A constitutional amendment is a modification of the constitution of a polity, organization or other type of entity. Amendments are often interwoven into the relevant sections of an existing constitution, directly altering the text. Conversely, they can be appended to the constitution as supplemental additions, thus changing the frame of government without altering the existing text of the document.

A referendum, in the Italian legal system is a request directed to the whole electorate to express their view on a determined question. It is the main instrument of direct democracy in Italy.

A referendum on the Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe was held in Spain on Sunday, 20 February 2005. The question asked was "Do you approve of the Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe?". The consultative referendum on ratification of the proposed Constitution for the European Union was approved by 81.8% of valid votes, although turnout was just 41.8%, the lowest since the end of the Franco era.
A four-part referendum was held in Ukraine on 16 April 2000. The referendum was called by President Leonid Kuchma, and asked voters whether they approved of four amendments to the constitution that would increase the powers of the President and introduce an upper chamber.

A four-part referendum was held in Russia on 25 April 1993. Voters were asked questions on confidence in President Boris Yeltsin, support for the government's socio-economic policies and early elections for both the presidency and parliament. The referendum was initiated by the Congress of People's Deputies, which stipulated that Yeltsin would need to obtain 50% of the electorate, rather than 50% of valid votes. However, the Constitutional Court ruled that the president required only a simple majority on two issues: confidence in him, and economic and social policy; though he would still need the support of more than half the electorate in order to call new parliamentary and presidential elections.

A referendum on allowing President Lukashenko to stand in further elections was held in Belarus on 17 October 2004, alongside parliamentary elections. Lukashenko was nearing the end of his constitutionally-limited two terms, and the change would allow him to run for a third term.
A constitutional and electoral age referendum was held in Denmark on 28 May 1953. Both proposals were approved by voters, leading to both a new constitution taking effect on 5 June, and the electoral age being lowered from 25 to 23 years, also starting on 5 June. Voter turnout was 59.1% for the constitution question and 57.1% for the voting age question.

A constitutional referendum was held in Spain on Wednesday, 6 December 1978, to gauge support for either the ratification or repealing of the Spanish Constitution which had been approved by the Cortes Generales on 31 October 1978. The question asked was "Do you approve of the Constitution Bill?". The referendum resulted in 91.8% of valid votes in support of the bill on a turnout of 67.1%.
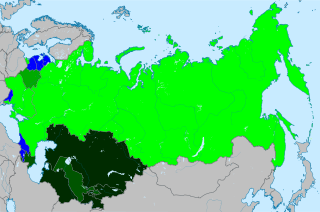
A referendum on the future of the Soviet Union was held on 17 March 1991 across the Soviet Union. It was the only national referendum in the history of the Soviet Union, although it was boycotted by authorities in six of the fifteen Soviet republics.
A referendum on political and economic reforms was held in Poland on 29 November 1987. The government's aim in holding the referendum was to obtain a mandate for difficult economic and political reforms. Around a third of eligible voters did not participate, defying the regime. Only 44% of Poland's 26 million eligible voters voted yes to the question on economic reform, and 46% voted yes to the second question on "democratisation" in Poland. Even though a majority of the votes cast supported the propositions, according to the rules of the referendum the majority of eligible voters had to vote yes in order for the referendum to pass. The resulting failure of the referendum was unprecedented, as it was the first time that Communist authorities in Eastern Europe had lost a vote.

A referendum on the electoral law was held in San Marino on 22 September 1996. Voters were asked four questions on changes to the electoral law and electoral system, all of which were approved by voters.

A referendum on the citizenship law was held in San Marino on 12 September 1999. Voters were asked whether the new citizenship law passed on 16 June should come into force. Although a majority voted in favour, the quorum of 32% of registered voters (9,663) was not achieved and the referendum failed.
A four-part referendum was held in Switzerland on 11 May 1884. All four were rejected by voters.
Five referendums were held in Switzerland in 1891. The first was held on 15 March on a federal law on federal officials who had become unemployable due to disability, and was rejected by 79.4% of voters. The second was held on 5 July on a constitutional amendment, and was approved by 60.3% of voters. Two referendums were held on 18 October, one on revising article 39 of the federal constitution and one on a federal law on Swiss tariffs; both were approved. The last was held on 6 December on the question of whether the federal government should purchase the Swiss Central Railway, but was rejected by 68.9% of voters.
A double referendum was held in Switzerland on 15 May 1927. Voters were asked whether they approved of amending article 30 of the constitution and a federal law on car and bicycle traffic. The constitutional amendment was approved by voters, whilst the traffic law was rejected.
Five referendums were held in Switzerland during 1929. The first three were held on 3 March on the issues of grain supply and a federal law on tariffs. The counter-proposal to the grain supply question and the tariffs law were both approved. The fourth and fifth referendums were held on 12 May on popular initiatives on road traffic and banning spirits. Both were rejected by voters.
Four referendums were held in Switzerland during 1935. The first was held on 24 February on a federal law reorganising the military, and was approved by voters. The second was held on 5 May on a federal law on the transport of goods and animals on roads, and was rejected by two-thirds of voters. The third was held on 2 June on a popular initiative "to combat the economic crisis" and was also rejected by voters. The fourth was held on 8 September on a popular initiative "for a total revision of the federal constitution", and was rejected by 72% of voters.
A fifteen-part constitutional referendum was held in Colombia on 25 October 2003. Whilst all fifteen proposals were approved by voters, only one question had a sufficient numbers of votes to pass the 25% quorum requirement.

Four referendums were held in San Marino on 15 May 2016. Three of the four proposals were approved, with the repeal of law 137 rejected.

A referendum was held in Hungary on 3 April 2022, coinciding with the parliamentary elections. While the overwhelming majority of valid votes were cast as "no" to the four referendum questions, the share of valid votes was below the 50% required for the result to be considered valid.








