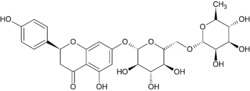 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name (2S)-4′,5-Dihydroxy-7-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosyloxy]flavan-4-one | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (22S,42S,43R,44S,45S,46R,72R,73R,74R,75R,76S)-14,25,43,44,45,73,74,75-Octahydroxy-76-methyl-22,23-dihydro-24H-3,6-dioxa-2(2,7)-[1]benzopyrana-4(2,6),7(2)-bis(oxana)-1(1)-benzenaheptaphan-24-one | |
| Other names Naringenin-7-O-rutinoside | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.655 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H32O14 | |
| Molar mass | 580.539 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Narirutin is a flavanone-7-O-glycoside, consisting of the flavanone naringenin bonded with the disaccharide rutinose. [1]
It is found in orange juice. [1] [2]
Narirutin is found in citrus fruits such as Yuzu, grapefruit, mandarins, especially in their peels. There are reports that Narirutin is abundant in Jabara [3] (A fruit discovered and grown in the Kitayama village, Wakayama prefecture, Japan).
Narirutin is reported to be effective for allergies caused by immunoglobulin E antibodies. [3] Those allergies include hayfever and some cases of food allergy.
- When an allergen (pollen, dust) enters the body, the body produces immunoglobulin E antibodies, resulting in an antigen-antibody reaction.
- The antibodies are attached to mast cells, which release bioactive substances such as histamine and serotonin.
- Histamine causes expansion of blood vessels, resulting in allergic reactions such as low blood pressure, increased heart rate, skin itchiness, sneezing, runny nose, etc.
Narirutin is said to prevent the release of histamine by the mast cells, reducing the allergic symptoms. [3]
