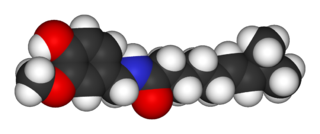
Capsaicin (8-methyl-N-vanillyl-6-nonenamide) is an active component of chili peppers, which are plants belonging to the genus Capsicum. It is a chemical irritant and neurotoxin for mammals, including humans, and produces a sensation of burning in any tissue with which it comes into contact. Capsaicin and several related amides (capsaicinoids) are produced as secondary metabolites by chili peppers, probably as deterrents against certain mammals and fungi. Pure capsaicin is a hydrophobic, colorless, highly pungent, crystalline solid.

Vanillin is an organic compound with the molecular formula C8H8O3. It is a phenolic aldehyde. Its functional groups include aldehyde, hydroxyl, and ether. It is the primary component of the extract of the vanilla bean. Synthetic vanillin is now used more often than natural vanilla extract as a flavoring in foods, beverages, and pharmaceuticals.

An aroma compound, also known as an odorant, aroma, fragrance or flavoring, is a chemical compound that has a smell or odor. For an individual chemical or class of chemical compounds to impart a smell or fragrance, it must be sufficiently volatile for transmission via the air to the olfactory system in the upper part of the nose. As examples, various fragrant fruits have diverse aroma compounds, particularly strawberries which are commercially cultivated to have appealing aromas, and contain several hundred aroma compounds.
Pyrazine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C4H4N2. It is a symmetrical molecule with point group D2h. Pyrazine is less basic than pyridine, pyridazine and pyrimidine. It is a "deliquescent crystal or wax-like solid with a pungent, sweet, corn-like, nutty odour".
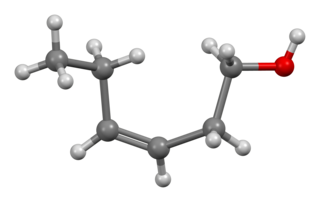
cis-3-Hexen-1-ol, also known as (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol and leaf alcohol, is a colorless oily liquid with an intense grassy-green odor of freshly cut green grass and leaves. It is produced in small amounts by most plants and it acts as an attractant to many predatory insects. cis-3-Hexen-1-ol is a very important aroma compound that is used in fruit and vegetable flavors and in perfumes. The yearly production is about 30 tonnes.

cis-3-Hexenal, also known as (Z)-3-hexenal and leaf aldehyde, is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CHO. It is classified as an unsaturated aldehyde. It is a colorless liquid and an aroma compound with an intense odor of freshly cut grass and leaves.

Piperonal, also known as heliotropin, is an organic compound which is commonly found in fragrances and flavors. The molecule is structurally related to other aromatic aldehydes such as benzaldehyde and vanillin.

Myrcene, or β-myrcene, is a monoterpene. A colorless oil, it occurs widely in essential oils. It is produced mainly semi-synthetically from Myrcia, from which it gets its name. It is an intermediate in the production of several fragrances. α-Myrcene is the name for the isomer 2-methyl-6-methylene-1,7-octadiene, which has not been found in nature.

Zingerone, also called vanillylacetone, is a major flavor component of ginger, providing the sweet flavor of cooked ginger. Zingerone is a crystalline solid that is sparingly soluble in water and soluble in ether.
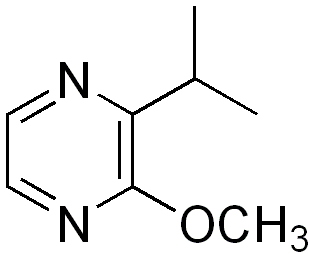
Methoxypyrazines are a class of chemical compounds that produce odors. The odors tend to be undesirable, as in the case of certain wines, or as defensive chemicals used by insects such as Harmonia axyridis which produces isopropyl methoxy pyrazine (IPMP). They have also been identified as additives in cigarette manufacture. Detection thresholds are very low, typically near 2 parts per trillion (1 ng/L).

Raspberry ketone is a natural phenolic compound that is the primary aroma compound of red raspberries.

3-Mercapto-3-methylbutan-1-ol, also known as MMB, is a common odorant found in food and cat urine. The aromas ascribed to MMB include catty, roasty, broth-like, meaty, and savory, or similar to cooked leeks.
Alkylpyrazines are chemical compounds based on pyrazine with different substitution patterns. Some alkylpyrazines are naturally occurring highly aromatic substances which often have a very low odor threshold and contribute to the taste and aroma of various foods including cocoa, baked goods, coffee and wines. Alkylpyrazines are also formed during the cooking of some foods via Maillard reactions.

Phenylacetaldehyde is an organic compound used in the synthesis of fragrances and polymers. Phenylacetaldehyde is an aldehyde that consists of acetaldehyde bearing a phenyl substituent; the parent member of the phenylacetaldehyde class of compounds. It has a role as a human metabolite, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is an alpha-CH2-containing aldehyde and a member of phenylacetaldehydes.

2-Methoxy-4-vinylphenol is an aromatic substance used as a flavoring agent. It is one of the compounds responsible for the natural aroma of buckwheat.

An odor or odour is caused by one or more volatilized chemical compounds that are generally found in low concentrations that humans and many animals can perceive via their sense of smell. An odor is also called a "smell" or a "scent", which can refer to either an unpleasant or a pleasant odor.

Isopropyl methoxypyrazine (IPMP) is a methoxypyrazine, a class of chemical compounds that produce odors. The odor is rather undesirable and is produced by the Asian lady beetle or by the actinomycete Streptomyces sp. It can be detected by human taste at concentrations of as low as 2 nanograms per litre.

6-Nonenal is an organic compound with the formula C2H5CH=CH(CH2)4CHO. Other isomeric nonenal compounds are also known to exist naturally, e.g. 2-nonenal. The cis-isomer of 6-nonenal is often listed as the principal component in the aromas of muskmelon fruits. The trans-isomer is listed as an off-flavor aroma of milk foams, and thought to be a possible polypropylene odorant.

4-Methylcyclohexanemethanol (MCHM, systematic name 4-methylcyclohexylmethanol) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H10CH2OH. Classified as a saturated higher alicyclic primary alcohol. Both cis and trans isomers exist, depending on the relative positions of the methyl (CH3) and hydroxymethyl (CH2OH) groups on the cyclohexane ring. Commercial samples of MCHM consists of a mixture of these isomers as well as other components that vary with the supplier.

















