
Abdullahi Yusuf Ahmed was a Somali politician and former colonel in the Somali National Army. He was one of the founders of the Somali Salvation Democratic Front, as well as the Puntland state of Somalia, the latter of which he served as the first president. In 2004, Ahmed also helped establish the Transitional Federal Government, which he led as President of Somalia from 2004 until 2008.

The Somali Civil War is an ongoing civil war that is taking place in Somalia. It grew out of resistance to the military junta which was led by Siad Barre during the 1980s. From 1988 to 1990, the Somali Armed Forces began engaging in combat against various armed rebel groups, including the Somali Salvation Democratic Front in the northeast, the Somali National Movement in the northwest, and the United Somali Congress in the south. The clan-based armed opposition groups overthrew the Barre government in 1991.

The Transitional Federal Government (TFG) was internationally recognized as a provisional government of the Somalia from 14 October 2004 until 20 August 2012, when its tenure officially ended and the Federal Government of Somalia (FGS) was inaugurated.

The 2006 Islamic Courts Union offensive is the period in the Somali Civil War that began in May 2006 with the Islamic Courts Union's (ICU) conquest of Mogadishu from the Alliance for the Restoration of Peace and Counter-Terrorism (ARPCT) and continued with further ICU expansion in the country. Following the outbreak of the war on December 21, 2006; by December 24, direct Ethiopian intervention in the conflict in support of the Transitional Federal Government (TFG) was no longer denied by the Ethiopian government. The Eritrean government denied any involvement despite Ethiopian claims to the contrary.
The Somali Rebellion was the beginning of the civil war in Somalia that occurred in the 1980s and early 1990s. The rebellion started in 1978 when President Siad Barre began using his special forces, the "Red Berets", to attack clan-based dissident groups opposed to his regime. The dissidents had been becoming more powerful for nearly a decade following his abrupt switch of allegiance from the Soviet Union to the United States and the disastrous 1977-78 Ogaden War.

The fall of Mogadishu occurred on 28 December 2006, when the Ethiopian National Defence Forces (ENDF) advanced into the capital to install the Transitional Federal Government (TFG). The Islamic Courts Union (ICU), which had controlled the capital since June 2006, withdrew from the city after a week of fighting ENDF/TFG forces in southern and central Somalia.

Villa Somalia in Mogadishu, is the palace and principal workplace of the president of Somalia. The current occupant of Villa Somalia is President Hassan Sheikh Mohamud (HSM) of the Federal Government of Somalia (FGS).
The timeline of events in the War in Somalia during 2006 is set out below.

The Somali Civil War (2009–present) is the ongoing phase of the Somali Civil War which is concentrated in southern and central Somalia. It began in late January 2009 with the present conflict mainly between the forces of the Federal Government of Somalia assisted by African Union peacekeeping troops and al-Shabaab militants who pledged alliegence to al-Qaeda during 2012.

The Battle of Mogadishu (2009) started in May with an Islamist offensive, when rebels from al-Shabaab and Hizbul Islam attacked and captured government bases in the capital of Mogadishu. The fighting soon spread, causing hundreds of casualties, and continued on at various levels of intensity until October. The battle's name usually includes the year, when referenced, in order to distinguish it amongst the nine major Battles of Mogadishu during the decades long Somali Civil War.
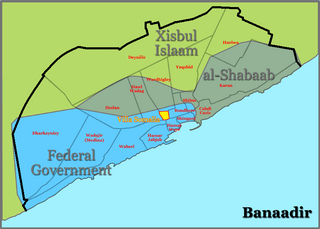
The Battle of Mogadishu (2010–11) began on 23 August 2010 when al-Shabaab insurgents began attacking government and African Union Mission to Somalia (AMISOM) positions in the Somali capital of Mogadishu. Al-Shabaab began its offensive after its spokesman said the group was declaring a "massive war" on troops sent by AMISOM, describing its 6,000 peacekeepers as "invaders". In December 2010 the number of AMISOM troops was increased to 8,000 and later to 9,000. The battle's name usually includes the years, when referenced, in order to distinguish it amongst the nine major Battles of Mogadishu during the decades long Somali Civil War.

Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed, also known as Farmaajo, is a Somali politician who served as president of Somalia from 2017 to 2022. He was prime minister of Somalia for six months, from November 2010 to June 2011. Mohamed is the founder and leader of the Tayo Party since 2012.

This is a 2015 timeline of events in the Somali Civil War (2009–present).
This article contains a timeline of events for the Somalimilitant group al-Shabaab.

Presidential elections were held in Somalia in 15 May 2022. The election was held indirectly and after the elections for the House of the People, which began on 1 November 2021 and ended on 13 April 2022.
Events in the year 2021 in Somalia.
The 2021–2022 Somali political crisis was a major political crisis and turmoil within the Somali government after President Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed's term ended on 8 February 2021. Parliamentary elections held during 2021, but were not completed during the year. Prime Minister Mohamed Hussein Roble opposed the president's decision, and called for him to step down. Following months of protests, a deal was struck in January 2022 to hold elections in February. After a delay, presidential elections were ultimately held in May which resulted in President Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed losing his bid for reelection to Hassan Sheikh Mohamud.

In 2021, elections for the Federal Parliament and subsequently the President of Somalia were due to take place, following a national agreement to reschedule them from the previous year due to the COVID-19 pandemic in the country.
The political history of Africa in the 2020s covers political events on the continent, other than elections, from 2020 onwards.
Events in the year 2022 in Somalia.










