
Strepsirrhini or Strepsirhini is a suborder of primates that includes the lemuriform primates, which consist of the lemurs of Madagascar, galagos ("bushbabies") and pottos from Africa, and the lorises from India and southeast Asia. Collectively they are referred to as strepsirrhines. Also belonging to the suborder are the extinct adapiform primates which thrived during the Eocene in Europe, North America, and Asia, but disappeared from most of the Northern Hemisphere as the climate cooled. Adapiforms are sometimes referred to as being "lemur-like", although the diversity of both lemurs and adapiforms does not support this comparison.

Lemuriformes is the sole extant infraorder of primate that falls under the suborder Strepsirrhini. It includes the lemurs of Madagascar, as well as the galagos and lorisids of Africa and Asia, although a popular alternative taxonomy places the lorisoids in their own infraorder, Lorisiformes.

The simians, anthropoids, or higher primates are an infraorder of primates containing all animals traditionally called monkeys and apes. More precisely, they consist of the parvorders Platyrrhini and Catarrhini, the latter of which consists of the family Cercopithecidae and the superfamily Hominoidea.

Eosimiidae is the possible family of extinct primates believed to be the earliest simians.
Calsoyasuchus is a genus of crocodylomorph that lived in the Early Jurassic. Its fossilized remains were found in the Sinemurian-Pliensbachian-age Kayenta Formation on Navajo Nation land in Coconino County, Arizona, United States. Formally described as C. valliceps, it is known from a single incomplete skull which is unusually derived for such an early crocodile relative. This genus was described in 2002 by Ronald Tykoski and colleagues; the specific name means "valley head" and refers to a deep groove along the midline of the nasal bones and frontal bones. It has often been interpreted as the earliest diverging member of Goniopholididae, but other studies have recovered it in various other positions.
Rooneyia viejaensis is a relatively small primate belonging to the extinct monotypic genus Rooneyia. Rooneyia viejaensis is known from the North American Eocene of the Sierra Vieja of West Texas; the species is only known from the type specimen. The lack of additional fossils at this time makes it difficult to hypothesize where and how Rooneyia may have evolved. The minimal wear upon the molar teeth of the specimen has led to the assumption that the type specimen is that of a young adult. Rooneyia does not consistently fall within any one group of fossil or extant primates.

Angulomastacator is a genus of duck-billed dinosaur from the Campanian-age Aguja Formation of Big Bend National Park, Texas. It is known from a single specimen, TMM 43681–1, a partial left maxilla. This bone is curved down approximately 45° at its anterior end, with the tooth row bent to fit, unlike any other hadrosaur. The unusual characteristics of the maxilla, which have not been reported from elsewhere, supports the hypothesis that the dinosaurs of the Aguja Formation were endemic forms. It was discovered in the upper shale member of the Aguja Formation, among plant, bone, and clam fragments in a bed interpreted as the deposits of a small tributary channel. This bed is just below rocks of the overlying Javelina Formation. Volcanic rocks at about the same level have been dated to 76.9 ± 1.2 million years ago.
Algeripithecus is an extinct genus of early fossil primate, weighing approximately 65 to 85 grams. Fossils have been found in Algeria dating from 50 to 46 million years ago.
Trimethylenemethane cycloaddition is the formal (3+2) annulation of trimethylenemethane (TMM) derivatives to two-atom pi systems. Although TMM itself is too reactive and unstable to be stored, reagents which can generate TMM or TMM synthons in situ can be used to effect cycloaddition reactions with appropriate electron acceptors. Generally, electron-deficient pi bonds undergo cyclization with TMMs more easily than electron-rich pi bonds.
Kayentachelys is an extinct genus of turtle known only from the "silty facies" of the Lower Jurassic Kayenta Formation in northeastern Arizona on the lands of the Navajo Nation.

Cantius is a genus of adapiform primates from the early Eocene of North America and Europe. It is extremely well represented in the fossil record in North America and has been hypothesized to be the direct ancestor of Notharctus in North America. The evolution of Cantius is characterized by a significant increase in body mass that nearly tripled in size. The earliest species were considered small-sized and weighed in around 1 kg (2.2 lb), while the later occurring species were considered medium-sized and likely weighed in around 3 kg (6.6 lb). Though significantly smaller, the fossil remains discovered of the various species of Cantius have striking similarities to that of Notharctus and Smilodectes. It is likely Cantius relied on arboreal quadrupedal locomotion, primarily running and leaping. This locomotor pattern comparable to that of extant lemurs, which has fostered the hypothesis that Cantius and other strepsirrhine adapiforms may have a close phylogenetic affinity to living lemurs.
Otischalkia is an extinct genus of archosauromoph from late Triassic deposits of Howard County, Texas, US It is known from the holotype TMM 31025-263, left humerus and from the referred specimens TMM 31025-262, TMM 31025-266, TMM 31025-264, TMM 31185-92 and TMM 31185-93. It was found in the Lower Dockum Group near the abandoned settlement of Otis Chalk. It was first named by Adrian P. Hunt and Spencer G. Lucas in 1991 and the type species is Otischalkia elderae.
Parapithecidae is an now extinct family of primates which lived in the Eocene and Oligocene periods in Egypt. Eocene fossils from Myanmar are sometimes included in the family in addition. They showed certain similarities in dentition to Condylarthra, but had short faces and jaws shaped like those of tarsiers. They are part of the superfamily Parapithecoidea, perhaps equally related to Ceboidea and Cercopithecoidea plus Hominoidea - but the placement of Parapithecoidea is substantially uncertain.
Azibiidae is an extinct family of fossil primate from the late early or early middle Eocene from the Glib Zegdou Formation in the Gour Lazib area of Algeria. They are thought to be related to the living toothcombed primates, the lemurs and lorisoids, although paleoanthropologists such as Marc Godinot have argued that they may be early simians. It includes the genera Azibius and Algeripithecus, the latter of which was originally considered the oldest known simian, not a strepsirrhine.
Azibius is an extinct genus of fossil primate from the late early or early middle Eocene from the Glib Zegdou Formation in the Gour Lazib area of Algeria. They are thought to be related to the living toothcombed primates, the lemurs and lorisoids, although paleoanthropologists such as Marc Godinot have argued that they may be early simians. Originally described as a type of plesiadapiform, its fragmentary remains have been interpreted as a hyopsodontid, an adapid, and a macroscelidid. Less fragmentary remains discovered between 2003 and 2009 demonstrated a close relationship between Azibius and Algeripithecus, a fossil primate once thought to be the oldest known simian. Descriptions of the talus in 2011 have helped to strengthen support for the strepsirrhine status of Azibius and Algeripithecus, which would indicate that the evolutionary history of lemurs and their kin is rooted in Africa.
Mahgarita stevensi is a genus of adapiform primate that lived in North America during the late Eocene. Fossils of the genus were found in the Duchesnean Laredo and Devil's Graveyard Formations of Texas.
Sivaladapis is a genus of adapiform primate that lived in Asia during the middle Miocene.
Afradapis is a genus of adapiform primate that lived during the Late Eocene. The only known species, Afradapis longicristatus, was discovered in the Birket Qarun Formation in northern Egypt in 2009. While its geographic distribution is confined to Afro-Arabia, Afradapis belongs to the predominantly European adapiform family Caenopithecinae. This taxonomic placement is supported by recent phylogenetic analyses that recover a close evolutionary relationship between Afradapis and adapiforms, including Darwinius. While adapiforms have been noted for their strepsirrhine-like morphology, no adapiform fossil possesses the unique anatomical traits to establish an ancestor-descent relationship between caenopithecids and living strepsirrhines. It ate leaves and moved around slowly like lorises.

Chinatichampsus is an extinct genus of crocodilian from the Devil's Graveyard Formation of Texas, specifically the Dalquest Desert Research Site. It is a monotypic genus, containing only the type species Chintanichampsus wilsonorum. A single specimen, TMM 45911–1, was first discovered in 2010. Chinatichampsus is the most basal Eocene caimanine, dating to between 42.8 and 41.5 million years ago, and is considered to be more basal than Protocaiman.
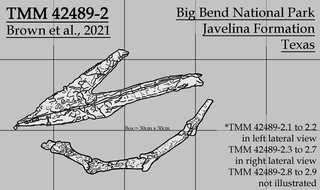
Wellnhopterus is an azhdarchid pterosaur recovered from the Late Cretaceous Javelina Formation in Texas that was previously identified as a thalassodromine. It consists of a set of upper and lower jaws, as well as some cervical vertebrae and a fragmentary long bone. In July 2021, the jaws were given the genus name "Javelinadactylus", with the type and only species as "J. sagebieli"; however, this article has now been retracted. In a paper published in December 2021, the complete holotype was independently named Wellnhopterus, with the only species being W. brevirostris. As of 2022, this is the formal name of this pterosaur.









