
Velvet spiders are a small group of spiders almost entirely limited to the Old World, with exception of a few species known from Brazil. The characteristics of this family of spiders are that they are entelegyne, eight-eyed araneomorph spiders that build unkempt webs. They are cribellate. Some species are nearly eusocial, lacking only a specialized caste system and a queen. They cooperate in brood rearing, unlike most other spiders except for some African agelenid spiders in the genus Agelena and a few others.

Phidippus is a genus in the family Salticidae. Some of the largest jumping spiders inhabit this genus, and many species are characterized by their brilliant, iridescent green chelicerae. Phidippus is distributed almost exclusively in North America, with the exception of two exported species. As of January 2021, there were about 80 described species in the genus. Species previously described in Phidippus which are found in India and Bangladesh do not belong in this genus.

Eresus, also called ladybird spiders, is a genus of velvet spiders that was first described by Charles Athanase Walckenaer in 1805. Members of the genus formerly called Eresus cinnaberinus or Eresus niger are now placed in one of three species: Eresus kollari, Eresus sandaliatus and Eresus moravicus.

Amycus is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1846.
Aphirape is a genus of South American jumping spiders that was first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1850.
Asaracus is a genus of South American jumping spiders that was first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1846.

Cocalus is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1846, and is named after Cocalus, a Sicilian king of Greek mythology.

Dendryphantes is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1837.

Evarcha is a genus of spiders in the family Salticidae with 85 species distributed across the world.

Freya is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1850. The name is derived from Freya, the fertility goddess of Norse mythology.

Frigga is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1850. The name is derived from Frigga, a Norse goddess.

Marpissa is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1846. The name is derived from Marpissa, an ancient Greek village.

Paraphidippus is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Frederick Octavius Pickard-Cambridge in 1901. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek "para" (παρά), meaning "alongside", and the salticid genus Phidippus.

Phiale is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1846. P. albovittata has been considered a junior synonym of Freya perelegans since 2006.

Psecas is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1850.

Thiania is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1846.

The Dendryphantina are a subtribe of jumping spiders that occur mainly in the New World. The subtribe was first defined by Anton Menge in 1879 as Dendryphantidae. Females of the subtribe generally show paired spots on the abdomen, and the males often have enlarged chelicerae. Females in this subtribe typically have S-shaped epigynal openings.
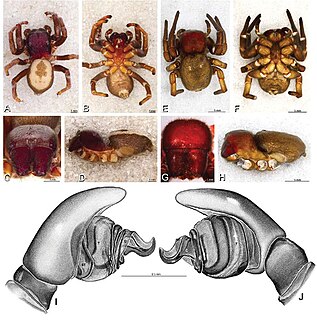
Dorceus is a genus of velvet spiders that was first described by C. L. Koch in 1846.

Toxeus is a genus of jumping spiders first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1846. The genus was synonymized with Myrmarachne by Eugène Simon in 1901, and remained a synonym until revived by Jerzy Prószyński in 2016, when he split up Myrmarachne.
















