
1,4-Dichlorobenzene (1,4-DCB, p-DCB, or para-dichlorobenzene, sometimes abbreviated as PDCB or para) is an aryl chloride and isomer of dichlorobenzene with the formula C6H4Cl2. This colorless solid has a strong odor. The molecule consists of a benzene ring with two chlorine atoms (replacing hydrogen atoms) on opposing sites of the ring.
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms, directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide. Haloarenes are different from haloalkanes because they exhibit many differences in methods of preparation and properties. The most important members are the aryl chlorides, but the class of compounds is so broad that there are many derivatives and applications.

In organic chemistry, nitration is a general class of chemical processes for the introduction of a nitro group into an organic compound. The term also is applied incorrectly to the different process of forming nitrate esters between alcohols and nitric acid. The difference between the resulting molecular structures of nitro compounds and nitrates is that the nitrogen atom in nitro compounds is directly bonded to a non-oxygen atom, whereas in nitrate esters, the nitrogen is bonded to an oxygen atom that in turn usually is bonded to a carbon atom.

Chlorobenzene (abbreviated PhCl) is an aryl chloride and the simplest of the chlorobenzenes, consisting of a benzene ring substituted with one chlorine atom. Its chemical formula is C6H5Cl. This colorless, flammable liquid is a common solvent and a widely used intermediate in the manufacture of other chemicals.

Thiophenol is an organosulfur compound with the formula C6H5SH, sometimes abbreviated as PhSH. This foul-smelling colorless liquid is the simplest aromatic thiol. The chemical structures of thiophenol and its derivatives are analogous to phenols, where the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to the aromatic ring in phenol is replaced by a sulfur atom. The prefix thio- implies a sulfur-containing compound and when used before a root word name for a compound which would normally contain an oxygen atom, in the case of 'thiol' that the alcohol oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom.
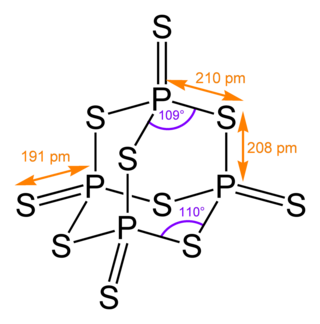
Phosphorus pentasulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula P2S5 (empirical) or P4S10 (molecular). This yellow solid is the one of two phosphorus sulfides of commercial value. Samples often appear greenish-gray due to impurities. It is soluble in carbon disulfide but reacts with many other solvents such as alcohols, DMSO, and DMF.
Chlorotoluenes are aryl chlorides based on toluene in which at least one aromatic hydrogen atom is replaced with a chlorine atom. They have the general formula C7H8–nCln, where n = 1–5 is the number of chlorine atoms.

Disulfur dichloride is the inorganic compound of sulfur and chlorine with the formula S2Cl2. It is an amber oily liquid.
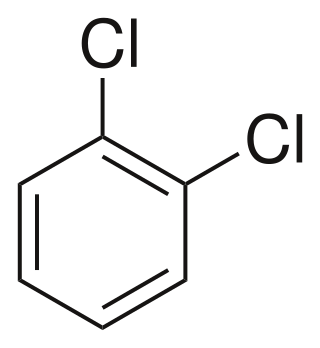
1,2-Dichlorobenzene, or orthodichlorobenzene (ODCB), is an aryl chloride and isomer of dichlorobenzene with the formula C6H4Cl2. This colourless liquid is poorly soluble in water but miscible with most organic solvents. It is a derivative of benzene, consisting of two adjacent chlorine atoms.
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene is an organochlorine compound, one of three isomers of trichlorobenzene. It is a derivative of benzene with three chloride substituents. It is a colorless liquid used as a solvent for a variety of compounds and materials.
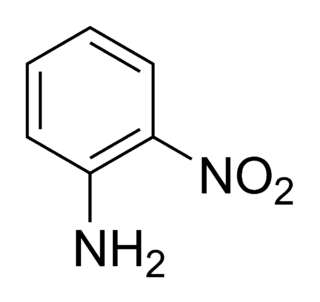
2-Nitroaniline is an organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4NO2. It is a derivative of aniline, carrying a nitro functional group in position 2. It is mainly used as a precursor to o-phenylenediamine.

4-Nitroaniline, p-nitroaniline or 1-amino-4-nitrobenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H6N2O2. A yellow solid, it is one of three isomers of nitroaniline. It is an intermediate in the production of dyes, antioxidants, pharmaceuticals, gasoline, gum inhibitors, poultry medicines, and as a corrosion inhibitor.
4-Chloroaniline is an organochlorine compound with the formula ClC6H4NH2. This pale yellow solid is one of the three isomers of chloroaniline.

o-Anisidine (2-anisidine) is an organic compound with the formula CH3OC6H4NH2. A colorless liquid, commercial samples can appear yellow owing to air oxidation. It is one of three isomers of the methoxy-containing aniline derivative.
4-Nitrotoluene or para-nitrotoluene is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4NO2. It is a pale yellow solid. It is one of three isomers of nitrotoluene.
3-Nitrotoluene or meta-nitrotoluene is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4NO2. It is one of three isomers of nitrotoluene. A yellow liquid, it is used in the manufacture of meta-toluidine, which is an intermediate in the production of various dyes.

2-Nitrochlorobenzene is an organic compound with the formula ClC6H4NO2. It is one of three isomeric nitrochlorobenzenes. It is a yellow crystalline solid that is important as a precursor to other compounds due to its two functional groups.
2-Nitrotoluene or ortho-nitrotoluene is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4NO2. It is pale yellow liquid that crystallizes in two forms, called α (−9.27 °C) and β (−3.17 °C). It is mainly a precursor to o-toluidine, which is an intermediate in the production of various dyes.
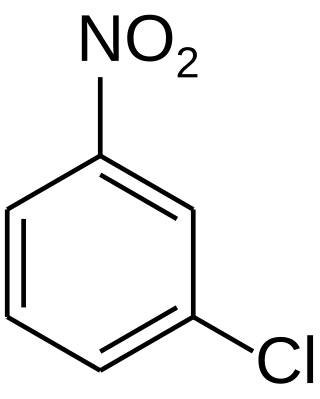
3-Nitrochlorobenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H4ClNO2. It is a yellow crystalline solid that is important as a precursor to other compounds due to the two reactive sites present on the molecule.

4-Nitrobiphenyl is an organic compound with the formula C6H5−C6H4NO2. It is one of three isomers of nitrobiphenyl and probably the most widely used. It is a precursor to the antioxidant 4-aminobiphenyl. 4-Nitrobiphenyl is readily prepared by nitration of biphenyl. It can also be prepared by cross-coupling reactions.

![4-Nitrochlorobenzene is the precursor to the anti-leprosy drug Dapsone (4-[(4-aminobenzene)sulfonyl]aniline). Dapsone.svg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c2/Dapsone.svg/230px-Dapsone.svg.png)












