
Strepsirrhini or Strepsirhini is a suborder of primates that includes the lemuriform primates, which consist of the lemurs of Madagascar, galagos ("bushbabies") and pottos from Africa, and the lorises from India and southeast Asia. Collectively they are referred to as strepsirrhines. Also belonging to the suborder are the extinct adapiform primates which thrived during the Eocene in Europe, North America, and Asia, but disappeared from most of the Northern Hemisphere as the climate cooled. Adapiforms are sometimes referred to as being "lemur-like", although the diversity of both lemurs and adapiforms does not support this comparison.

Omomyidae is a group of early primates that radiated during the Eocene epoch between about 55 to 34 million years ago (mya). Fossil omomyids are found in North America, Europe & Asia making it one of two groups of Eocene primates with a geographic distribution spanning holarctic continents, the other being the adapids. Early representatives of the Omomyidae and Adapidae appear suddenly at the beginning of the Eocene in North America, Europe, and Asia, and are the earliest known crown primates.

Tarsiiformes are a group of primates that once ranged across Europe, northern Africa, Asia, and North America, but whose extant species are all found in the islands of Southeast Asia. Tarsiers are the only living members of the infraorder, and also include the extinct Tarsius eocaenus from the Eocene and Tarsius thailandicus from the Miocene. Two extinct genera, Xanthorhysis and Afrotarsius, are considered to be close relatives of the living tarsiers and are generally classified within Tarsiiformes, with the former grouped within family Tarsiidae and the latter listed as incertae sedis (undefined). Omomyids are generally considered to be extinct relatives, or even ancestors, of the living tarsiers and are often classified within Tarsiiformes. Other fossil primates, which include Microchoeridae, Carpolestidae, and Eosimiidae, have been included in this classification, although the fossil evidence is debated. Eosimiidae has also been classified under the infraorder Simiiformes. Likewise, Carpolestidae is often classified within the order Plesiadapiformes, a very close, extinct relative of primates. These conflicting classifications lie at the heart of the debate over early primate evolution. Even the placement of Tarsiiformes within suborder Haplorhini is still debated.

Lemuriformes is an infraorder of primate that falls under the suborder Strepsirrhini. It includes the lemurs of Madagascar, as well as the galagos and lorisids of Africa and Asia, although a popular alternative taxonomy places the lorisoids in their own infraorder, Lorisiformes.

Adapiformes is a group of early primates. Adapiforms radiated throughout much of the northern continental mass, reaching as far south as northern Africa and tropical Asia. They existed from the Eocene to the Miocene epoch. Some adapiforms resembled living lemurs.
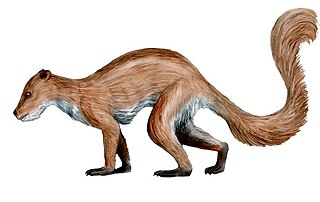
Plesiadapiformes is a group of Primates, as sister of the Dermoptera. While none of the groups normally directly assigned to this group survived, the group appears actually not to be literally extinct as the remaining primates appear to be derived Plesiadapiformes, as sister of e.g. the Carpolestidae. The term Plesiadapiformes may still be used for all primates which are not crown primates, but this usage is obviously paraphyletic. When the crown primates are cladistically granted, it becomes an obsolete junior synonym to primates. Purgatorius is believed to be a basal Plesiadapiformes.
The postorbital bar is a bony arched structure that connects the frontal bone of the skull to the zygomatic arch, which runs laterally around the eye socket. It is a trait that only occurs in mammalian taxa, such as most strepsirrhine primates and the hyrax, while haplorhine primates have evolved fully enclosed sockets. One theory for this evolutionary difference is the relative importance of vision to both orders. As haplorrhines tend to be diurnal, and rely heavily on visual input, many strepsirrhines are nocturnal and have a decreased reliance on visual input.

Notharctinae is an extinct subfamily of primates that were common in North America during the early and middle Eocene. The six genera that make up the group contain species that are among the most primitive of the adapiform group, which is one of the most primitive groups of primates. The evolutionary history of this subfamily has been comparatively well documented and has been used to argue for evolutionary gradualism. Though it is generally accepted that adapiforms gave rise to modern day lemurs and lorises, it is not currently known which branch of Adapiformes these living species are most closely related to. Notharctines became extinct in the middle Eocene, most likely because of a combination of factors including climatic change and competition with other North American primates.

A toothcomb is a dental structure found in some mammals, comprising a group of front teeth arranged in a manner that facilitates grooming, similar to a hair comb. The toothcomb occurs in lemuriform primates, treeshrews, colugos, hyraxes, and some African antelopes. The structures evolved independently in different types of mammals through convergent evolution and varies both in dental composition and structure. In most mammals the comb is formed by a group of teeth with fine spaces between them. The toothcombs in most mammals include incisors only, while in lemuriform primates they include incisors and canine teeth that tilt forward at the front of the lower jaw, followed by a canine-shaped first premolar. The toothcombs of colugos and hyraxes take a different form with the individual incisors being serrated, providing multiple tines per tooth.
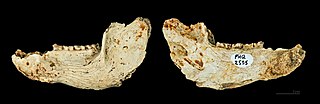
Adapis is an extinct genus of Adapidae primate belonging to the subfamily Adapinae. The genus was named by Cuvier in 1821 and contains up to three species. Males were larger than females.

Europolemur is a genus of adapiformes primates that lived in Europe during the middle Eocene.

Babakotia is an extinct genus of medium-sized lemur, or strepsirrhine primate, from Madagascar that contains a single species, Babakotia radofilai. Together with Palaeopropithecus, Archaeoindris, and Mesopropithecus, it forms the family Palaeopropithecidae, commonly known as the sloth lemurs. The name Babakotia comes from the Malagasy name for the indri, babakoto, to which it and all other sloth lemurs are closely related. Due to its mix of morphological traits that show intermediate stages between the slow-moving smaller sloth lemurs and the suspensory large sloth lemurs, it has helped determine the relationship between both groups and the closely related and extinct monkey lemurs.
Ekgmowechashala is an extinct genus of primate belonging to Adapiformes.
Azibiidae is an extinct family of fossil primate from the late early or early middle Eocene from the Glib Zegdou Formation in the Gour Lazib area of Algeria. They are thought to be related to the living toothcombed primates, the lemurs and lorisoids, although paleoanthropologists such as Marc Godinot have argued that they may be early simians. It includes the genera Azibius and Algeripithecus, the latter of which was originally considered the oldest known simian, not a strepsirrhine.
Azibius is an extinct genus of fossil primate from the late early or early middle Eocene from the Glib Zegdou Formation in the Gour Lazib area of Algeria. They are thought to be related to the living toothcombed primates, the lemurs and lorisoids, although paleoanthropologists such as Marc Godinot have argued that they may be early simians. Originally described as a type of plesiadapiform, its fragmentary remains have been interpreted as a hyopsodontid, an adapid, and a macroscelidid. Less fragmentary remains discovered between 2003 and 2009 demonstrated a close relationship between Azibius and Algeripithecus, a fossil primate once thought to be the oldest known simian. Descriptions of the talus in 2011 have helped to strengthen support for the strepsirrhine status of Azibius and Algeripithecus, which would indicate that the evolutionary history of lemurs and their kin is rooted in Africa.
Djebelemur is an extinct genus of early strepsirrhine primate from the late early or early middle Eocene period from the Chambi locality in Tunisia. Although they probably lacked a toothcomb, a specialized dental structure found in living lemuriforms, they are thought to be a related stem group. The one recognized species, Djebelemur martinezi, was very small, approximately 100 g (3.5 oz).
Djebelemuridae is an extinct family of early strepsirrhine primates from Africa. It consists of five genera. The organisms in this family were exceptionally small, and were insectivores. It is predicted that this family existed from early to late Eocene, they lacked a teeth comb and were able to fully rotate their heads. It is also predicted that this family was a pivotal point for primate evolution, and that they were the cause for the adaption of a tooth comb.
Plesiopithecus is an extinct genus of early strepsirrhine primate from the late Eocene.

The evolutionary history of the primates can be traced back 57-85/90 million years. One of the oldest known primate-like mammal species, Plesiadapis, came from North America; another, Archicebus, came from China. Other similar basal primates were widespread in Eurasia and Africa during the tropical conditions of the Paleocene and Eocene. Purgatorius is the genus of the four extinct species believed to be the earliest example of a primate or a proto-primate, a primatomorph precursor to the Plesiadapiformes, dating to as old as 66 million years ago.
Sivaladapis is a genus of adapiform primate that lived in Asia during the middle Miocene.













