
Rail transport is an important mode of transport in India.

Mumbai Suburban Railway consists of exclusive inner suburban railway lines augmented by commuter rail on main lines serving outlying suburbs to serve the Mumbai Metropolitan Region. Spread over 390 kilometres (240 mi), the suburban railway operates 2,342 train services and carries more than 7.5 million commuters daily. By annual ridership, the Mumbai Suburban Railway is one of the busiest commuter rail systems in the world and it has the most severe overcrowding in the world. Trains run from 04:00 until 01:00, and some trains also run up to 02:30.

Kharagpurpronunciation (help·info) is a city and a municipality in Paschim Medinipur district of West Bengal, India. It is the headquarters of the Kharagpur subdivision. It is the most populated, multi-cultural and cosmopolitan city of the district. The first Indian Institutes of Technology (IIT), a group of Institutes of National Importance, was founded in Kharagpur as early as in May 1950. It has one of the largest railway workshops in India, and the third longest railway platform in the world.
The Secunderabad Junction railway station, is a major intercity railway station and a commuter rail hub in the Hyderabad urban area. In the city centre, the station is in the South Central Railway zone of Indian Railways. Built in 1874 by the Nizam of Hyderabad during the British era, it was the main station of Nizam's Guaranteed State Railway until the Kachiguda railway station opened in 1916. The station was taken over by Indian Railways in 1951, when NGSR was nationalized. Its main portico and concourse are influenced by Nizamesque architecture. The station, which resembles a fort, is a tourist attraction in the twin cities of Hyderabad and Secunderabad.
India does not have any railways that can be classified as high-speed rail (HSR) by international standards, i.e. railways with operational speeds exceeding 200 km/h (120 mph). The current fastest train in India is the Train 18 with a top speed of 180 km/h (110 mph), which runs between New Delhi and Varanasi.

Vijayawada railway station is an Indian railway station in Vijayawada of Andhra Pradesh. It is classified as one of the A-1 and Model station in the Vijayawada railway division of South Coast Railway zone. It is the fourth busiest railway station in the country after Howrah Junction, Kanpur Central and New Delhi. at the junction of Howrah-Chennai and New Delhi–Chennai main lines. The station everyday serves about 1.40 lakh passengers, over 180 express and 150 freight trains.

Latur is an A-Category railway station in Central Railway Zone which serves the city of Latur, Maharashtra. It is the start of the Latur–Miraj section section of the Solapur (SUR) Division of Central Railway (CR). Latur is well connected to Bangalore, Hyderabad, Pandharpur Bidar Pune, Ahmedabad, Latur Road junction, Mumbai,Panvel Kurla Lonavla, Nanded, Amravati, Nagpur, Kolhapur, Miraj, Vikarabad

The Mainline Electric Multiple Unit (MEMU) are electric multiple (EMU) trains that serve short- and medium-distance routes in India, as compared to normal EMU trains that connect urban and suburban areas.

Panvel is a railway station on the Harbour Line and Central zone of the Mumbai Suburban Railway network.
The Nellore train fire occurred on 30 July 2012, when the Chennai-bound Tamil Nadu Express train caught fire at 4:22 am near Nellore, Andhra Pradesh, India. At least 32 passengers died and 27 were injured. The fire gutted the S-11 sleeper coach in 20 minutes. A railway emergency crew prevented the fire from spreading to the other coaches.
Modern Coach Factory, Raebareli is a rail coach manufacturing unit of the Indian Railways at Lalganj near Raebareli in Uttar Pradesh. The factory is the third facility in India that produces railway compartments besides the Integral Coach Factory at Perambur in Tamil Nadu and the Rail Coach Factory at Kapurthala in Punjab. The factory was inaugurated on 7 November 2012.

Kollam Junction railway station is a junction station situated in the city of Kollam in Kerala, India. It is the second largest railway station in Kerala in terms of area and is one of the oldest railway stations in the state. World's second longest railway platform is situated at Kollam railway station.

Vijayawada railway division is one of the four railway divisions under South Coast Railway zone of the Indian Railways. The headquarters of the division are located at Vijayawada.

2015 Railway Budget of India refers to the Railway Budget of the Indian Railways in the fiscal year 2015–16. The budget was presented by the Railway Minister Suresh Prabhu in the Parliament on 26 February 2015.
The Indian government is undertaking several initiatives as to upgrading its aged railway infrastructure and enhance its quality of service. The Railway Ministry has announced plans to invest ₹905,000 crore (US$126 billion) to upgrade the railways by 2020. IR's Research Design and Standards Organisation (RDSO) undertakes all research, designs and standardisation work for modernisation.

Mahamana Express is a ModelRake based superfast express series trains operated by Indian Railways in India.

Antyodaya Express are completely Unreserved/General coaches designed by Indian Railways. These are going to be overnight trains. Antyodaya Express was proposed in 2016 Railway Budget of India to operate on peak routes having more rush. The trains are completely general coach trains designed by Indian Railways with features Bio toilets in compartments as well as facility for mobile charging points.
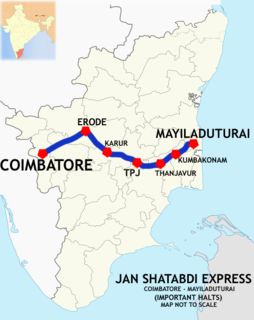
Mayiladuthurai–Coimbatore Jan Shatabdi Express is a Jan Shatabdi Express train connecting Mayiladuthurai Junction and Coimbatore Junction in Tamil Nadu, India. The passenger service is one among the twenty Jan Shatabdi Express trains in India other than Chennai Central–Vijayawada Jan Shatabdi Express that runs within Tamil Nadu.


















