
The Araneomorphae are an infraorder of spiders. They are distinguishable by chelicerae (fangs) that point diagonally forward and cross in a pinching action, in contrast to the Mygalomorphae, where they point straight down. Araneomorphs comprise the vast majority of living spiders.

Deinopidae, also known as net casting spiders, is a family of cribellate spiders first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1850. It consists of stick-like elongated spiders that catch prey by stretching a web across their front legs before propelling themselves forward. These unusual webs will stretch two or three times their relaxed size, entangling any prey that touch them. The posterior median eyes have excellent night vision, allowing them to cast nets accurately in low-light conditions. These eyes are larger than the others, and sometimes makes these spiders appear to only have two eyes. Ogre-faced spiders (Deinopis) are the best known genus in this family. The name refers to the perceived physical similarity to the mythological creature of the same name. This family also includes the humped-back spiders (Menneus).
The Halidae were a tiny spider family with only three described species in two genera. As of 2006, this family was no longer considered valid; the two genera are instead grouped in the family Pisauridae.

Dolichopterus is a genus of prehistoric sea scorpions, arthropods in the order Eurypterida. Fossils of Dolichopterus have been discovered in deposits ranging from Silurian to Devonian, and have been referred to several different species, some of them of dubious affinity to this genus.

Brachyopterus is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid of the family Rhenopteridae. It is one of the earliest known eurypterids, having been recovered from Middle Ordovician deposits in Montgomeryshire, Wales. Though other species have been assigned to it in the past, Brachyopterus is today recognized as containing one valid species, B. stubblefieldi.

Ctenopterus is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid of the family Stylonuridae. It contains only one species, Ctenopterus cestrotus from the Early Silurian of Otisville, New York, United States.

Waeringopterus is a genus of prehistoric eurypterids from the Silurian of North America. The genus contains two species, W. apfeli from the Syracuse and Vernon Formations of New York and Ontario and W. cumberlandicus from the Wills Creek Formation, West Virginia. Fossils of the genus also were found in the Indian Point Formation of Quebec.

Erieopterus is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid found in Silurian to Devonian-aged marine and freshwater strata of Europe and North America. The genus contains eight species from the Silurian to the Devonian, recovered from both North America and Europe.

Stylonurus is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid of the family Stylonuridae. The genus contains three species: Stylonurus powriensis from the Devonian of Scotland, Stylonurus shaffneri from the Devonian of Pennsylvania and Stylonurus perspicillum from the Devonian of Germany.

Hardieopterus is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid classified within the family Hardieopteridae. The genus contains four species, all Silurian in age; H. lanarkensis and H. macrophthalmus from Scotland, H. megalops from England and H. myops from the United States.

Laurieipterus is a genus of a eurypterid classified as part of the family Stylonuridae. It contains one species, L. elegans from the Early Silurian of Scotland.

Eurypteroidea are an extinct superfamily of eurypterids. It contains three families and two genera of uncertain classification, Paraeurypterus and Pentlandopterus.
Speleoticus is a spider genus in the family Nesticidae. Its species are found in Japan and China.
Aituaria pontica is an araneomorph spider of the family Nesticidae. It occurs in the Krasnodar region of Russia and in Georgia.
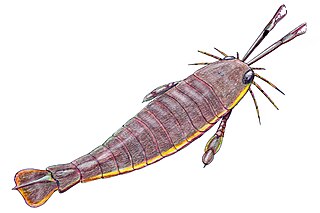
Diploperculata is an infraorder of eurypterids, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". The name, derived from Greek διπλόω ("double") and operculum, refers to the distinguishing feature that unites the superfamilies included in the group, that the genital operculum is made up of two fused segments.

Onychopterellidae are an extinct family of eurypterids. The family is the only family classified as part of the superfamily Onychopterelloidea. Genera included are Alkenopterus, Onychopterella and Tylopterella.

Moselopteridae are an extinct family of eurypterids. It is the only family classified as part of the superfamily Moselopteroidea, and contains three genera: Moselopterus, Stoermeropterus and Vinetopterus.

The Selenocosmiinae are a subfamily of tarantulas found throughout South-East Asia and Australia. This subfamily is defined by the presence of a lyra on the maxillae and strikers on the chelicerae, allowing these spiders to stridulate and produce a "hissing" sound. However some species within Phlogiellus may have secondary lost their lyra but retain their strikers. The monophyly of the subfamily has been only tested using genetic data with a handful of genera or species in a few studies. However, these studies found genera that had been previously placed in this subfamily were actual their own separate subfamily (Poecilotheria) and that Selenocosmiinae is most closely related to the Indian Thrigmopoeinae. As of 2021, Selenocosmiinae contains 11 genera.
Saphrys tehuelche is a species of jumping spider. The species was classified in the genus Euophrys from 1968, when it was first described by María Elena Galiano, until 2015. It can be found in Chile.

Trachycosmidae, is a family of spiders in the infraorder Araneomorphae.















