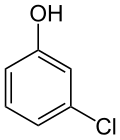
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 3-Chlorophenol [1] | |
| Other names m-Chlorophenol meta-Chlorophenol 3-Hydroxychlorobenzene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.257 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H5ClO | |
| Molar mass | 128.56 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless or white oily solid |
| Density | 1.245 g/cm3 at 45 °C [2] |
| Melting point | 32.5 °C (90.5 °F; 305.6 K) [2] |
| Boiling point | 210 °C (410 °F; 483 K) [2] |
| 20 g/L at 20 °C | |
| Solubility in other solvents | Soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, benzene |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.12 [3] |
| −77.6·10−6 cm3/mol [4] | |
Refractive index (nD) | 1.5565 [2] |
| Thermochemistry [5] | |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | −206.4 kJ·mol−1 (s) −189.3 kJ·mol−1 (l) |
Enthalpy of fusion (ΔfH⦵fus) | 14.9 kJ·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards | Corrosive – causes burns |
| Flash point | 120 °C (248 °F; 393 K) |
| 550 °C (1,022 °F; 823 K) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Related aromatic hydrocarbons | Benzene Phenol Chlorobenzene |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
3-Chlorophenol is an organic compound with the molecular formula C6H4ClOH. It is one of three isomers of monochlorophenol. It is a colorless or white solid that melts easily and exhibits significant solubility in water. Together with 3,5-dichlorophenol, it is prepared industrially by dechlorination of polychlorophenols. Alternatively, it arises via the cumene process, which starts with the alkylation of chlorobenzene with propylene. [6]