| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 2012 in the Republic of South Sudan .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 2012 in the Republic of South Sudan .
The presidents of both Sudan and South Sudan meet in Ethiopia, and after days of discussion, agree on trade, oil and security deals. [5]

Jonglei State is a state of South Sudan with Bor as its centre of government and the biggest city. Jonglei state comprises nine counties: Bor, Akobo, Ayod, Uror, Duk, Nyirol, Pigi, Twic East, and Fangak. Jonglei State is the largest state by area before reorganisation, with an area of approximately 122,581 km2, as well as the most populous according to the 2008 census conducted in present-day South Sudan's second period of autonomy. The boundaries of the state were again changed as a result of a peace agreement signed on 22 February 2020.

The Second Sudanese Civil War was a conflict from 1983 to 2005 between the central Sudanese government and the Sudan People's Liberation Army. It was largely a continuation of the First Sudanese Civil War of 1955 to 1972. Although it originated in southern Sudan, the civil war spread to the Nuba mountains and the Blue Nile. It lasted for almost 22 years and is one of the longest civil wars on record. The war resulted in the independence of South Sudan 6 years after the war ended.

Salva Kiir Mayardit, commonly known as Salva Kiir, is a South Sudanese politician who has been the President of South Sudan since its independence on 9 July 2011. Prior to independence, he was the President of the Government of Southern Sudan, as well as First Vice President of Sudan, from 2005 to 2011. He was named Commander-in-Chief of the Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA) in 2005, following the death of John Garang.

The War in Darfur, also nicknamed the Land Cruiser War, was a major armed conflict in the Darfur region of Sudan that began in February 2003 when the Sudan Liberation Movement (SLM) and the Justice and Equality Movement (JEM) rebel groups began fighting against the government of Sudan, which they accused of oppressing Darfur's non-Arab population. The government responded to attacks by carrying out a campaign of ethnic cleansing against Darfur's non-Arabs. This resulted in the death of hundreds of thousands of civilians and the indictment of Sudan's president, Omar al-Bashir, for genocide, war crimes, and crimes against humanity by the International Criminal Court.

Bentiu, also spelled Bantiu, is a city in South Sudan. It is the capital of Unity State.
Events from the year 2007 in Chad.
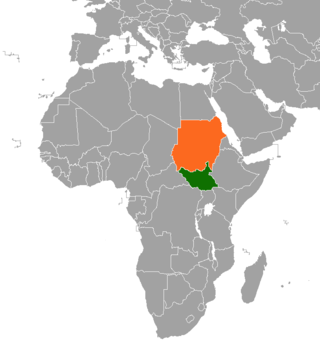
Sudanese nomadic conflicts are non-state conflicts between rival nomadic tribes taking place in the territory of Sudan and, since 2011, South Sudan. Conflict between nomadic tribes in Sudan is common, with fights breaking out over scarce resources, including grazing land, cattle and drinking water. Some of the tribes involved in these clashes have been the Messiria, Maalia, Rizeigat and Bani Hussein Arabic tribes inhabiting Darfur and West Kordofan, and the Dinka, Nuer and Murle African ethnic groups inhabiting South Sudan. Conflicts have been fueled by other major wars taking place in the same regions, in particular the Second Sudanese Civil War, the War in Darfur and the Sudanese conflict in South Kordofan and Blue Nile.

The States of South Sudan were created out of the three historic former provinces of Bahr el Ghazal (northwest), Equatoria (southern), and Greater Upper Nile (northeast). The states are further divided into 79 counties.

The Sudanese conflict in South Kordofan and Blue Nile was an armed conflict and insurgency in the Sudanese states of South Kordofan and Blue Nile between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and the Sudan People's Liberation Movement–North (SPLM-N), a northern affiliate of the Sudan People's Liberation Movement (SPLM) in South Sudan. After some years of relative calm following the 2005 agreement which ended the second Sudanese civil war between the Sudanese government and SPLM rebels, fighting broke out again in the lead-up to South Sudan independence on 9 July 2011, starting in South Kordofan on 5 June and spreading to the neighboring Blue Nile state in September. SPLM-N, splitting from newly independent SPLM, took up arms against the inclusion of the two southern states in Sudan with no popular consultation and against the lack of democratic elections. The conflict is intertwined with the War in Darfur, since in November 2011 SPLM-N established a loose alliance with Darfuri rebels, called Sudan Revolutionary Front (SRF).

South Sudan, officially the Republic of South Sudan, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered on the north by Sudan; on the east by Ethiopia; on the south by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda and Kenya; and on the west by the Central African Republic. South Sudan's diverse landscape includes vast plains and plateaus, dry and tropical savannahs, inland floodplains, and forested mountains. The Nile River system is the defining physical feature of the country, running south to north across its center, which is dominated by a large swamp known as the Sudd. South Sudan has a population of 12.7 million. Juba is the capital and largest city.
The history of South Sudan comprises the history of the territory of present-day South Sudan and the peoples inhabiting the region.

Human rights in South Sudan are a contentious issue, owing at least in part to the country's violent history.
Ethnic violence in South Sudan has a long history among South Sudan's varied ethnic groups. South Sudan has 64 tribes with the largest being the Dinka, who constitute about 35% of the population and predominate in government. The second largest are the Nuers. Conflict is often aggravated among nomadic groups over the issue of cattle and grazing land and is part of the wider Sudanese nomadic conflicts.

The United Nations Mission in South Sudan (UNMISS) is a United Nations peacekeeping mission for South Sudan, which became independent on 9 July 2011. UNMISS was established on 8 July 2011 by United Nations Security Council Resolution 1996 (2011).
The South Sudan Democratic Movement (SSDM), sometimes called the South Sudan Democratic Movement/Army (SSDM/A), was a South Sudanese militant group. Along with its armed wing, the South Sudan Defence Army (SSDA), rebelled against the government of South Sudan led by President Salva Kiir Mayardit and the Sudan People's Liberation Movement.

The Heglig Crisis was a brief war fought between the countries of Sudan and South Sudan in 2012 over oil-rich regions between South Sudan's Unity and Sudan's South Kordofan states. South Sudan invaded and briefly occupied the small border town of Heglig before being pushed back by the Sudanese army. Small-scale clashes continued until an agreement on borders and natural resources was signed on 26 September, resolving most aspects of the conflict.

David Yau Yau is a South Sudanese politician and former militant. He served as Governor of Boma State from 2018 to 2020 and as the Chief Administrator of the Greater Pibor Administrative Area of South Sudan. He was previously the leader of a Murle insurrection against the South Sudanese government.

The South Sudanese Civil War was a multi-sided civil war in South Sudan fought from 2013 to 2020, between forces of the government and opposition forces. The Civil War caused rampant human rights abuses, including forced displacement, ethnic massacres, and killings of journalists by various parties. Since its end South Sudan has been governed by a coalition formed by leaders of the former warring factions, Salva Kiir Mayardit and Riek Machar. In 2024, the country continues to recover from the war while experiencing ongoing and systemic ethnic violence.
The following lists events that happened during 2011 in Sudan.
This article lists events from the year 2020 in South Sudan