
The Western Ghats, also known as the Sahyadri mountain range, is a mountain range that covers an area of 160,000 km2 (62,000 sq mi) in a stretch of 1,600 km (990 mi) parallel to the western coast of the Indian peninsula, traversing the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the 36 biodiversity hotspots in the world. It is sometimes called the Great Escarpment of India. It contains a very large proportion of the country's flora and fauna, many of which are endemic to this region. The Western Ghats are older than the Himalayas. They influence Indian monsoon weather patterns by intercepting the rain-laden monsoon winds that sweep in from the south-west during late summer. The range runs north to south along the western edge of the Deccan Plateau and separates the plateau from a narrow coastal plain called the Western Coastal Plains along the Arabian Sea. A total of 39 areas in the Western Ghats, including national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and reserve forests, were designated as world heritage sites in 2012 – twenty of them in Kerala, ten in Karnataka, six in Tamil Nadu and four in Maharashtra.

The South Western Ghats montane rain forests is an ecoregion in South India, covering the southern portion of the Western Ghats in Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu at elevations from 1,000 to 2,695 m. Annual rainfall in this ecoregion exceeds 2,800 mm (110 in).

Silent Valley National Park is a national park in Kerala, India. It is located in the Nilgiri hills and has a core area of 89.52 km2 (34.56 sq mi). It is surrounded by a buffer zone of 148 km2 (57 sq mi). This national park has some rare species of flora and fauna. Silent Valley National Park was explored in 1847 by the botanist Robert Wight. It is located in the border of Mannarkkad Taluk of Palakkad district, Nilambur Taluk of Malappuram district, Kerala, and Nilgiris district of Tamil Nadu.
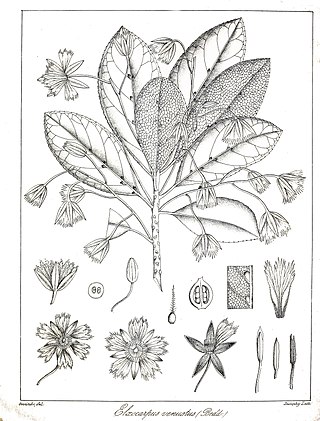
Elaeocarpus venustus is a species of flowering plant in the Elaeocarpaceae family. It is found only in the Western Ghats of Tamil Nadu state in southern India. It is Critically Endangered, and threatened by habitat loss.
Leptolaena abrahamii is a species of flowering plant in the family Sarcolaenaceae. It is found only in Madagascar. Its natural habitat is mid-elevation humid tropical forests. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Garcinia rubroechinata, commonly known as malamkongu and sometimes known as Garcinia rubro-echinata, is a species of flowering plant in the family Clusiaceae. It is a tree which grows to 20 meters tall. It is found only in the Western Ghats of southern India.

Lemurophoenix halleuxii is a species of palm tree, the only species in the genus Lemurophoenix. It is found only in Madagascar. It is threatened by habitat loss and overcollection. There are perhaps 300 mature individuals remaining in the wild.

Raorchestes munnarensis is a species of frog in the family Rhacophoridae endemic to Munnar, Kerala, along the Ghat road to Devikulam in the southern Western Ghats, India.
Actinodaphne bourneae is a species of plant in the family Lauraceae. It is endemic to Tamil Nadu in India. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Actinodaphne fragilis is a species of plant in the family Lauraceae. It is a tree endemic to Peninsular Malaysia.
Actinodaphne johorensis is a species of plant in the family Lauraceae. It is endemic to Peninsular Malaysia. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Anacolosa densiflora is a species of plant in the Olacaceae family. Currently, it is an endangered species that is endemic to India.

Goniothalamus wynaadensis is a species of plant in the Annonaceae family. It is endemic to the Western Ghats of southern India.

Khaya madagascariensis is a species of plant in the family Meliaceae. It is found in Comoros and Madagascar.
Melanophylla alnifolia is a species of plant in the Torricelliaceae family. It is endemic to eastern Madagascar. Its natural habitat is tropical moist lowland and montane forests. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Nothofagus stylosa is a species of plant in the family Nothofagaceae. It is endemic to West Papua (Indonesia). It is a Critically Endangered species threatened by habitat loss.

A vulnerable species is a species which has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as being threatened with extinction unless the circumstances that are threatening its survival and reproduction improve.

Actinodaphne bourdillonii is a species of the genus Actinodaphne of the flowering plant family Lauraceae, commonly called the malavirinji, eeyoli, and pisa. It is endemic to the Southern Western Ghats. Its general habitat is shola and montane evergreen forests from 600 to 2,000 metres elevation.
Humbertiodendron is a monotypic genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Trigoniaceae. The only species is Humbertiodendron saboureaui.

Hernandia voyronii, commonly known as Hazomalany, is a species of plant in the Hernandiaceae family. It is endemic to Madagascar.












