
The American National Standards Institute is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organization also coordinates U.S. standards with international standards so that American products can be used worldwide.
A management system is a set of policies, processes and procedures used by an organization to ensure that it can fulfill the tasks required to achieve its objectives. These objectives cover many aspects of the organization's operations. For instance, an environmental management system enables organizations to improve their environmental performance, and an occupational safety and health management system enables an organization to control its occupational health and safety risks.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration is a regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. The United States Congress established the agency under the Occupational Safety and Health Act, which President Richard M. Nixon signed into law on December 29, 1970. OSHA's mission is to "assure safe and healthy working conditions for working men and women by setting and enforcing standards and by providing training, outreach, education, and assistance." The agency is also charged with enforcing a variety of whistleblower statutes and regulations. OSHA's workplace safety inspections have been shown to reduce injury rates and injury costs without adverse effects on employment, sales, credit ratings, or firm survival.
ABET , formerly known as the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology, Inc., is a non-governmental accreditation organization for post-secondary programs in engineering, engineering technology, computing, and applied and natural sciences.

Occupational hygiene or industrial hygiene (IH) is the anticipation, recognition, evaluation, control, and confirmation (ARECC) of protection from risks associated with exposures to hazards in, or arising from, the workplace that may result in injury, illness, impairment, or affect the well-being of workers and members of the community. These hazards or stressors are typically divided into the categories biological, chemical, physical, ergonomic and psychosocial. The risk of a health effect from a given stressor is a function of the hazard multiplied by the exposure to the individual or group. For chemicals, the hazard can be understood by the dose response profile most often based on toxicological studies or models. Occupational hygienists work closely with toxicologists (see Toxicology) for understanding chemical hazards, physicists (see Physics) for physical hazards, and physicians and microbiologists for biological hazards (see Microbiology, Tropical medicine, Infection). Environmental and occupational hygienists are considered experts in exposure science and exposure risk management. Depending on an individual's type of job, a hygienist will apply their exposure science expertise for the protection of workers, consumers and/or communities.
Certified safety professional is a certification offered by the Board of Certified Safety Professionals. The accreditation is used in the United States by the National Commission for Certifying Agencies and internationally by the International Organization for Standardization/International Electrotechnical Commission and 193 Countries Consortium.
North American Occupational Safety and Health (NAOSH) Week is an annual celebration that happens during the first full week of May. The aim of the event is to raise awareness about occupational safety, health, and the environment (OSH&E) in order to avoid workplace injuries and illnesses.
Occupational Safety and Health Professional (OSHP) Day recognizes the efforts and commitment of occupational safety, health and environmental professionals to protect people, property and the environment. The American Society of Safety Engineers’ Board of Directors approved the creation of Occupational Safety and Health Professional (OSHP) Day in March 2006 to be held in conjunction with North American Occupational Safety and Health Week (NAOSH). OSHP Day takes place on the Wednesday of NAOSH Week each year and is celebrated internationally. OSHP Day 2012 took place on May 9, 2012.
A safety management system (SMS) is a management system designed to manage occupational safety and health risks in the workplace. If the system contains elements of management of longer-term health impacts and occupational disease, it may be referred to as a safety and health management system (SHMS) or health and safety management system.
ANSI Z535 are American-developed standards designed to improve the identification of potential hazards to workers and/or property. The identifications are called Hazardous Communication (HazCom). ANSI Z535 sets the design and application standards for all HazCom used across North America and globally, in most industrialized nations. ANSI Z535 standards integrate with international ISO 3864 standards, ensuring the widest compliance, globally, with export/import laws. ANSI Z535 standardized HazCom may appear on workplace walls, industrial machines, at industrial access points, on electrical controls, inside product user guides, and on export documentation.
OHSAS 18001, Occupational Health and Safety Assessment Series, was an international standard for occupational health and safety management systems that was subsequently adopted as a British Standard. Compliance with it enabled organizations to demonstrate that they had a system in place for occupational health and safety. BSI cancelled OHSAS 18001 to adopt ISO 45001. ISO 45001 was published in March 2018 by the International Organization for Standardization. Organizations that are certified to OHSAS 18001 were able to migrate to ISO 45001 by March 2021 to retain a recognized certification.

NSF is a public health organization headquartered in Ann Arbor, Michigan that tests and certifies foods, water, and consumer products. It also facilitates the development of standards for these products, labeling products it has certified to meet these standards with the NSF mark.

Occupational safety and health (OSH) or occupational health and safety (OHS) is a multidisciplinary field concerned with the safety, health, and welfare of people at work. OSH is related to the fields of occupational medicine and occupational hygiene and aligns with workplace health promotion initiatives. OSH also protects all the general public who may be affected by the occupational environment.
The Occupational Safety and Health Consultants Register (OSHCR) is a public register of UK-based occupational health and safety advice consultants, set up to assist UK employers and business owners with general advice on workplace health and safety issues. The register was established in response to the Government’s October 2010 report on 'Common Sense, Common Safety', which recommended that all health and safety consultants should be accredited to professional bodies and a web-based directory established.
The SA8000 Standard is an auditable certification standard that encourages organizations to develop, maintain, and apply socially acceptable practices in the workplace. It was developed in 1997 by Social Accountability International, formerly the Council on Economic Priorities, by an advisory board consisting of trade unions, NGOs, civil society organizations and companies. The SA8000's criteria were developed from various industry and corporate codes to create a common standard for social welfare compliance. The current (2014) version of the standard is built on earlier 2001, 2004 and 2008 versions.
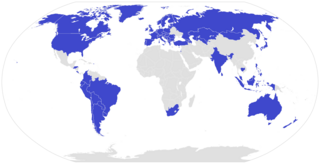
ISO 45001 is an International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standard for management systems of occupational health and safety (OHS), published in March 2018. The goal of ISO 45001 is the reduction of occupational injuries and diseases, including promoting and protecting physical and mental health.
The Board of Canadian Registered Safety Professionals (BCRSP) provides certification of occupational health and safety professionals in Canada and has an established Code of Ethics.
A psychosocial hazard or work stressor is any occupational hazard related to the way work is designed, organized and managed, as well as the economic and social contexts of work. Unlike the other three categories of occupational hazard, they do not arise from a physical substance, object, or hazardous energy.
Anticipate, recognize, evaluate, control, and confirm (ARECC) is a decision-making framework and process used in the field of industrial hygiene (IH) to anticipate and recognize hazards, evaluate exposures, and control and confirm protection from risks. ARECC supports exposure- and population-informed hazard assessment, hazard- and population-informed exposure assessment, hazard- and exposure-informed population assessment, and risk-informed decision making in any endeavor.
Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) literacy is the degree to which individuals have the functional capacity to access, process and use the occupational safety and health (OSH) information, services and skills needed to eliminate or reduce risk in the workplace.




