
The Norwegian Sea is a marginal sea, grouped with either the Atlantic Ocean or the Arctic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to the northeast. In the southwest, it is separated from the Atlantic Ocean by a submarine ridge running between Iceland and the Faroe Islands. To the north, the Jan Mayen Ridge separates it from the Greenland Sea.

The black-throated loon, also known as the Arctic loon and the black-throated diver, is a migratory aquatic bird found in the northern hemisphere, primarily breeding in freshwater lakes in northern Europe and Asia. It winters along sheltered, ice-free coasts of the north-east Atlantic Ocean and the eastern and western Pacific Ocean. This loon was first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 and has two subspecies. It was previously considered to be the same species as the Pacific loon, of which it is traditionally considered to be a sister species, although this is debated. In a study that used mitochondrial and nuclear intron DNA, the black-throated loon was found to be sister to a clade consisting of the Pacific loon and two sister species, the common loon and the yellow-billed loon.

The beluga whale is an Arctic and sub-Arctic cetacean. It is one of two members of the family Monodontidae, along with the narwhal, and the only member of the genus Delphinapterus. It is also known as the white whale, as it is the only cetacean to regularly occur with this colour; the sea canary, due to its high-pitched calls; and the melonhead, though that more commonly refers to the melon-headed whale, which is an oceanic dolphin.

The black guillemot or tystie is a medium-sized seabird of the Alcidae family, native throughout northern Atlantic coasts and eastern North American coasts. It is resident in much of its range, but large populations from the high arctic migrate southwards in winter. The bird can be seen in and around its breeding habitat of rocky shores, cliffs and islands in single or smalls groups of pairs. They feed mainly by diving towards the sea floor feeding on fish, crustaceans or other benthic invertebrates. They are listed on the IUCN red list as a species of least concern.

The bearded seal, also called the square flipper seal, is a medium-sized pinniped that is found in and near to the Arctic Ocean. It gets its generic name from two Greek words that refer to its heavy jaw. The other part of its Linnaean name means bearded and refers to its most characteristic feature, the conspicuous and very abundant whiskers. When dry, these whiskers curl very elegantly, giving the bearded seal a "raffish" look.

Boreogadus saida, known as the polar cod or as the Arctic cod, is a fish of the cod family Gadidae, related to the true cod. Another fish species for which both the common names Arctic cod and polar cod are used is Arctogadus glacialis.

Grenadiers or rattails are generally large, brown to black gadiform marine fish of the subfamily Macrourinae, the largest subfamily of the family Macrouridae. Found at great depths from the Arctic to Antarctic, members of this subfamily are amongst the most abundant of the deep-sea fish.
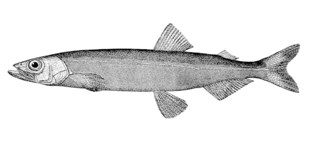
The capelin or caplin is a small forage fish of the smelt family found in the North Atlantic, North Pacific and Arctic oceans. In summer, it grazes on dense swarms of plankton at the edge of the ice shelf. Larger capelin also eat a great deal of krill and other crustaceans. Among others, whales, seals, Atlantic cod, Atlantic mackerel, squid and seabirds prey on capelin, in particular during the spawning season while the capelin migrate south. Capelin spawn on sand and gravel bottoms or sandy beaches at the age of two to six years. When spawning on beaches, capelin have an extremely high post-spawning mortality rate which, for males, is close to 100%. Males reach 20 cm (8 in) in length, while females are up to 25.2 cm (10 in) long. They are olive-coloured dorsally, shading to silver on sides. Males have a translucent ridge on both sides of their bodies. The ventral aspects of the males iridesce reddish at the time of spawn.

King crabs are decapod crustaceans in the family Lithodidae that are chiefly found in deep waters and are adapted to cold environments. They are composed of two subfamilies: Lithodinae, which tend to inhabit deep waters, are globally distributed, and comprise the majority of the family's species diversity; and Hapalogastrinae, which are endemic to the North Pacific and inhabit exclusively shallow waters. King crabs are not true crabs and are generally thought to be derived from hermit crab ancestors within the Paguridae, which may explain the asymmetry still found in the adult forms. This ancestry is supported by several anatomical peculiarities which are present only in king crabs and hermit crabs. Although some doubt still exists about this hypothesis, king crabs are the most widely quoted example of carcinisation among decapods. Several species of king crabs, especially in Alaskan and southern South American waters, are targeted by commercial fisheries and have been subject to overfishing.

The Arctic char or Arctic charr is a cold-water fish in the family Salmonidae, native to alpine lakes, as well as Arctic and subarctic coastal waters in the Holarctic.

The silver trout is an extinct char species or subspecies that inhabited a few waters in New Hampshire in the United States prior to 1939, when a biological survey conducted on the Connecticut watershed by the New Hampshire Fish and Game Department found none.

The Greenland shark, also known as the gurry shark or grey shark, is a large shark of the family Somniosidae, closely related to the Pacific and southern sleeper sharks. Inhabiting the North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, they are notable for their exceptional longevity, although they are poorly studied due to the depth and remoteness of their natural habitat.

The round whitefish is a freshwater species of fish that is found in North American drainages from Alaska to New England, including the Great Lakes except for Lake Erie, and in Arctic tributaries of northeast Asia, as well as northern Kamchatka Peninsula and the northern coasts of the Sea of Okhotsk. It has an olive-brown back with light silvery sides and underside and its length is generally between 9 and 19 inches. They are bottom feeders, feeding mostly on invertebrates, such as crustaceans, insect larvae, and fish eggs. Some other fish species, like white sucker in turn eat their eggs. Lake trout, northern pike and burbot are natural predators. Other common names of the round whitefish are Menominee, pilot fish, frost fish, round-fish, and Menominee whitefish. The common name "round whitefish" is also sometimes used to describe Coregonus huntsmani, a salmonid more commonly known as the Atlantic whitefish.

Diel vertical migration (DVM), also known as diurnal vertical migration, is a pattern of movement used by some organisms, such as copepods, living in the ocean and in lakes. The adjective "diel" comes from Latin: diēs, lit. 'day', and refers to a 24-hour period. The migration occurs when organisms move up to the uppermost layer of the water at night and return to the bottom of the daylight zone of the oceans or to the dense, bottom layer of lakes during the day. DVM is important to the functioning of deep-sea food webs and the biologically-driven sequestration of carbon.

The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five oceanic divisions. It spans an area of approximately 14,060,000 km2 (5,430,000 sq mi) and is the coldest of the world's oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea. It has also been described as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing world ocean.

Togiak National Wildlife Refuge is in the Dillingham and Bethel Census Areas, Alaska. It is dominated by the Ahklun Mountains in the north and the cold waters of Bristol Bay to the south. The natural forces that have shaped this land range from the violent and powerful to the geologically patient. Earthquakes and volcanoes filled the former role, and their marks can still be found, but it was the gradual advance and retreat of glacial ice that carved many of the physical features of this refuge.

Pavoclinus is a genus of clinids found in the southeastern Atlantic and western Indian Ocean coastal waters of southern Africa.

Salvelinus killinensis, also known as Haddy charr is a variety of charr found in certain lakes in Scotland.

Boltenia ovifera is a species of ascidian tunicate in the family Pyuridae. It is found in the Arctic to the South of Cape Cod.
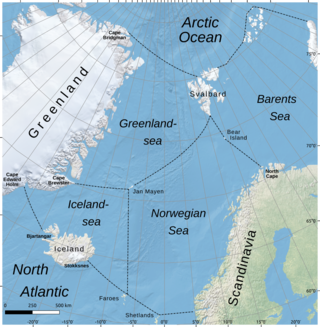
The Iceland Sea, a relatively small body of water, is bounded by Iceland. It is characterized by its proximity to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which transforms into the Kolbeinsey Ridge, and the Greenland-Scotland Ridge, and it lies just south of the Arctic Circle. This region is typically delineated by Greenland to the west, the Denmark Strait, and the continental shelf break south of Iceland to the south. Next in the boundary line are Jan Mayen, being a small Norwegian volcanic island, and the Jan Mayen Fracture Zone to the north, with the Jan Mayen Ridge to the east of the sea. This ridge serves as the northern boundary of the Iceland Sea, acting as the dividing line from the Greenland Sea. To the immediate south of Jan Mayen, the Iceland-Jan Mayen Ridge stretches towards the Iceland-Faroe Ridge, creating a boundary between the Iceland Sea and the Norwegian Sea to the east.



















