
Software is a collection of instructions that tell a computer how to work. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.

Morphine is a pain medication of the opiate family that is found naturally in a dark brown, resinous form, from the poppy plant. It can be taken orally, sublingually, via inhalation, the trans-dermal route, inter-anally as well as via injection (both subcutaneously as well as more commonly intravenously. It acts directly on the central nervous system to induce analgesia and alter perception and emotional response to pain. Physical and psychological dependence and tolerance may develop with repeated administration. It can be taken for both acute pain and chronic pain and is frequently used for pain from myocardial infarction, kidney stones, and during labor. Morphine can be administered by mouth, by injection into a muscle, by injection under the skin, intravenously, injection into the space around the spinal cord, or rectally. Its maximum effect is reached after about 20 minutes when administered intravenously and 60 minutes when administered by mouth, while the duration of its effect is 3–7 hours. Long-acting formulations of morphine are available as MS-Contin, Kadian, and other brand names as well as generically.

SMS is a text messaging service component of most telephone, Internet, and mobile device systems. It uses standardized communication protocols that let mobile devices exchange short text messages. An intermediary service can facilitate a text-to-voice conversion to be sent to landlines.

Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area may feel heavy, and affected joints may be hard to move. Other symptoms depend on the underlying cause.
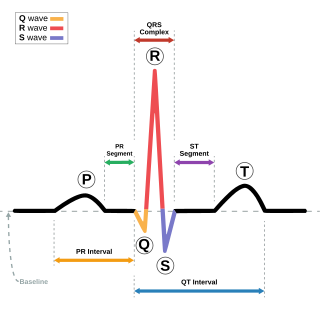
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram, a recording of the heart's electrical activity. It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle depolarization followed by repolarization during each cardiac cycle (heartbeat). Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur in numerous cardiac abnormalities, including cardiac rhythm disturbances, inadequate coronary artery blood flow, and electrolyte disturbances.
The excretory system is a passive biological system that removes excess, unnecessary materials from the body fluids of an organism, so as to help maintain internal chemical homeostasis and prevent damage to the body. The dual function of excretory systems is the elimination of the waste products of metabolism and to drain the body of used up and broken down components in a liquid and gaseous state. In humans and other amniotes most of these substances leave the body as urine and to some degree exhalation, mammals also expel them through sweating.

In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity that expresses the internal forces that neighbouring particles of a continuous material exert on each other, while strain is the measure of the deformation of the material. For example, when a solid vertical bar is supporting an overhead weight, each particle in the bar pushes on the particles immediately below it. When a liquid is in a closed container under pressure, each particle gets pushed against by all the surrounding particles. The container walls and the pressure-inducing surface push against them in (Newtonian) reaction. These macroscopic forces are actually the net result of a very large number of intermolecular forces and collisions between the particles in those molecules. Stress is frequently represented by a lowercase Greek letter sigma (σ).

Addison's disease, also known as primary adrenal insufficiency, is a rare long-term endocrine disorder characterized by inadequate production of the steroid hormones cortisol and aldosterone by the two outer layers of the cells of the adrenal glands, causing adrenal insufficiency. Symptoms generally come on slowly and insidiously and may include abdominal pain and gastrointestinal abnormalities, weakness, and weight loss. Darkening of the skin in certain areas may also occur. Under certain circumstances, an adrenal crisis may occur with low blood pressure, vomiting, lower back pain, and loss of consciousness. Mood changes may also occur. Rapid onset of symptoms indicates acute adrenal failure which is a serious and emergent condition. An adrenal crisis can be triggered by stress, such as from an injury, surgery, or infection.
Paresthesia is an abnormal sensation of the skin with no apparent physical cause. Paresthesia may be transient or chronic, and may have any of dozens of possible underlying causes. Paresthesias are usually painless and can occur anywhere on the body, but most commonly occur in the arms and legs.
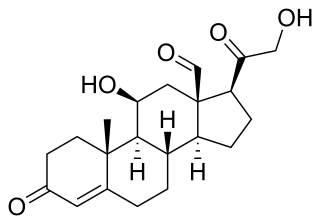
Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which in turn are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are produced in the adrenal cortex and influence salt and water balances. The primary mineralocorticoid is aldosterone.
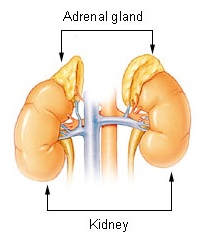
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones, primarily cortisol; but may also include impaired production of aldosterone, which regulates sodium conservation, potassium secretion, and water retention. Craving for salt or salty foods due to the urinary losses of sodium is common.

Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ or a tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion is measured as the rate at which blood is delivered to tissue, or volume of blood per unit time per unit tissue mass. The SI unit is m3/(s·kg), although for human organs perfusion is typically reported in ml/min/g. The word is derived from the French verb "perfuser" meaning to "pour over or through". All animal tissues require an adequate blood supply for health and life. Poor perfusion (malperfusion), that is, ischemia, causes health problems, as seen in cardiovascular disease, including coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral artery disease, and many other conditions.
Laryngospasm is an uncontrolled or involuntary muscular contraction (spasm) of the vocal folds. The condition typically lasts less than 60 seconds, but in some cases can last 20–30 minutes and causes a partial blocking of breathing in, while breathing out remains easier. It may be triggered when the vocal cords or the area of the trachea below the vocal folds detects the entry of water, mucus, blood, or other substance. It is characterized by stridor and/or retractions. Some people suffer from frequent laryngospasms, whether awake or asleep. In an ear, nose, and throat practice, it is typically seen in people who have silent reflux disease. It is also a well known, infrequent, but serious perioperative complication.

Vomiting is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Gallbladder diseases are diseases involving the gallbladder and is closely linked to biliary disease, with the most common cause being gallstones (cholelithiasis).

A dynamo is an electrical generator that creates direct current using a commutator. Dynamos were the first electrical generators capable of delivering power for industry, and the foundation upon which many other later electric-power conversion devices were based, including the electric motor, the alternating-current alternator, and the rotary converter.
High-definition television describes a television system providing a substantially higher image resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since 1936, in more recent times it refers to the generation following standard-definition television (SDTV), often abbreviated to HDTV or HD-TV. It is the current de facto standard video format used in most broadcasts: terrestrial broadcast television, cable television, satellite television and Blu-ray Discs.

In mathematics, a rational number is a number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction p/q of two integers, a numerator p and a non-zero denominator q. For example, −3/7 is a rational number, as is every integer. The set of all rational numbers, also referred to as "the rationals", the field of rationals or the field of rational numbers is usually denoted by a boldface Q ; it was thus denoted in 1895 by Giuseppe Peano after quoziente, Italian for "quotient", and first appeared in Bourbaki's Algèbre.
The Xanthogranulomatous Process (XP), is a form of acute and chronic inflammation characterized by an exuberant clustering of foamy macrophages among other inflammatory cells. Localization in the kidney and renal pelvis has been the most frequent and better known occurrence followed by that in the gallbladder but many others have been subsequently recorded. The pathological findings of the process and etiopathogenetic and clinical observations have been reviewed by Cozzutto and Carbone.

The Samsung Galaxy Note 4 is an Android smartphone developed and produced by Samsung Electronics. It was unveiled during a Samsung press conference at IFA Berlin on 3 September 2014 and was released globally in October 2014 as successor to the Samsung Galaxy Note 3. Improvements include expanded stylus-related functionality, an optically stabilized rear camera, significantly increased charging rate, revised multi-windowing, and fingerprint unlocking. It is the last in the Samsung Galaxy Note series with interchangeable battery. Its subsequent model, the Samsung Galaxy Note 5, was unveiled on 13 August 2015.














