
Uttama, also known as Madhurantaka, was a Chola Emperor who ruled from 970 CE to 985 CE in present-day Tamil Nadu, India. According to Tiruvalangadu plates of Rajendra Chola, Madhurantaka Uttama's reign is placed after Aditya II. The latter may have been a co-regent of Parantaka II and seems to have died before he could formally ascend the throne. Uttama was the cousin of Parantaka II and was the son of the illustrious Sembiyan Mahadevi and Gandaraditya.

Rajaraja I, also known as Rajaraja the Great, was a Chola emperor who reigned from 985 CE to 1014 CE. He is known for his conquests of South India and parts of Sri Lanka, and increasing Chola influence across the Indian Ocean.

Kulottunga Chola I also spelt Kulothunga, born Rajendra Chalukya, was a Chola Emperor who reigned from 1070 to 1122 succeeding his cousin Athirajendra Chola. He also served as the Eastern Chalukya monarch from 1061 to 1118, succeeding his father Rajaraja Narendra. He is related to the Chola dynasty through his mother's side and the Eastern Chalukyas through his father's side. His mother, Ammangaidevi, was a Chola princess and the daughter of emperor Rajendra Chola I. His father was king Rajaraja Narendra of the Eastern Chalukya dynasty who was the nephew of Rajendra and maternal grandson of Rajaraja Chola I. According to historian Sailendra Nath Sen, his accession marked the beginning of a new era and ushered in a period of internal peace and benevolent administration. He was succeeded by his son Vikrama Chola

Rajendra Chola I, often referred to as Rajendra the Great, Gangaikonda Cholan, and Kadaram Kondan, was a Chola Emperor who reigned from 1014 and 1044 CE. He was born in Thanjavur to Rajaraja I and his queen Vanavan Mahadevi and assumed royal power as co-regent with his father in 1012 until his father died in 1014, when Rajendra ascended to the Chola throne. During his reign, the Chola Empire reached its zenith in the Indian subcontinent; it extended its reach via trade and conquest across the Indian Ocean, making Rajendra one of only a few Indian monarchs who conquered territory beyond South Asia.

The Chola dynasty was a Tamil dynasty originating from southern India. At its height, it ruled over the Chola Empire, an expansive maritime empire. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century BCE during the reign of Ashoka of the Maurya empire. The Chola empire was at its peak and achieved imperialism under the Medieval Cholas in the mid-9th century CE. As one of the Three Crowned Kings of Tamilakam, along with the Chera and Pandya, the dynasty continued to govern over varying territories until the 13th century CE.

Parantaka Chola I was a Chola emperor who ruled for forty-eight years, annexing Pandya by defeating Rajasimhan II and in the Deccan won the Battle of Vallala against Rashtrakutas which happened before 916 CE. The best part of his reign was marked by increasing success and prosperity.
Gandaraditha Chola succeeded his father Parantaka I and became the Chola king about 955 CE. He was also a Tamil literary poet in the Thiruvisaippa Palandu. He had a son named Madurantaka Chola also known as Uttama Chola, who became Chola emperor after his cousin Sundara Chola.
Arinjaya Chola was a ruler of the Chola kingdom. He was the third son of Parantaka I and the younger brother of Gandaraditya Chola, whom he is thought to have succeeded in about 956. Arinjaya Chola was succeeded by his son Sundara Chola as Madurantaka Uttama Chola was not old enough to ascend the throne. Arinjaya seems to have ruled for a very short time.
Parantaka II was a Chola emperor. He is also known as Sundara Chola as he was considered an epitome of male beauty. He was the son of Arinjaya Chola and queen Kalyani, a princess of Vaidumba family. Parantaka II ascended the Chola throne despite the fact that his cousin Madurantaka Uttama Chola, the son of Gandaraditya Chola was alive and he had equal if not more claim to the Chola throne. During his reign, Parantaka Sundara Chola defeated the Pandyas and Ceylon and then recaptured the Tondaimandalam from Rashtrakutas.

Karikala often referred to as Karikala the Great was a Tamil Emperor of the Early Cholas of the Chola dynasty who ruled ancient Tamilakam from Uraiyur. He is credited with the construction of the flood banks of the river Kaveri and conquest of Tamilakam, Andhra and Sri Lanka. He is recognised as the greatest of the Early Cholas. In Thiruvalangadu plates of Rajendra Chola I, Medieval Tamil Cholas listed Karikala Chola as one of their ancestors.

Rajendra Chola II often referred to as Rajendradeva Chola was a Chola emperor who reigned from 1052 CE to 1064 CE. Rajendra II succeeded his brother Rajadhiraja I after his death at the Battle of Koppam. Rajendra had served as a Co-regent under his brother from 1044 CE to 1052 CE. When he acceded the throne, the Chola Empire was at its peak stretching from Southern India to Vengai(Bengal) to parts of Southeast Asia. Rajendra has maintained the territories of his predecessor. During his reign, the Chola Empire was prosperous and had a large influence in trade throughout the Indian Ocean.
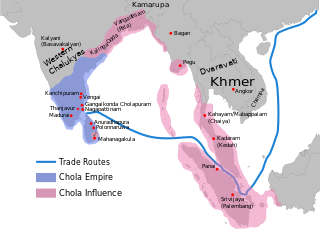
The Chola Empire, which is often referred to as the Imperial Cholas, was a medieval Indian, thalassocratic empire that was established by the Chola dynasty that rose to prominence during the middle of the ninth century and united southern India under their rule.

Vikrama Chola, known as Kō Parakēsari Varman, was a 12th-century ruler of the Chola Empire in southern India. He succeeded his father Kulothunga I to the throne. Vikrama Chola was crowned as the heir-apparent by his father early in his life. He was appointed as viceroy of the Vengi province in 1089 C.E., succeeding his brother Rajaraja Chodaganga. Vikrama during his tenure successfully managed to check the ambitions of the Western Chalukya Vikramaditya VI on the Vengi kingdom.Vikrama Chola inherited the territories which included Tamil Nadu and some parts of Andhra Pradesh.

Kulothunga III was a Chola emperor who ruled from 1178 to 1218 CE, after succeeding his elder brother Rajadhiraja II. Kulothunga Chola III gained success in war against his traditional foes. He gained victories in war against the Hoysalas, Pandyas of Madurai, Cheras of Venad, the Sinhalese kings of Polonnaruwa, as well as the Telugu Cholas of Velanadu and Nellore. He also restored Chola control over Karur, which were ruled by the Adigaman chiefs as vassals of the Cholas. He drove out the Hoysalas under Veera Ballala II who had made inroads in the Gangavadi and adjoining areas of Tagadur in Kongu country in an effort expand their territory. However, during the last two years of his reign, he lost in war to the resurgent Pandyas, heralded a period of steady decline and ultimately, demise of the Cholas by 1280 CE. Kulottunga III had alliances with the Hoysalas. The Hoysala king Veera Ballala married a Chola queen called Cholamahadevi and gave his daughter Somaladevi in marriage to Kulottunga III.

The Chola military was the combined armed forces of the Chola Empire organized during two separate Tamil golden ages, the Sangam Period and the Medieval Era. The Chola military fought dozens of wars, and it also underwent numerous changes in structure, organization, equipment and tactics, while conserving a core of lasting Tamil traditions.

Vallavaraiyan Vandiyadevan was a general of the Chola Army. He was one among the famous chieftains of the Chola emperors Rajaraja I and Rajendra I and chief of the Samanthas of Chittoor and also the husband of Rajaraja's elder sister Kunthavai Pirattiyar. He was also the chieftain of the Sri Lanka Front Army of Rajaraja l and Rajendra I. Territory under his authority was known as Vallavaraiyanadu. He ruled Brahmadesam. Vandiyathevan is idealized in Kalki Krishnamurthy's (Kalki) famous novel Ponniyin Selvan and also in many other novels like Vandiyadevan Vaal, Vandiyadevan Senai Thalaivan.

Kundavai Pirattiyar, commonly known mononymously as Kundavai, was a Chola Indian princess who lived in the tenth century in South India. She was the daughter of Parantaka II and Vanavan Mahadevi. She was born in Tirukoilur and was the elder sister of Chola emperor Rajaraja I. She had title as Ilaiyapirātti Kundavai Nachiyar.
Ponniyin Selvan is a Tamil language historical fiction novel by Indian author Kalki Krishnamurthy. It was first serialised in the weekly editions of Kalki, a Tamil magazine, from 29 October 1950 to 16 May 1954 and later integrated into five volumes in 1955. In about 2,210 pages, it tells the story of early days of Chola prince Arulmozhivarman. Kalki visited Sri Lanka three times to gather information and for inspiration.

Ponniyin Selvan: I is a 2022 Indian Tamil-language epic action drama film directed by Mani Ratnam, who co-wrote it with Elango Kumaravel and B. Jeyamohan. Produced by Ratnam and Subaskaran Allirajah under Madras Talkies and Lyca Productions, it is the first of two cinematic parts based on Kalki Krishnamurthy's 1955 novel, Ponniyin Selvan. The film stars an ensemble cast including Vikram, Jayam Ravi, Aishwarya Rai Bachchan, Trisha, Karthi, Jayaram, Aishwarya Lekshmi, Sobhita Dhulipala, Prakash Raj, Prabhu, R. Sarathkumar, R. Parthiban, Rahman, Lal and Vikram Prabhu. The music was composed by A. R. Rahman, with cinematography by Ravi Varman, editing by A. Sreekar Prasad, and production design by Thota Tharani. Ponniyin Selvan: I dramatises the early life of Chola prince Arunmozhi Varman, who would become the renowned emperor Rajaraja I (947–1014). In the film, Vandiyathevan sets out to cross the Chola land to deliver a message from the crown prince Aditha Karikalan. Meanwhile, Kundavai attempts to establish political peace as vassals and petty chieftains plot against the throne.

Ponniyin Selvan: II is a 2023 Indian Tamil-language epic historical action drama film directed by Mani Ratnam, who co-wrote it with Elango Kumaravel and B. Jeyamohan. The film is produced by Mani Ratnam and Subaskaran Allirajah under Madras Talkies and Lyca Productions. The second of two cinematic parts based on the 1954 novel Ponniyin Selvan by Kalki Krishnamurthy, it serves as a direct sequel to Ponniyin Selvan: I (2022). The film stars an ensemble cast including Aishwarya Rai Bachchan, Vikram, Jayam Ravi, Karthi, Trisha, Jayaram, Prabhu, R. Sarathkumar, Sobhita Dhulipala, Aishwarya Lekshmi, Vikram Prabhu, Prakash Raj, Rahman and R. Parthiban. It continues to follow the prince Arulmozhi Varman and his family as they deal with threats to the Chola Empire.
















