American French (French: le français d'Amérique) is a collective term used for the varieties of the French language that are spoken in North America,[ citation needed ] which include:

Haiti is the 83rd most populous country in the world, with an estimated population of 11,123,178 as of July 2018. The last national census in Haiti was done in 2003. Although much of that data has not been released, the population recorded was 8,812,245.

The Cajuns, also known as Louisiana Acadians, are a Louisiana French ethnicity mainly found in the US state of Louisiana and surrounding Gulf Coast states.

The United States does not have an official language at the federal level, but the most commonly used language is English, which is the de facto national language. In addition, 32 U.S. states out of 50 and all five U.S. territories have declared English as an official language. The majority of the U.S. population (78%) speaks only English at home as of 2023, according to the American Community Survey (ACS) of the U.S. Census Bureau. The remainder of the population speaks many other languages at home, most notably Spanish. Asian languages such as Chinese, Tagalog, and Vietnamese are also widely spoken, in addition to the Indigenous languages of Native Americans, Alaska Natives, Native Hawaiians, and native populations in the U.S. unincorporated territories. Many languages were brought into the United States during its earliest history from Europe, Africa, Asia, other parts of the Americas, and Oceania, with some of them developing into dialects, creole languages, and pidgin languages. American Sign Language (ASL) and Interlingua, an international auxiliary language, were created in the United States.
The French language is spoken as a minority language in the United States. Roughly 1.18 million Americans over the age of five reported speaking the language at home in the federal 2020 American Community Survey, making French the seventh most spoken language in the country behind English, Spanish, Chinese, Tagalog, Vietnamese, and Arabic. Several varieties of French evolved in what is now the United States:

Haitian Creole, or simply Creole, is a French-based creole language spoken by 10 to 12 million people worldwide, and is one of the two official languages of Haiti, where it is the native language of the vast majority of the population, and is also the most widely spoken creole language in the world. Northern, Central, and Southern dialects are the three main dialects of Haitian Creole. The Northern dialect is predominantly spoken in Cap-Haïtien, Central is spoken in Port-au-Prince, and Southern in the Cayes area.

French America, sometimes called Franco-America, in contrast to Anglo-America, is the French-speaking community of people and their diaspora, notably those tracing back origins to New France, the early French colonization of the Americas. The Canadian province of Quebec is the centre of the community and is the point of origin of most of French America. It also includes communities in all provinces of Canada, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Saint Martin, Saint Barthélemy, Martinique, Guadeloupe, Saint Lucia and Haiti in the Caribbean; French Guiana in South America. Also there are minorities of French speakers in part of the United States, the Dominican Republic, Dominica, Grenada and Trinidad and Tobago.
French Creole may refer to:
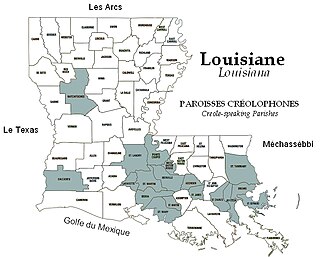
Louisiana Creole is a French-based creole language spoken by fewer than 10,000 people, mostly in the U.S. state of Louisiana. Also known as Kouri-Vini, it is spoken today by people who may racially identify as white, black, mixed, and Native American, as well as Cajun and Creole. It should not be confused with its sister language, Louisiana French, a dialect of the French language. Many Louisiana Creoles do not speak the Louisiana Creole language and may instead use French or English as their everyday languages.

Varieties of the French language are spoken in France and around the world. The Francophones of France generally use Metropolitan French although some also use regional dialects or varieties such as Meridional French. In Europe outside France there are Belgian French, Swiss French, and in Italy Aostan French. In Canada, French is an official language along with English; the two main dialects of French in Canada are Canadian French and Acadian French. Standard French is also commonly grouped as Canadian French. In Lebanon, French was an official language until 1941 and the main dialect spoken there is Lebanese French or Levantine French. Levantine French was also spoken by Sephardic Jews in Salonica, Istanbul and Smyrna, by Armenians and Greek bourgeois in the urban centres of Asia Minor, by Syrian Catholics and Melkites in Aleppo and Beirut.

French Americans or Franco-Americans are citizens or nationals of the United States who identify themselves with having full or partial French or French-Canadian heritage, ethnicity and/or ancestral ties. They include French-Canadian Americans, whose experience and identity differ from the broader community.

A French creole, or French-based creole language, is a creole for which French is the lexifier. Most often this lexifier is not modern French but rather a 17th- or 18th-century koiné of French from Paris, the French Atlantic harbors, and the nascent French colonies. This article also contains information on French pidgin languages, contact languages that lack native speakers.

Louisiana Creoles are a Louisiana French ethnic group descended from the inhabitants of colonial Louisiana before it became a part of the United States during the periods of French and Spanish rule. They share cultural ties such as the traditional use of the French, Spanish, and Creole languages and predominant practice of Catholicism.
The languages of North America reflect not only that continent's indigenous peoples, but the European colonization as well. The most widely spoken languages in North America are English, Spanish, and to a lesser extent French, and especially in the Caribbean, creole languages lexified by them.

Louisiana is a South Central US state, with a 2020 US census resident population of 4,657,757, and apportioned population of 4,661,468. Much of the state's population is concentrated in southern Louisiana in the Greater New Orleans, Florida Parishes, and Acadiana regions, with the remainder in North and Central Louisiana's major metropolitan areas. The center of population of Louisiana is located in Pointe Coupee Parish, in the city of New Roads.

The languages of the Caribbean reflect the region's diverse history and culture. There are six official languages spoken in the Caribbean:
The culture of North America refers to the arts and other manifestations of human activities and achievements from the continent of North America. Cultures of North America reflect not only that of the continent's indigenous peoples but those cultures that followed European colonisation as well.
Haitian French is the variety of French spoken in Haiti. Haitian French is close to standard French. It should be distinguished from Haitian Creole, which is not mutually intelligible with French.
Louisiana French is an umbrella term for the dialects and varieties of the French language spoken traditionally by French Louisianians in colonial Lower Louisiana. As of today Louisiana French is primarily used in the state of Louisiana, specifically in its southern parishes.