Djibouti is a country in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Somalia to the southeast, Eritrea and the Red Sea to the north and northeast, Ethiopia to the west and south, and the Gulf of Aden to the east.

The Djibouti Armed Forces (DJAF) are the military forces of Djibouti. They consist of the Djiboutian Army and its sub-branches the Djibouti Air Force and Djiboutian Navy. As of 2018, the Djibouti Armed Forces consists of 20,470 ground troops, which are divided into several regiments and battalions garrisoned in various areas throughout the country. Djibouti Armed Forces are an important player in the Bab-el-Mandeb and Red Sea.
"Eritrea" is an ancient name, associated in the past with its Greek form Erythraia, Ἐρυθραία, and its derived Latin form Erythræa. This name relates to that of the Red Sea, then called the Erythræan Sea, from the Greek for "red", ἐρυθρός, erythros. The Italians created the colony of Eritrea in the 19th century around Asmara, and named it with its current name. After World War II Eritrea was annexed to Ethiopia. In 1991 the Eritrean People's Liberation Front defeated the Ethiopian government. Tigray is a region of Ethiopia whose religions, food, language and culture are the same as that of the greater part of Eritrea. A lot of people have families on both sides of the border between Eritrea and Tigray. Eritrea officially celebrated its 1st anniversary of independence on May 24, 1991.

The Ethiopian National Defense Force (ENDF) is the military of Ethiopia. Civil direction of the military is carried out through the Ministry of Defense, which oversees the ground forces, air force, as well as the Defense Industry Sector. The current defense minister is Motuma Mekassa.

Many historians trace modern Ethiopia's foreign policy to the reign of Emperor Tewodros II, whose primary concerns were the security of Ethiopia's traditional borders, obtaining technology from Europe, and to a lesser degree Ethiopian rights to the monastery of Dar-es-Sultan in the city of Jerusalem. Tewodros' diplomatic efforts, however, ended disastrously with the British expedition of 1868 which concluded with his death. Despite the efforts of his successor Emperor Yohannes IV to establish a relationship with the United Kingdom, Ethiopia was ignored by the world powers until the opening of the Suez Canal, and more important, the Mahdist War, drew outside attention to her once more.

The Somali National Armed Forces (SNAF) are the military forces of Somalia, officially known as the Federal Republic of Somalia. Headed by the President as Commander in Chief, they are constitutionally mandated to ensure the nation's sovereignty, independence and territorial integrity. Before the Somali civil war broke out, Somalia had the largest and strongest army in the African continent until the collapse of the central government during 1991.

The Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD) is an eight-country trade bloc in Africa. It includes governments from the Horn of Africa, Nile Valley and the African Great Lakes. Its headquarters are in Djibouti City.

The Islamic Courts Union was a group of Sharia courts that united themselves to form a rival administration to the Transitional Federal Government (TFG) of Somalia, with Sharif Sheikh Ahmed as their head. They were also known as the Joint Islamic Courts, Union of Islamic Courts (UIC), Supreme Islamic Courts Council (SICC) or the Supreme Council of Islamic Courts (SCIC).

The Somali Civil War was an armed conflict involving largely Ethiopian and Somali Transitional Federal Government (TFG) forces and Somali troops from Puntland versus the Somali Islamist umbrella group, the Islamic Court Union (ICU), and other affiliated militias for control of the country. There is a clear connection between War in Somalia (2009–) and the War of 2006. The war officially began shortly before July 20, 2006 when U.S. backed Ethiopian troops invaded Somalia to prop up the TFG in Baidoa. The TFG in Somalia invited Ethiopians to intervene, which became an "unpopular decision". Subsequently, the leader of the ICU, Sheik Hassan Dahir Aweys, declared "Somalia is in a state of war, and all Somalis should take part in this struggle against Ethiopia". On December 24, Ethiopia stated it would actively combat the ICU.
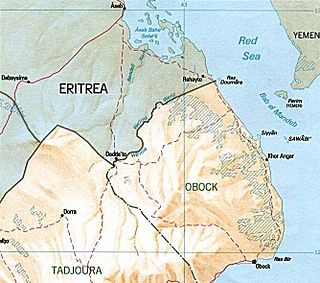
The Djiboutian–Eritrean border conflict between the forces of Djibouti and Eritrea occurred between June 10 and June 13, 2008. It was triggered by tension which began on April 16, 2008, when Djibouti reported that Eritrean armed forces had penetrated into Djibouti and dug trenches on both sides of the border. The crisis deepened when armed clashes broke out between the two armed forces in the border area on June 10, 2008. During the conflict, France provided logistical, medical and intelligence support to Djibouti, but did not participate in direct combat.

The 2009–present phase of the Somali Civil War is concentrated in southern Somalia. It began in early February 2009 with the conflict between the forces of the Federal Government of Somalia, assisted by African Union peacekeeping troops, and various militant terrorist groups and factions. The violence has displaced thousands of people in the southern part of the country. The conflict has also seen fighting between the Sufi Ahlu Sunna Waljama'a and Al-Shabaab.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1907, adopted on December 23, 2009, imposed an arms embargo on Eritrea, travel bans on its leaders, and froze the assets of some of the country's political and military officials after accusing the Eritrean government of aiding Al-Shabaab in Somalia and reportedly refusing to withdraw troops from its disputed border with Djibouti, following a conflict in 2008. The African Union and other organisations had been calling on the Security Council to sanction Eritrea for several months.

Operation Linda Nchi was the Kenya Defence Forces operation - in many ways an invasion - covering the entry of Kenyan military forces into southern Somalia beginning in 2011. The Kenyan government declared the operation completed in March 2012, but its forces joined AMISOM in Somalia and are not expected to leave before 2020.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1862 was unanimously adopted on 14 January 2009.

The Djiboutian Army is the largest branch of the Djibouti Armed Forces and is based in the Djiboutian capital of Djibouti City. Djibouti has upgraded its Ground Forces with advanced additions from domestic engineering and modifications. It must operate in mountainous and other rugged terrain, but it must do this without affecting the mechanized capability that is needed to confront regional forces. The official tasks of the armed forces include strengthening the country against external attack, maintaining border security. It is responsible for the defence of mainland Djibouti. During peacetime the military of Djibouti numbers approximately 9,000 with a reserve force of approximately 7,000
The military history of Djibouti encompasses the major conflicts involving the historic empires and sultanates in the territory of present-day Djibouti, through to modern times. It also covers the martial traditions and hardware employed by Djiboutian armies and their opponents.

The Eritrean–Ethiopian border conflict was a violent standoff and a proxy conflict between Eritrea and Ethiopia, as part of the more general violence in the Horn of Africa. It consisted of a series of incidents along the then-disputed border; including the Eritrean–Ethiopian War of 1998–2000 and the subsequent Second Afar Insurgency. The border conflict was a continuation of the Eritrean–Ethiopian War of 1998–2000. It included multiple clashes with numerous casualties, including the Battle of Tsorona in 2016. Ethiopia stated in 2018 that it would cede Badme to Eritrea. This led to the Eritrea–Ethiopia summit on 9 July 2018, where an agreement was signed which demarcated the border and agreed a resumption of diplomatic relations.


















