
The adrenal glands are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three main zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.

Addison's disease, also known as primary adrenal insufficiency, is a rare long-term endocrine disorder characterized by inadequate production of the steroid hormones cortisol and aldosterone by the two outer layers of the cells of the adrenal glands, causing adrenal insufficiency. Symptoms generally come on slowly and insidiously and may include abdominal pain and gastrointestinal abnormalities, weakness, and weight loss. Darkening of the skin in certain areas may also occur. Under certain circumstances, an adrenal crisis may occur with low blood pressure, vomiting, lower back pain, and loss of consciousness. Mood changes may also occur. Rapid onset of symptoms indicates acute adrenal failure, which is a clinical emergency. An adrenal crisis can be triggered by stress, such as from an injury, surgery, or infection.
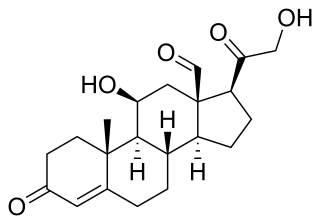
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays a central role in the homeostatic regulation of blood pressure, plasma sodium (Na+), and potassium (K+) levels. It does so primarily by acting on the mineralocorticoid receptors in the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the nephron. It influences the reabsorption of sodium and excretion of potassium (from and into the tubular fluids, respectively) of the kidney, thereby indirectly influencing water retention or loss, blood pressure, and blood volume. When dysregulated, aldosterone is pathogenic and contributes to the development and progression of cardiovascular and kidney disease. Aldosterone has exactly the opposite function of the atrial natriuretic hormone secreted by the heart.

Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which in turn are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are produced in the adrenal cortex and influence salt and water balances. The primary mineralocorticoid is aldosterone.
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal glands—also referred to as the adrenal cortex—normally secrete glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and androgens. These hormones are important in regulating blood pressure, electrolytes, and metabolism as a whole. Deficiency of these hormones leads to symptoms ranging from abdominal pain, vomiting, muscle weakness and fatigue, low blood pressure, depression, mood and personality changes to organ failure and shock. Adrenal crisis may occur if a person having adrenal insufficiency experiences stresses, such as an accident, injury, surgery, or severe infection; this is a life-threatening medical condition resulting from severe deficiency of cortisol in the body. Death may quickly follow.
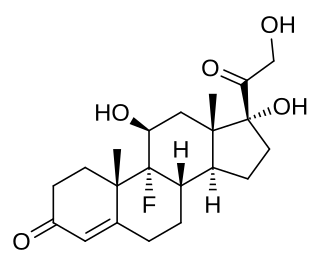
Fludrocortisone, sold under the brand name Florinef, among others, is a corticosteroid used to treat adrenogenital syndrome, postural hypotension, and adrenal insufficiency. In adrenal insufficiency, it is generally taken together with hydrocortisone. Fludrocortisone is taken by mouth and is most commonly used in its acetate form.
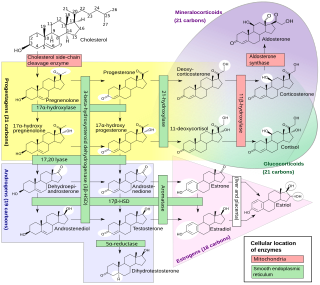
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency is a form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) which produces a higher than normal amount of androgen, resulting from a defect in the gene encoding the enzyme steroid 11β-hydroxylase (11β-OH) which mediates the final step of cortisol synthesis in the adrenal. 11β-OH CAH results in hypertension due to excessive mineralocorticoid effects. It also causes excessive androgen production both before and after birth and can virilize a genetically female fetus or a child of either sex.

Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency is an uncommon form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) resulting from a mutation in the gene for one of the key enzymes in cortisol synthesis by the adrenal gland, 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3β-HSD) type II (HSD3B2). As a result, higher levels of 17α-hydroxypregnenolone appear in the blood with adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) challenge, which stimulates adrenal corticosteroid synthesis.
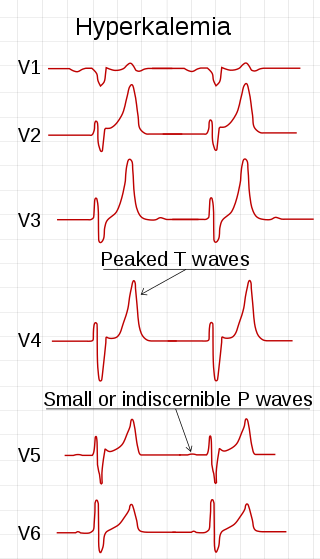
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K+) in the blood. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0 mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0 mEq/L) with levels above 5.5 mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Occasionally when severe it can cause palpitations, muscle pain, muscle weakness, or numbness. Hyperkalemia can cause an abnormal heart rhythm which can result in cardiac arrest and death.

Potassium-sparing diuretics or antikaliuretics refer to drugs that cause diuresis without causing potassium loss in the urine. They are typically used as an adjunct in management of hypertension, cirrhosis, and congestive heart failure. The steroidal aldosterone antagonists can also be used for treatment of primary hyperaldosteronism. Spironolactone, a steroidal aldosterone antagonist, is also used in management of female hirsutism and acne from PCOS or other causes.

Hyperaldosteronism is a medical condition wherein too much aldosterone is produced. High aldosterone levels can lead to lowered levels of potassium in the blood (hypokalemia) and increased hydrogen ion excretion (alkalosis). Aldosterone is normally produced in the adrenal glands.

Apparent mineralocorticoid excess is an autosomal recessive disorder causing hypertension, hypernatremia and hypokalemia. It results from mutations in the HSD11B2 gene, which encodes the kidney isozyme of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2. In an unaffected individual, this isozyme inactivates circulating cortisol to the less active metabolite cortisone. The inactivating mutation leads to elevated local concentrations of cortisol in the aldosterone sensitive tissues like the kidney. Cortisol at high concentrations can cross-react and activate the mineralocorticoid receptor due to the non-selectivity of the receptor, leading to aldosterone-like effects in the kidney. This is what causes the hypokalemia, hypertension, and hypernatremia associated with the syndrome. Patients often present with severe hypertension and end-organ changes associated with it like left ventricular hypertrophy, retinal, renal and neurological vascular changes along with growth retardation and failure to thrive. In serum both aldosterone and renin levels are low.

Bartter syndrome (BS) is a rare inherited disease characterised by a defect in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle, which results in low potassium levels (hypokalemia), increased blood pH (alkalosis), and normal to low blood pressure. There are two types of Bartter syndrome: neonatal and classic. A closely associated disorder, Gitelman syndrome, is milder than both subtypes of Bartter syndrome.
Pseudohyperaldosteronism is a medical condition which mimics the effects of elevated aldosterone (hyperaldosteronism) by presenting with high blood pressure, low blood potassium levels (hypokalemia), metabolic alkalosis, and low levels of plasma renin activity (PRA). However, unlike hyperaldosteronism, this conditions exhibits low or normal levels of aldosterone in the blood. Causes include genetic disorders, acquired conditions, metabolic disorders, and dietary imbalances including excessive consumption of licorice. Confirmatory diagnosis depends on the specific cause and may involve blood tests, urine tests, or genetic testing; however, all forms of this condition exhibit abnormally low concentrations of both plasma renin activity (PRA) and plasma aldosterone concentration (PAC) which differentiates this group of conditions from other forms of secondary hypertension. Treatment is tailored to the specific cause and focuses on symptom control, blood pressure management, and avoidance of triggers.

11-Deoxycorticosterone (DOC), or simply deoxycorticosterone, also known as 21-hydroxyprogesterone, as well as desoxycortone (INN), deoxycortone, and cortexone, is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal gland that possesses mineralocorticoid activity and acts as a precursor to aldosterone. It is an active (Na+-retaining) mineralocorticoid. As its names indicate, 11-deoxycorticosterone can be understood as the 21-hydroxy-variant of progesterone or as the 11-deoxy-variant of corticosterone.
Pseudohypoaldosteronism (PHA) is a condition that mimics hypoaldosteronism. Two major types of primary pseudohypoaldosteronism are recognized and these have major differences in etiology and presentation.
The ACTH test is a medical test usually requested and interpreted by endocrinologists to assess the functioning of the adrenal glands' stress response by measuring the adrenal response to adrenocorticotropic hormone or another corticotropic agent such as tetracosactide or alsactide (Synchrodyn). ACTH is a hormone produced in the anterior pituitary gland that stimulates the adrenal glands to release cortisol, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S), and aldosterone.

Adrenal crisis, also known as Addisonian crisis or acute adrenal insufficiency, is a life-threatening complication of adrenal insufficiency. Hypotension, and hypovolemic shock, are the main symptoms of adrenal crisis. Other symptoms include weakness, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, fever, fatigue, abnormal electrolytes, confusion, and coma. Laboratory testing may detect low sodium (hyponatremia), high potassium (hyperkalemia), high lymphocyte count (lymphocytosis), high eosinophils (eosinophilia), low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), and rarely high calcium (hypercalcemia).
Hypoadrenocorticism in dogs, or, as it is known in people, Addison's disease, is an endocrine system disorder that occurs when the adrenal glands fail to produce enough hormones for normal function. The adrenal glands secrete glucocorticoids such as cortisol and mineralocorticoids such as aldosterone; when proper amounts of these are not produced, the metabolic and electrolyte balance is upset. Mineralocorticoids control the amount of potassium, sodium, and water in the body. Hypoadrenocorticism is fatal if left untreated.

Adrenal gland disorders are conditions that interfere with the normal functioning of the adrenal glands. Your body produces too much or too little of one or more hormones when you have an adrenal gland dysfunction. The type of issue you have and the degree to which it affects your body's hormone levels determine the symptoms.














