
Acanthus mollis, commonly known as bear's breeches, sea dock, bear's foot plant, sea holly, gator plant or oyster plant, is a species of plant in the family Acanthaceae and is native to the Mediterranean region. It is a leafy, clump-forming perennial herb, with a rosette of relatively large, lobed or toothed leaves, and purplish and white flowers on an erect spike.

Adelia barbinervis is a species of flowering plant in the family Euphorbiaceae that is native to southern Mexico and northern Central America. The Huastec Maya cultivated the plant as a famine food.

Acanthus is a genus of about 30 species of flowering plants in the family Acanthaceae, native to tropical and warm temperate regions, with the highest species diversity in the Mediterranean Basin and Asia. This flowering plant is nectar-producing and depends on butterflies, such as Anartia fatima, and other nectar-feeding organisms to distribute its pollen. Common names include Acanthus and bear's breeches. The generic name derives from the Greek term ἄκανθος (akanthos) for Acanthus mollis, a plant that was commonly imitated in Corinthian capitals.

Anisotes is a genus of Afrotropical plants in the family Acanthaceae. The genus is morphologically similar to Metarungia, from which it differs mainly in the dehiscence of the fruit capsule, and the nature of the placenta. Placentas remain attached to the inner surface of fruit capsules in Anisotes.

Dendrobium antennatum, commonly known as the green antelope orchid, is an epiphytic orchid in the family Orchidaceae. It has cylindrical pseudobulbs with up to twelve leaves near their tips and up to fifteen white flowers with green petals and a white labellum with purple stripes. It grows in New Guinea and in tropical North Queensland where it is rare.

Dendrobium tetragonum, commonly known as the tree spider orchid, is a variable species of epiphytic or lithophytic orchid endemic to eastern Australia. Tree spider orchids are unusual in having pendulous pseudobulbs that are thin and wiry near the base then expand into a fleshy, four-sided upper section before tapering at the tip. There are only a few thin but leathery leaves at the end of the pseudobulbs and up to five flowers on relatively short flowering stems. To allow for the variations in the species there are five subspecies and a variety, some with a unique common name.

Bulbophyllum wadsworthii, commonly known as the yellow rope orchid, is a species of epiphytic or lithophytic orchid that forms clumps that hang off the surface on which the plant is growing. The pseudobulbs are small and partly hidden by brown, papery bracts. Each pseudobulb has a single fleshy, dark green leaf and a single star-shaped, cream-coloured or pale green flower with an orange labellum. It mainly grows on trees and rocks in rainforest and is endemic to Queensland.

Anisotes pubinervius is an Afrotropical plant species in the acanthus family, which is native to forest understorey in the Afromontane archipelago. It is widespread in eastern Africa, with isolated populations in southern Africa and Nigeria. The species is named for the fine down that covers the main leaf veins (-nervia).
Stenandriopsis is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Acanthaceae. It includes 20 species native to tropical Africa and Madagascar. Molecular phylogenies have placed the Old World Stenandriopsis apart from New World Stenandrium, and the genus is accepted in a classification of the family Acanthaceae published in 2022.
Liparis nugentiae, commonly known as the large sphinx orchid, is a plant in the orchid family and is endemic to Queensland. It is an epiphytic or lithophytic orchid which forms clumps with flattened pseudobulbs, two to four thin leaves and up to twenty greenish or pale yellow flowers. It grows in rainforest at altitudes above 600 m (2,000 ft) in tropical far North Queensland.
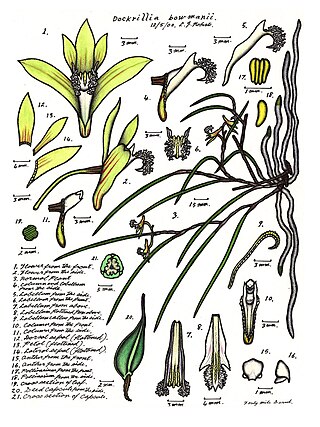
Dendrobium bowmanii, commonly known as the straggly pencil orchid, is an epiphytic or lithophytic orchid in the family Orchidaceae. It has thin wiry, straggly stems with a small number of small leaves and up to four greenish or brownish flowers with a conspicuous white labellum. It grows in drier rainforests and coastal scrub in New South Wales, southern Queensland and New Caledonia.
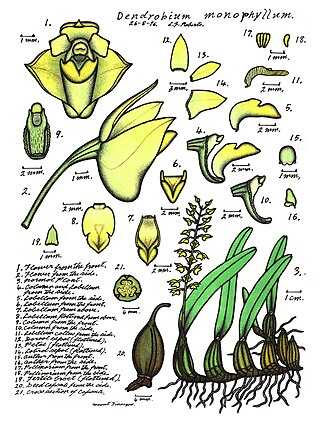
Dendrobium monophyllum, commonly known as the lily-of-the-valley orchid, is an epiphytic or lithophytic orchid in the family Orchidaceae. It has pale green to yellowish pseudobulbs with one or two leaves, and between five and twenty bell-shaped yellow flowers. It grows in rainforest in New South Wales and Queensland, Australia.

Bossiaea sericea is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae and is endemic to higher areas of south-eastern continental Australia. It is an erect shrub with more or less round to heart-shaped leaves with the narrower end towards the base, and yellow flowers.

Mackaya bella, called the forest bell bush, is a species of flowering plant in the acanthus family Acanthaceae, native to South Africa and Eswatini.

Pseuduvaria guineensis is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to New Guinea. James Sinclair, the Scottish botanist who first formally described the species, named it after New Guinea where the specimen he examined was collected near Kokoda.

Uvariopsis guineensis is a species of plant in the Annonaceae family. It is native to Guinea, Ivory Coast, Liberia, and Sierra Leone. Ronald William John Keay, the botanist who first formally described the species, named it after Guinea, then called French Guinea, where the specimens he examined were collected near a locality he identifies as Fassakoidou.
Acanthus gaed is a species of flowering plant in the genus of Acanthus. It is native to North Somalia and grows primarily in subtropical biomes.
Acanthus kulalensis is a species of flowering plant in the genus of Acanthus. It is native to North Kenya and grows primarily in seasonal dry tropical biome.
Bidens acuticaulis is an annual herbaceous flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is found in parts of tropical Africa. There are two currently accepted varieties of this species – B. acuticaulis var. acuticaulis, and B. acuticaulis var. filirostris.

Thunbergia mildbraediana is a species of flowering plant within the family Acanthaceae.













