
Acacia harpophylla, commonly known as brigalow, brigalow spearwood or orkor is an endemic tree of Australia. The Indigenous Australian group the Gamilaraay peoples know the tree as Barranbaa or Burrii. It is found in central and coastal Queensland to northern New South Wales. It can reach up to 25 m (82 ft) tall and forms extensive open-forest communities on clay soils.

Acacia complanata, known as long-pod wattle and flat-stemmed wattle, is a perennial tree native to eastern Australia.
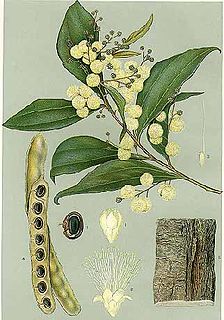
Acacia binervata, commonly known as two-veined hickory, is a shrub or tree that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia howittii, commonly known as sticky wattle or Howitt's wattle, is a tree species that is endemic to Victoria, Australia.

Acacia hammondii, also known as Hammond's wattle, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native across northern Australia.

Acacia latifolia is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to tropical parts of northern Australia.

Acacia limbata is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic across northern Australia.

Acacia oncinocarpa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to northern Australia.

Acacia juncifolia, commonly known as rush-leaf wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to north eastern Australia.

Acacia obtusata, commonly known as blunt-leaf wattle or obtuse wattle, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to eastern Australia.

Acacia semirigida, also known as stony ridge wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia kydrensis, commonly known as Kydra wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south eastern Australia.

Acacia blakei, commonly known as Blake's wattle or Wollomombi wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia caroleae, also known as Carol's wattle or narrow leaf currawong, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia cretata is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia jackesiana, also known as Betsy's wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia striatifolia is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia torulosa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia pycnostachya, also known as Bolivia wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to eastern Australia.

Acacia subporosa, also commonly known as river wattle, bower wattle, narrow-leaf bower wattle and sticky bower wattle, is a tree or shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south eastern Australia. It is considered to be rare in Victoria




















