxypyridine is an alkaloid with the molecular formula C5H3N(OH)2. It is a colorless solid. 2,6-Dihyroxypyridine is an intermediate in the degradation of nicotine.
Nicotine blue oxidoreductase (EC 1.1.1.328, nboR (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 3,3'-bipyridine-2,2',5,5',6,6'-hexol:NADP+ 11-oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Pseudooxynicotine oxidase (EC 1.4.3.24) is an enzyme with systematic name 4-(methylamino)-1-(pyridin-3-yl)butan-1-one:oxygen oxidoreductase (methylamine releasing). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
4-methylaminobutanoate oxidase (formaldehyde-forming) (EC 1.5.3.19, mabO (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 4-methylaminobutanoate:oxygen oxidoreductase (formaldehyde-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
4-methylaminobutanoate oxidase (methylamine-forming) (EC 1.5.3.21, mao (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 4-methylaminobutanoate methylamidohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
6-hydroxypseudooxynicotine dehydrogenase (EC 1.5.99.14) is an enzyme with systematic name 1-(6-hydroxypyridin-3-yl)-4-(methylamino)butan-1-one:acceptor 6-oxidoreductase (hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
6-hydroxy-3-succinoylpyridine 3-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.163, 6-hydroxy-3-succinoylpyridine hydroxylase, hspA (gene), hspB (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 4-(6-hydroxypyridin-3-yl)-4-oxobutanoate,NADH:oxygen oxidoreductase (3-hydroxylating, succinate semialdehyde releasing). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
4,5:9,10-diseco-3-hydroxy-5,9,17-trioxoandrosta-1(10),2-diene-4-oate hydrolase (EC 3.7.1.17, tesD (gene), hsaD (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 4,5:9,10-diseco-3-hydroxy-5,9,17-trioxoandrosta-1(10),2-diene-4-oate hydrolase ( (2Z,4Z)-2-hydroxyhexa-2,4-dienoate-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
6-oxocamphor hydrolase (EC 3.7.1.18, OCH, camK (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name bornane-2,6-dione hydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Dichlorochromopyrrolate synthase (EC 1.21.3.9, RebD, dichlorochromopyrrolic acid synthase) is an enzyme with systematic name 2-imino-3-(7-chloroindol-3-yl)propanoate ammonia-lyase (dichlorochromopyrrolate-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Paenarthrobacter nicotinovorans is a Gram-positive and aerobic bacterium species from the genus Paenarthrobacter. This bacterium has the ability to degrade atrazine, nicotine, and creatine. and produces nicotine dehydrogenase






