
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordered by Pakistan to the east and south, Iran to the west, Turkmenistan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, Tajikistan to the northeast, and China to the northeast and east. Occupying 652,864 square kilometres (252,072 sq mi) of land, the country is predominantly mountainous with plains in the north and the southwest, which are separated by the Hindu Kush mountain range. Kabul is the country's largest city and serves as its capital. As of 2021, Afghanistan's population is 40.2 million, composed of ethnic Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras, Uzbeks, Turkmens, Qizilbash, Aimak, Pashayi, Baloch, Pamiris, Nuristanis, and others.

The foreign relations of Afghanistan are in a transitional phase since the 2021 fall of Kabul to the Taliban and the collapse of the internationally-recognized Islamic Republic of Afghanistan. No country has recognised the new regime, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan. Although some countries have engaged in informal diplomatic contact with the Islamic Emirate, formal relations remain limited to representatives of the Islamic Republic.

Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. According to 2023 estimates, the population of Kabul was 5 million people. In contemporary times, the city has served as Afghanistan's political, cultural, and economical center, and rapid urbanisation has made Kabul the 75th-largest city in the world and the country's primate city.

The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 31 member states – 29 European and two North American. Established in the aftermath of World War II, the organization implemented the North Atlantic Treaty, signed in Washington, D.C., on 4 April 1949. NATO is a collective security system: its independent member states agree to defend each other against attacks by third parties. During the Cold War, NATO operated as a check on the threat posed by the Soviet Union. The alliance remained in place after the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact, and has been involved in military operations in the Balkans, the Middle East, South Asia, and Africa. The organization's motto is animus in consulendo liber.

Operation Enduring Freedom (OEF) was the official name used synonymously by the U.S. government for both the War in Afghanistan (2001–2021) and the larger-scale Global War on Terrorism. On 7 October 2001, in response to the September 11 attacks, President George W. Bush announced that airstrikes targeting Al-Qaeda and the Taliban had begun in Afghanistan. Operation Enduring Freedom primarily refers to the War in Afghanistan, but it was also affiliated with counterterrorism operations in other countries, such as OEFnced the end of Operation Enduring Freedom in Afghanistan. Subsequent operations in Afghanistan by the United States' military forces, both non-combat and combat, occurred under the name Operation Freedom's Sentinel.

The Taliban, which also refers to itself by its state name, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a Deobandi Islamic fundamentalist and Pashtun nationalist militant political movement in Afghanistan. It ruled approximately three-quarters of the country from 1996 to 2001, before being overthrown following the United States invasion. It recaptured Kabul on 15 August 2021 after nearly 20 years of insurgency, and currently controls all of the country, although its government has not yet been recognized by any country. The Taliban government has been criticized for restricting human rights in Afghanistan, including the right of women and girls to work and to have an education.

Pashtuns, also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Eastern Iranian ethnic group primarily residing in southern and eastern Afghanistan and northwestern Pakistan. They historically were also referred to as Afghans until the 1970s, after the term's meaning had become a demonym for members of all ethnic groups in Afghanistan.

The population of Afghanistan is around 41 million as of 2023. The nation is composed of a multi-ethnic and multilingual society, reflecting its location astride historic trade and invasion routes between Central Asia, South Asia, and Western Asia. Ethnic groups in the country include Pashtun, Tajik, Hazara, Uzbeks, Nuristanis, Aimaq, Turkmen, Baloch and some others which are less known. Together they make up the contemporary Afghan people.

The national flag of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, also used as the flag of the Taliban, consists of a white field with a black Shahada. It was adopted on 15 August 2021 with the victory of the Taliban in the 2001–2021 war. Since the Anglo-Afghan War of 1919, also known as the War of Independence, Afghanistan has used about 19 national flags, more than any other country in this period. The national flag had black, red and green colors most of the time during the period.

Uruzgan, also spelled as Urozgan or Oruzgan, is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan. Uruzgan is located in the center of the country. The population is 436,079, and the province is mostly a tribal society. Tarinkot serves as the capital of the province.

The House of Representatives of the People, or Da Afghanistan Wolesi Jirga, was the lower house of the bicameral National Assembly of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, alongside the upper House of Elders.

Jalaluddin Haqqani was an Afghan insurgent commander who founded the Haqqani network, an insurgent group fighting in guerilla warfare against US-led NATO forces and the now former government of Afghanistan they support.

Afghanistan is a multiethnic and mostly tribal society. The population of the country consists of numerous ethnolinguistic groups: Pashtun, Tajik, Hazara, Uzbek, Aimaq, Turkmen, Baloch, Pashai, Nuristani, Kurds, Gujjar, Arab, Brahui, Qizilbash, Pamiri, Kyrgyz, Sadat and others. Altogether they make up the Afghan people.

Bangi District is a district of Takhar Province, Afghanistan.

Chal District is a district of Takhar Province, Afghanistan. It was considered to be largely under control of the Afghan government in 2018.
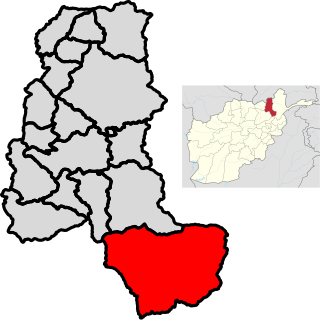
Warsaj District is a district of Takhar Province, northern Afghanistan.
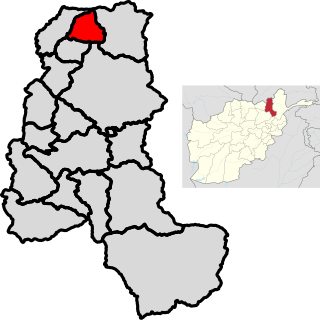
Yangi Qala District is a district in Takhar Province, Afghanistan. Economically the population of this district is primarily involved in agriculture. The main crops are rice and wheat, and the surplus rice is exporting to neighboring districts and provinces. There are 64 villages in the district. As of August 2021, the Taliban has full control over this district.

The Afghanistan War was an armed conflict from 2001 to 2021. It began when an international military coalition led by the United States launched an invasion of Afghanistan, toppling the Taliban-ruled Islamic Emirate and establishing the internationally recognized Islamic Republic three years later. The conflict ultimately ended with the 2021 Taliban offensive, which overthrew the Islamic Republic, and re-established the Islamic Emirate. It was the longest war in the military history of the United States, surpassing the length of the Vietnam War (1955–1975) by approximately 6 months.

The Islamic State – Khorasan Province is an affiliate of the Islamic State militant group active in South Asia and Central Asia. Some media sources also use the terms ISK, ISISK, ISKP, Daesh–Khorasan or Daesh–K in referring to the group. ISIS-K has been active in Afghanistan, Pakistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan, where they claimed attacks. The ISIS-K and Taliban consider each other enemies.

The Islamic Republic of Afghanistan was a presidential republic that ruled Afghanistan from 2004 to 2021. The state was established to replace the Afghan interim (2001–2002) and transitional (2002–2004) administrations, which were formed after the 2001 United States invasion of Afghanistan that had toppled the partially recognized Taliban-ruled Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan. However, on 15 August 2021, the country was recaptured by the Taliban, which marked the end of the 2001–2021 war, the longest war in US history. This led to the overthrow of the Islamic Republic, led by President Ashraf Ghani, and the reinstatement of the Islamic Emirate under the control of the Taliban. The United Nations still recognizes the Islamic Republic as the legitimate government of Afghanistan instead of the Islamic Emirate, the de facto ruling government. The US–Taliban deal, signed on 29 February 2020 in Qatar, was one of the critical events that caused the collapse of the Afghan National Security Forces (ANSF). Following the deal, the US dramatically reduced the number of air attacks and deprived the ANSF of a critical edge in fighting the Taliban insurgency, leading to the Taliban takeover of Kabul.


















