The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle, or TCA cycle —is a series of biochemical reactions to release the energy stored in nutrients through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and alcohol. The chemical energy released is available in the form of ATP. The Krebs cycle is used by organisms that respire to generate energy, either by anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration. In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH, that are used in numerous other reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest components of metabolism. Even though it is branded as a "cycle", it is not necessary for metabolites to follow only one specific route; at least three alternative segments of the citric acid cycle have been recognized.

isoleucine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a hydrocarbon side chain with a branch. It is classified as a non-polar, uncharged, branched-chain, aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it. Essential amino acids are necessary in the human diet. In plants isoleucine can be synthesized from threonine and methionine. In plants and bacteria, isoleucine is synthesized from a pyruvate employing leucine biosynthesis enzymes. It is encoded by the codons AUU, AUC, and AUA.

Leucine (symbol Leu or L) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Leucine is an α-amino acid, meaning it contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain isobutyl group, making it a non-polar aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it; it must be obtained from the diet. Human dietary sources are foods that contain protein, such as meats, dairy products, soy products, and beans and other legumes. It is encoded by the codons UUA, UUG, CUU, CUC, CUA, and CUG. Leucine is named after the Greek word for "white": λευκός (leukós, "white"), after its common appearance as a white powder, a property it shares with many other amino acids.

N-acetylcysteine, also known as Acetylcysteine and NAC, is a medication that is used to treat paracetamol (acetaminophen) overdose and to loosen thick mucus in individuals with chronic bronchopulmonary disorders, such as pneumonia and bronchitis. It has been used to treat lactobezoar in infants. It can be taken intravenously, orally, or inhaled as a mist. It is also sometimes used as a dietary supplement.

Atomoxetine, formerly sold under the brand name Strattera, is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (sNRI) medication used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and, to a lesser extent, cognitive disengagement syndrome (CDS). It may be used alone or along with stimulant medication. It enhances the executive functions of self-motivation, sustained attention, inhibition, working memory, reaction time, and emotional self-regulation. Use of atomoxetine is only recommended for those who are at least six years old. It is taken orally. The effectiveness of atomoxetine is comparable to the commonly prescribed stimulant medication methylphenidate.
Ataxia–telangiectasia, also referred to as ataxia–telangiectasia syndrome or Louis–Bar syndrome, is a rare, neurodegenerative disease causing severe disability. Ataxia refers to poor coordination and telangiectasia to small dilated blood vessels, both of which are hallmarks of the disease. A–T affects many parts of the body:

Spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) is a progressive, degenerative, genetic disease with multiple types, each of which could be considered a neurological condition in its own right. An estimated 150,000 people in the United States have a diagnosis of spinocerebellar ataxia at any given time. SCA is hereditary, progressive, degenerative, and often fatal. There is no known effective treatment or cure. SCA can affect anyone of any age. The disease is caused by either a recessive or dominant gene. In many cases people are not aware that they carry a relevant gene until they have children who begin to show signs of having the disorder. Currently, research is being conducted at Universities, such as the University of Minnesota, to elucidate many of the unknown characteristics of the disease.

β-Hydroxy β-methylbutyric acid (HMB), otherwise known as its conjugate base, β-hydroxyβ-methylbutyrate, is a naturally produced substance in humans that is used as a dietary supplement and as an ingredient in certain medical foods that are intended to promote wound healing and provide nutritional support for people with muscle wasting due to cancer or HIV/AIDS. In healthy adults, supplementation with HMB has been shown to increase exercise-induced gains in muscle size, muscle strength, and lean body mass, reduce skeletal muscle damage from exercise, improve aerobic exercise performance, and expedite recovery from exercise. Medical reviews and meta-analyses indicate that HMB supplementation also helps to preserve or increase lean body mass and muscle strength in individuals experiencing age-related muscle loss. HMB produces these effects in part by stimulating the production of proteins and inhibiting the breakdown of proteins in muscle tissue. No adverse effects from long-term use as a dietary supplement in adults have been found.

β-Hydroxybutyric acid, also known as 3-hydroxybutyric acid or BHB, is an organic compound and a beta hydroxy acid with the chemical formula CH3CH(OH)CH2CO2H; its conjugate base is β-hydroxybutyrate, also known as 3-hydroxybutyrate. β-Hydroxybutyric acid is a chiral compound with two enantiomers: D-β-hydroxybutyric acid and L-β-hydroxybutyric acid. Its oxidized and polymeric derivatives occur widely in nature. In humans, D-β-hydroxybutyric acid is one of two primary endogenous agonists of hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2 (HCA2), a Gi/o-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR).
The GM2 gangliosidoses are a group of three related genetic disorders that result from a deficiency of the enzyme beta-hexosaminidase. This enzyme catalyzes the biodegradation of fatty acid derivatives known as gangliosides. The diseases are better known by their individual names: Tay–Sachs disease, AB variant, and Sandhoff disease.

β-Hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), also known as 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A, is an intermediate in the mevalonate and ketogenesis pathways. It is formed from acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA by HMG-CoA synthase. The research of Minor J. Coon and Bimal Kumar Bachhawat in the 1950s at University of Illinois led to its discovery.

Enoyl-CoA hydratase (ECH) or crotonase is an enzyme EC 4.2.1.17 that hydrates the double bond between the second and third carbons on 2-trans/cis-enoyl-CoA:
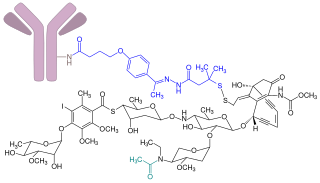
Inotuzumab ozogamicin, sold under the brand name Besponsa, is an antibody-drug conjugate medication used to treat relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. It is administered by intravenous infusion.

In enzymology, an isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a leucine N-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Niemann–Pick type C (NPC) is a lysosomal storage disease associated with mutations in NPC1 and NPC2 genes. Niemann–Pick type C affects an estimated 1:150,000 people. Approximately 50% of cases present before ten years of age, but manifestations may first be recognized as late as the sixth decade. Despite its name, Niemann-Pick disease, type C has very little to do with SMPD1-associated Niemann–Pick disease, although they were once thought to be the same disease.

Gabapentinoids, also known as α2δ ligands, are a class of drugs that are chemically derivatives of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) which bind selectively to the α2δ protein that was first described as an auxiliary subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs).

β-Leucine (beta-leucine) is a beta amino acid and positional isomer of L-leucine which is naturally produced in humans via the metabolism of L-leucine by the enzyme leucine 2,3-aminomutase. In cobalamin (vitamin B12) deficient individuals, plasma concentrations of β-leucine are elevated.

Monomethyl fumarate, sold under the brand name Bafiertam is a medication used for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis, to include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, in adults. It is taken by mouth.

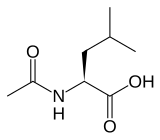
Levacetylleucine, sold under the brand name Aqneursa, is a medication used for the treatment of neurological manifestations of Niemann-Pick disease type C. Levacetylleucine is a modified version of the amino acid leucine (N-Acetyl-L-Leucine). It is the L form of acetylleucine. It is taken by mouth.