
The 2001 Gujarat earthquake, also known as the Bhuj earthquake, occurred on 26 January at . The epicentre was about 9 km south-southwest of the village of Chobari in Bhachau Taluka of Kutch district in Gujarat, India. The earthquake had a maximum Mercalli intensity of XII (Extreme).
The 2002 Bou'in-Zahra earthquake occurred on 22 June 2002. The epicenter was near the city of Bou'in-Zahra in Qazvin province, a region of northwestern Iran which is crossed by several major faults that is known for destructive earthquakes. The shock measured 6.5 on the scale, had a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe), and was followed by more than 20 aftershocks. At least 230 people were killed and 1,500 more were injured.

The 2008 Chechnya earthquake occurred October 11 at 09:06:10 UTC in Chechnya, Russia, with a magnitude of 5.8. At least 13 people from the districts of Gudermes, Shalinsky and Kurchaloyevsky were killed. The mainshock and a series of aftershocks were felt throughout the North Caucasus, and even in Armenia and Georgia. About 116 people were injured.
The 1997 Ardabil earthquake occurred on 28 February with a moment magnitude of 6.1 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). The strike-slip earthquake occurred in northern Iran, near the city of Ardabil.

The 2008 Ziarat earthquakes hit the Pakistani province of Balochistan on October 29 with a moment magnitude of 6.4. The US Geological Survey reported that the first earthquake occurred 60 km (37 mi) north of Quetta and 185 km (115 mi) southeast of the Afghanistan city of Kandahar at 04:09 local time at a depth of 15 km (9.3 mi), at 30.653°N, 67.323°E. It was followed by another shallower magnitude 6.4 earthquake at a depth of 14 km (8.7 mi) approximately 12 hours after the initial shock, at 30.546°N, 67.447°E. 215 people were confirmed dead. More than 200 were injured, and 120,000 were rendered homeless. Qamar Zaman Chaudhry, director general of Pakistan Meteorological Department, stated the quake epicenter was 70 miles (110 km) north of Quetta, and about 600 km (370 mi) southwest of Islamabad.
The 2009 Cinchona earthquake occurred at on January 8 with an magnitude of 6.1 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX ( Violent). The shock took place in northern Costa Rica, 30 kilometres (19 mi) north-northwest of San José and was felt throughout Costa Rica and in southern central Nicaragua.
The 2009 Yunnan earthquake occurred with a moment magnitude of 5.7 in Yao'an County, Yunnan province, People's Republic of China on 9 July. At least one person died and over 300 were injured, with over 50 of these sustaining serious injuries.
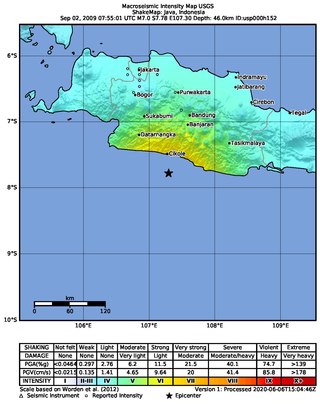
An earthquake occurred on September 2, 2009, at 14:55:01 local time in West Java, Indonesia. The magnitude 7.0 earthquake killed at least 81 people, injured over 1,297, and displaced over 210,000. The quake was felt in the capital Jakarta, although damage there was minimal, and it was Indonesia's deadliest earthquake since the 2006 Pangandaran earthquake and tsunami.
The 2010 Elazığ earthquake was a 6.1 Mw earthquake that occurred on 8 March 2010 at 02:32 UTC. The epicentre was Başyurt in Elazığ Province, in eastern Turkey. Initial reports in global media said as many as 57 people had died. By 10 March, reports in the Turkish media placed the death toll at 41 and later, the death toll rose to 42. Another 74 were injured, many after falling and jumping from buildings. A stampede through the streets led to further injuries.
The 1982 Flores earthquake struck the island of Flores in Indonesia on December 25. Registering a moment magnitude of 5.9, according to the International Seismological Centre, it created landslides and was reportedly accompanied by a tsunami. The earthquake killed thirteen people and left 390 injured, also destroying 1,875 houses and 121 other buildings. The villages of Layahong and Oyong Barang were damaged by seven seconds of shaking.

The 2013 Bushehr earthquake occurred with a moment magnitude of 6.3 on April 9 in Iran. The shock's epicenter was in the province of Bushehr, near the city of Khvormuj and the towns of Kaki and Shonbeh. At least 37 people were killed, mostly from the town of Shonbeh and villages of Shonbeh-Tasuj district, and an estimated 850 people were injured.
The 1954 Chlef earthquake struck El Asnam Province in French Algeria on 9 September at . The shock measured 6.7 on the moment magnitude scale and had a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (Extreme). It destroyed Chlef, then named Orléansville, leaving over 1,243 people dead and 5,000 injured. Damage was estimated at $6 million. It was followed by multiple aftershocks. Algeria faces annual earthquakes and has undergone several changes to its earthquake building codes since its first earthquake engineering regulations from 1717.

The October 2015 Hindu Kush earthquake was a magnitude 7.5 earthquake that struck South Asia on 26 October 2015, at 13:39 AFT with the epicenter 45 km north of Kuran wa Munjan, Afghanistan, at a depth of 231.0 km.
On 7 December 2015, an earthquake measuring 7.2 on the moment magnitude scale struck Tajikistan 105 km (65 mi) west of Murghab at 07:50 UTC at a depth of 26.0 km (16.2 mi). The earthquake was also felt in neighboring Xinjiang in China, India, Afghanistan, Pakistan and Kyrgyzstan.

On May 4, 2018, an earthquake with a magnitude of 6.9 struck Hawaii island in the Hawaii archipelago at around 12:33 p.m. local time. The earthquake's epicenter was near the south flank of Kīlauea, which has been the site of seismic and volcanic activity since late April of that year. According to the United States Geological Survey the quake was related to the new lava outbreaks at the volcano, and it resulted in the Hilina Slump moving about two feet. It was the largest earthquake to affect Hawaii since the 1975 earthquake, which affected the same region, killing two people and injuring another 28.
The 2019 Cotabato earthquakes were an earthquake swarm which struck the province of Cotabato on the island of Mindanao in the Philippines in October 2019. Three of these earthquakes were above 6.0 on the moment magnitude scale with a Mercalli intensity of VIII. More than 40 people have been reported dead or missing and nearly 800 were injured as a result of these events.

On 18 August 2020, at 8:03 PST, a 6.6 magnitude earthquake struck the island province of Masbate in the Philippines, leaving at least 2 dead and 170 injured.
The 1902 Turkestan earthquake devastated Xinjiang, China, near the Kyrgyzstan border. It occurred on August 22, 1902, at 03:00:22 with an epicenter in the Tien Shan mountains. The thrust earthquake measured 7.7 on the moment magnitude scale (Mw ) and had a depth of 18 km (11 mi).
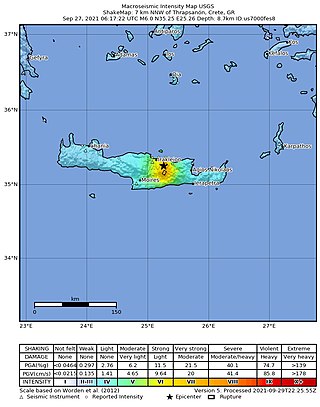
A moment magnitude 6.0 earthquake struck the island of Crete in Greece at a depth of 6 km on 27 September 2021. The epicenter of the earthquake was located southeast of Heraklion. The quake killed one person, injured 36 and damaged over 5,000 old buildings on the island.
On 23 January 2024, at 02:09 CST, a Ms 7.1 or Mw 7.0 earthquake occurred in Uqturpan County, also known as Wushi County, in Xinjiang, China, near the border with Kyrgyzstan. Three people died in Xinjiang, while 74 others were injured, mostly in neighbouring Kazakhstan.










