
Zingiberaceae or the ginger family is a family of flowering plants made up of about 50 genera with a total of about 1600 known species of aromatic perennial herbs with creeping horizontal or tuberous rhizomes distributed throughout tropical Africa, Asia, and the Americas. Many of the family's species are important ornamental, spice, or medicinal plants. Ornamental genera include the shell gingers (Alpinia), Siam or summer tulip, Globba, ginger lily (Hedychium), Kaempferia, torch-ginger Etlingera elatior, Renealmia, and ginger (Zingiber). Spices include ginger (Zingiber), galangal or Thai ginger, melegueta pepper, myoga, korarima, turmeric (Curcuma), and cardamom.

Kavalactones are a class of lactone compounds found in kava roots and Alpinia zerumbet. Kavalactones are under research for potential to have various psychotropic effects, including anxiolytic and sedative/hypnotic activities.

Eugenol is an allyl chain-substituted guaiacol, a member of the allylbenzene class of chemical compounds. It is a colorless to pale yellow, aromatic oily liquid extracted from certain essential oils especially from clove, nutmeg, cinnamon, basil and bay leaf. It is present in concentrations of 80–90% in clove bud oil and at 82–88% in clove leaf oil. Eugenol has a pleasant, spicy, clove-like scent. The name is derived from Eugenia caryophyllata, the former Linnean nomenclature term for cloves. The currently accepted name is Syzygium aromaticum.

Alpinia nutans, the shellflower, or dwarf cardamom, is a Southeast Asian plant of the ginger family (Zingiberaceae), and is a medicinal plant used to control hypertension, as diuretic, antifungal, and antiulcer. In Japan it is used as food preservative.

Alpinia zerumbet, commonly known as shell ginger among other names, is a perennial species of ginger native to East Asia. The plants can grow up to 2.5 to 3 meters tall and bear colorful funnel-shaped flowers. They are grown as ornamentals and their leaves are used in cuisine and traditional medicine.
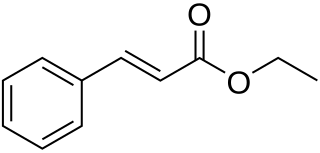
Ethyl cinnamate is the ester of cinnamic acid and ethanol. It is present in the essential oil of cinnamon. Pure ethyl cinnamate has a "fruity and balsamic odor, reminiscent of cinnamon with an amber note".

Alpinia galanga, a plant in the ginger family, bears a rhizome used largely as an herb in Unani medicine and as a spice in Arab cuisine and Southeast Asian cookery. It is one of four plants known as "galangal". Its common names include greater galangal, lengkuas, and blue ginger.

Alpinia officinarum, known as lesser galangal, is a plant in the ginger family, cultivated in Southeast Asia. It originated in China, where its name ultimately derives. It can grow 1.5 to 2 m high, with long leaves and reddish-white flowers. The rhizomes, known as galangal, are valued for their sweet spicy flavor and aromatic scent. These are used throughout Asia in curries and perfumes, and were previously used widely in Europe. They are also used as a herbal remedy.

Kaempferia galanga, commonly known as kencur, aromatic ginger, sand ginger, cutcherry, is a monocotyledonous plant in the ginger family, and one of four plants called galangal. It is found primarily in open areas in Indonesia, southern China, Taiwan, Cambodia, and India, but is also widely cultivated throughout Southeast Asia.

Galangin is a flavonol, a type of flavonoid.

Cardamomin is a chalconoid that has been isolated from several plants including Alpinia katsumadai and Alpinia conchigera. It has received growing attention from the scientific community due to the expectations toward its benefits to human health.
Alpinia nigra is a medium-sized herb belonging to the ginger family. The rhizome is well known in many Asian cultures as a medicinal and culinary item. In many Asian tribal communities it is a part of the diet along with rice.

Renealmia alpinia is a flowering plant species native to the Americas, where it grows from southern Mexico through much of South America, though not in the Southern Cone. It can also be found on several Caribbean islands.

Ochrosia oppositifolia grows as a small to medium-sized tree up to 25 metres (82 ft) tall, with a trunk diameter of up to 50 centimetres (20 in). Its flowers feature a creamy to white corolla. Its habitat is coastal forest, bush or open areas to 100 metres (330 ft) altitude, rarely inland. Local medicinal uses include as a carminative and in high doses as an abortifacient. Ochrosia oppositifolia is native to regions from the Seychelles through tropical Asia to the Pacific.

Chrysoeriol is a flavone, chemically the 3'-methoxy derivative of luteolin.
1,7-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,4,6-heptatrien-3-one is a natural product, a curcuminoid antioxidant found in turmeric and torch ginger.
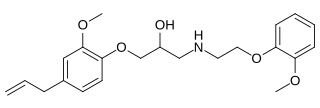
Eugenodilol is an alpha-1 blocker and beta blocker with weak β2-adrenergic receptor agonist activity derived from eugenol.
Heptatriacontanoic acid, or heptatriacontylic acid, is a 37-carbon saturated fatty acid.
Alpinia rafflesiana, commonly known in Malaysia as tepus telor, is a perennial herb belonging to the family Zingiberaceae. It is native to peninsular Malaysia.
Rosemary Margaret Smith (1933–2004) was a Scottish botanist and illustrator who specialized in the taxonomy of the Zingiberaceae, or ginger family. Many of the species she classified and identified as being placed into improper genera were found in Asian countries, especially in the isolated island of Borneo.















