
The treeshrews are small mammals native to the tropical forests of South and Southeast Asia. They make up the entire order Scandentia, which split into two families: the Tupaiidae, and the Ptilocercidae.

Placental mammals are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placental mammals contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguished from monotremes and marsupials in that the fetus is carried in the uterus of its mother to a relatively late stage of development. The name is something of a misnomer, considering that marsupials also nourish their fetuses via a placenta, though for a relatively briefer period, giving birth to less-developed young, which are then nurtured for a period inside the mother's pouch. Placental mammals represents the only living group within Eutheria, which contains all mammals that are more closely related to placental mammals than they are to marsupials.

The order Insectivora is a now-abandoned biological grouping within the class of mammals. Some species have now been moved out, leaving the remaining ones in the order Eulipotyphla within the larger clade Laurasiatheria, which makes up one of the basal clades of placental mammals.

Elephant shrews, also called jumping shrews or sengis, are small insectivorous mammals native to Africa, belonging to the family Macroscelididae, in the order Macroscelidea. Their traditional common English name "elephant shrew" comes from a perceived resemblance between their long noses and the trunk of an elephant, and their superficial similarity with shrews in the order Eulipotyphla. However, phylogenetic analysis has revealed that elephant shrews are not properly classified with true shrews, but are in fact more closely related to elephants than to shrews. In 1997, the biologist Jonathan Kingdon proposed that they instead be called "sengis", a term derived from the Bantu languages of Africa, and in 1998, they were classified into the new clade Afrotheria.

The clade Afrosoricida contains the golden moles of Southern Africa, the otter shrews of equatorial Africa and the tenrecs of Madagascar. These three groups of small mammals were for most of the 19th and 20th centuries regarded as a part of the Insectivora or Lipotyphla, but both of those groups, as traditionally used, are polyphyletic.

A tenrec is a mammal belonging to any species within the afrotherian family Tenrecidae, which is endemic to Madagascar. Tenrecs are a very diverse group; as a result of convergent evolution, some resemble hedgehogs, shrews, opossums, rats, and mice. They occupy aquatic, arboreal, terrestrial, and fossorial environments. Some of these species, including the greater hedgehog tenrec, can be found in the Madagascar dry deciduous forests. However, the speciation rate in this group has been higher in humid forests.

Afrotheria is a superorder of placental mammals, the living members of which belong to groups that are either currently living in Africa or of African origin: golden moles, elephant shrews, otter shrews, tenrecs, aardvarks, hyraxes, elephants, sea cows, and several extinct clades. Most groups of afrotheres share little or no superficial resemblance, and their similarities have only become known in recent times because of genetics and molecular studies. Many afrothere groups are found mostly or exclusively in Africa, reflecting the fact that Africa was an island continent from the Cretaceous until the early Miocene around 20 million years ago, when Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia.

The family Talpidae includes the true moles who are small insectivorous mammals of the order Eulipotyphla. Talpids are all digging animals to various degrees: moles are completely subterranean animals; shrew moles and shrew-like moles somewhat less so; and desmans, while basically aquatic, excavate dry sleeping chambers; whilst the quite unique star-nosed mole is equally adept in the water and underground. Talpids are found across the Northern Hemisphere of Eurasia and North America, and range as far south as the montane regions of tropical Southeast Asia.

Mammalia is a class of animal within the phylum Chordata. Mammal classification has been through several iterations since Carl Linnaeus initially defined the class. No classification system is universally accepted; McKenna & Bell (1997) and Wilson & Reader (2005) provide useful recent compendiums. Many earlier ideas from Linnaeus et al. have been completely abandoned by modern taxonomists, among these are the idea that bats are related to birds or that humans represent a group outside of other living things. Competing ideas about the relationships of mammal orders do persist and are currently in development. Most significantly in recent years, cladistic thinking has led to an effort to ensure that all taxonomic designations represent monophyletic groups. The field has also seen a recent surge in interest and modification due to the results of molecular phylogenetics.

The subfamily Talpinae, sometimes called "Old World moles" or "Old World moles and relatives", is one of three subfamilies of the mole family Talpidae, the others being the Scalopinae, or New World moles, and the Uropsilinae, or shrew-like moles.
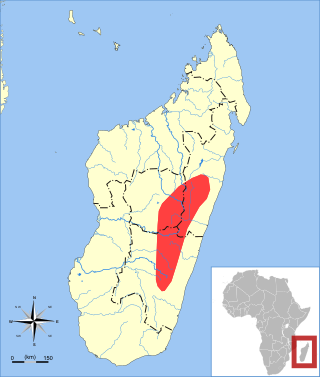
The web-footed tenrec, Malagasy otter shrew, or aquatic tenrec is the only known semiaquatic tenrec, and is found in eastern Madagascar, especially in and around Ranomafana National Park. It grows to between 25 and 39 cm, and was once thought to be extinct. It feeds on crabs, aquatic insects, and crayfish. The population is considered vulnerable. It was formerly placed in the monotypic genus Limnogale, but has been moved to Microgale based on molecular data showing it to be deeply nested within the latter.

Mammaliaformes is a clade of synapsid tetrapods that includes the crown group mammals and their closest extinct relatives; the group radiated from earlier probainognathian cynodonts during the Late Triassic. It is defined as the clade originating from the most recent common ancestor of Morganucodonta and the crown group mammals; the latter is the clade originating with the most recent common ancestor of extant Monotremata, Marsupialia and Placentalia. Besides Morganucodonta and the crown group mammals, Mammaliaformes also includes Docodonta and Hadrocodium.

The theriodonts are a major group of therapsids which appeared during the Middle Permian and which includes the gorgonopsians and the eutheriodonts, itself including the therocephalians and the cynodonts.

The Afroinsectiphilia is a clade that has been proposed based on the results of recent molecular phylogenetic studies. Many of the taxa within it were once regarded as part of the order Insectivora, but Insectivora is now considered to be polyphyletic and obsolete. This proposed classification is based on molecular studies only, and there is no morphological evidence for it.

Myosorex is a mammal genus in the Soricidae (shrew) family. The genus, collectively referred to as the mouse shrews, contains these species:

The large-toothed shrew or Mexican large-toothed shrew is one of 77 species within the genus Sorex. Registered on the IUCN Red List as vulnerable with a decreasing population, the Mexican large-toothed shrew has been recorded only 14 times in seven locations. The shrew is a member of the red-toothed shrew subfamily Soricinae, and the more taxonomically defined tribe Soricini. Members of the latter category exhibit long tails relative to body size.

Anagaloidea is a former order of extinct placental mammals that first appeared during the Paleocene epoch.

The Bornean shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is found only on Borneo, throughout most of the island; it may or may not be present in Brunei.

Paenungulatomorpha is a clade of afrotherian mammals that can be characterized according to Gheerbrant et al. (2016):
by a mandibular retromolar fossa, the absence of hypocone, an ectoloph selenodont and linked to strong styles such as mesostyle in basal taxa, and a more or less developed pseudohypocone.




















