
Hyoliths are animals with small conical shells, known as fossils from the Palaeozoic era. They are at least considered as lophotrochozoan, and possibly being lophophorates, a group which includes the brachiopods, while others consider them as being basal lophotrochozoans, or even molluscs.

The Rostroconchia is a class of extinct molluscs dating from the early Cambrian to the Late Permian. They were initially thought to be bivalves, but were later given their own class. They have a single shell in their larval stage, and the adult typically has a single, pseudo-bivalved shell enclosing the mantle and muscular foot. The anterior part of the shell probably pointed downward and had a gap from which the foot could probably emerge. Rostroconchs probably lived a sedentary semi-infaunal lifestyle. There were probably more than 1,000 species of members of this class.
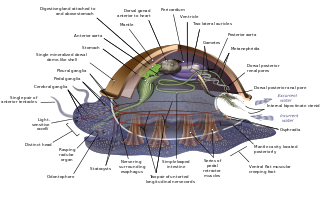
The evolution of the molluscs is the way in which the Mollusca, one of the largest groups of invertebrate animals, evolved. This phylum includes gastropods, bivalves, scaphopods, cephalopods, and several other groups. The fossil record of mollusks is relatively complete, and they are well represented in most fossil-bearing marine strata. Very early organisms which have dubiously been compared to molluscs include Kimberella and Odontogriphus.

Latouchella is an extinct genus of marine invertebrate animal, that is considered to be a mollusk and which may be a sea snail, a gastropod. It is a helcionellid from the Tommotian epoch of what is now Siberia. Its tightly coiled, spiral shell contains a number of low "walls" running up the front surface of the interior; these would have directed water currents within its shell. Between these walls are a series of furrows, parallel to the shell's aperture, giving casts of the internal structure the appearance of a railway line, with sleepers tying together paired rails that run towards the apex of the shell.

Haplophrentis is a genus of tiny shelled hyolithid which lived in the Cambrian Period. Its shell was long and conical, with the open end protected by an operculum, from which two fleshy arms called helens protruded at the sides. These arms served to elevate the opening of the shells above the sea floor, acting like stilts.

Yochelcionella is an extinct genus of basal molluscs which lived during the Tommotian epoch, the first epoch of the Cambrian period. This genus is often reconstructed to resemble snails.

Helcionellid or Helcionelliformes is an order of small fossil shells that are universally interpreted as molluscs, though no sources spell out why this taxonomic interpretation is preferred. These animals are first found about 540 to 530 million years ago in the late Nemakit-Daldynian age, which is the earliest part of the Cambrian period. A single species persisted to the Early Ordovician. These fossils are component of the small shelly fossils (SSF) assemblages.
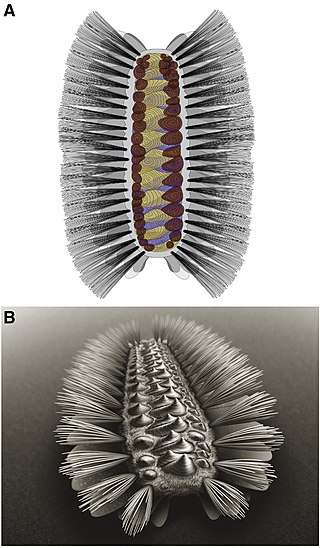
Tommotiids are an extinct group of Cambrian invertebrates thought to be early lophophorates.
Aldanellidae is an extinct family of paleozoic molluscs that have been assigned to the Gastropod stem group but may also belong to a paraphyletic "Monoplacophora".

Fordilla is an extinct genus of early bivalves, one of two genera in the extinct family Fordillidae. The genus is known solely from Early Cambrian fossils found in North America, Greenland, Europe, the Middle East, and Asia. The genus currently contains three described species, Fordilla germanica, Fordilla sibirica, and the type species Fordilla troyensis.
Stenothecoida is a taxon of bivalved fossils from the Early to middle Cambrian period. They look a bit like brachiopods or bivalve molluscs.
Mongolitubulus is a form genus encapsulating a range of ornamented conical small shelly fossils of the Cambrian period. It is potentially synonymous with Rushtonites, Tubuterium and certain species of Rhombocorniculum, and owing to the similarity of the genera, they are all dealt with herein. Organisms that bore Mongolitubulus-like projections include trilobites, bradoriid arthropods and hallucigeniid lobopodians.
Pojetaia is an extinct genus of early bivalves, one of two genera in the extinct family Fordillidae. The genus is known solely from Early to Middle Cambrian fossils found in North America, Greenland, Europe, North Africa, Asia, and Australia. The genus currently contains two accepted species, Pojetaia runnegari, the type species, and Pojetaia sarhroensis, though up to seven species have been proposed. The genera Buluniella, Jellia, and Oryzoconcha are all considered synonyms of Pojetaia.
Watsonella is a genus of 'mollusc' known from early (Terreneuvian) Cambrian strata.
Mickwitziids are a Cambrian group of shelly fossils with originally phosphatic valves, belonging to the Brachiopod stem group, and exemplified by the genus Mickwitzia – the other genera are Heliomedusa and Setatella. The family Mickwitziidae is conceivably paraphyletic with respect to certain crown-group brachiopods.

Fordillidae is an extinct family of early bivalves and one of two families in the extinct superfamily Fordilloidea. The family is known from fossils of early to middle Cambrian age found in North America, Greenland, Europe, the Middle East, Asia, and Australia. The family currently contains two genera, Fordilla and Pojetaia, each with up to three described species. Due to the size and age of the fossil specimens, Fordillidae species are included as part of the Turkish Small shelly fauna.

Fordilloidea is an extinct superfamily of early bivalves containing two described families, Fordillidae and Camyidae and the only superfamily in the order Fordillida. The superfamily is known from fossils of early to middle Cambrian age found in North America, Greenland, Europe, the Middle East, Asia, and Australia. Fordillidae currently contains two genera, Fordilla and Pojetaia each with up to three described species while Camyidae only contains a single genus Camya with one described species, Camya asy. Due to the size and age of the fossil specimens, Fordillidae species are included as part of the Turkish Small shelly fauna.
Tuarangia is a Cambrian shelly fossil interpreted as an early bivalve, though alternative classifications have been proposed and its systematic position remains controversial. It is the only genus in the extinct family Tuarangiidae and order Tuarangiida. The genus is known solely from Middle to Late Cambrian fossils found in Europe and New Zealand. The genus currently contains two accepted species, Tuarangia gravgaerdensis and the type species Tuarangia paparua.
Tannuolina is a genus of tommotiid, belonging to the brachiopod stem lineage.
Micrina is an extinct genus of tommotiids with affinities to brachiopods.






