
The Buthidae are the largest family of scorpions, containing about 100 genera and 1339 species as of 2022. A few very large genera are known, but a high number of species-poor or monotypic ones also exist. New taxa are being described at a rate of several new species per year. They have a cosmopolitan distribution throughout tropical and subtropical environments worldwide. Together with four other families, the Buthidae make up the superfamily Buthoidea. The family was established by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1837.

Centruroides is a genus of scorpions of the family Buthidae. Several North American species are known by the common vernacular name bark scorpion. Numerous species are extensively found throughout the southern United States, Mexico, Central America, the Antilles and northern South America. Some are known for their interesting patterning or large size ; most if not all fluoresce strongly under ultraviolet illumination, except after moulting. They contain several highly venomous species, and fatalities are known to occur. The venom of the Mexican scorpion Centruroides limpidus limpidus contains the neurotoxins Cll1 and Cll2.
Tityus pintodarochai is a species of scorpion belonging to the family Buthidae. It is only known from a single female collected in Paraná state, Brazil.

Hottentotta is a genus of scorpions of the family Buthidae. It is distributed widely across Africa, except for most of the Sahara desert. Species in the genus also occur in the Middle East, the Arabian Peninsula, southeastern Turkey, Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, India, Nepal, Cape Verde Islands, and Sri Lanka (introduced).

Leiurus is a genus of scorpion of the family Buthidae. The most common species, L. quinquestriatus, is also known under the common name Deathstalker. It is distributed widely across North Africa and the Middle East, including the western and southern Arabian Peninsula and southeastern Turkey. At least one species occurs in West Africa.

Tityus serrulatus, the Brazilian yellow scorpion, is a species of scorpion of the family Buthidae. It is native to Brazil, and its venom is extremely toxic. It is the most dangerous scorpion in South America and is responsible for the most fatal cases.

Mesobuthus eupeus is a polymorphic scorpion species belonging to the well-known family Buthidae. Commonly known as the lesser Asian scorpion or the mottled scorpion. It is thought to be the most widely dispersed species of the genus Mesobuthus, perhaps even of the family Buthidae.
Uintascorpio is an extinct genus of scorpion in the family Buthidae and containing the single species Uintascorpio halandrasorum. The species is known only from the Middle Eocene Parachute Member, part of the Green River Formation, in the Piceance Creek Basin, Garfield County, northwestern Colorado, USA.

Buthus is a genus of scorpion belonging and being eponymous to the family Buthidae. It is distributed widely across northern Africa, including Morocco, Mauritania, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt, Senegal, Guinea-Bissau, Nigeria, Sudan, Somalia, Ethiopia, Djibouti, as well as the Middle East, including Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon, Iraq, Yemen, and possibly Saudi Arabia and southern Turkey. Its European range includes the Iberian Peninsula, southern France, and Cyprus.

Tityus stigmurus is a species of scorpion from the family Buthidae that can be found in Brazil. The species are 4.5–6 centimetres (1.8–2.4 in) in length and are either golden-tan or yellowish-brown coloured. It takes them a year to mature into an adult, which makes them a fast-growing species. They also have a dark stripe over the mesosoma with either yellowish or orange pedipalps.

Isometrus is a genus of scorpion belonging and being eponymous to the family Buthidae. Some species are currently assigned to the genus Reddyanus.

Buthoidea is the largest superfamily of scorpions. Its members are known as fat-tailed scorpions and bark scorpions. A few very large genera are known, but a high number of species-poor or monotypic ones also exist. They occur in the warmer parts of every major landmass on Earth, except on New Zealand. The superfamily was established by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1837.

Ananteris balzanii is a scorpion species found in Argentina, Paraguay and Brazil. It is the type species of the Ananteris genus. The species will autotomize its Metasoma when threatened, and doing so decreases their ability to successfully subdue prey.
Ananteris nairae is a scorpion species found in Brazilian Amazonia. The species has the most western distribution of the species in Ananteris. The specific epithet refers to Nair Otaviano Aguiar.
Wilson R. Lourenço is a French-Brazilian arachnologist specializing in scorpions.
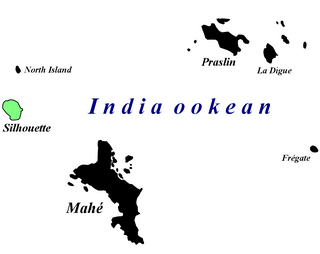
Afrolychas braueri, commonly known as the Seychelles forest scorpion, is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae. It is currently thought to survive only on Silhouette Island, Seychelles, although the species was historically found on two additional Seychellois islands. This scorpion lives in leaf litter in forests that are largely unaffected by invasive plant species. It is a small yellowish-brown scorpion with three prominent keels on the dorsal surface of its mesosoma, which distinguishes it from other scorpions. While not much is known about the Seychelles forest scorpion's ecology due to the paucity of sightings, it is known to rely solely on its venom to capture its prey and defend its young. Its venom is not dangerous to humans.

Reddyanus is a genus of buthid scorpions native to Oriental region from India, Sri Lanka, China: Tibet, to Melanesia. The genus was previously described as a subgenus of Isometrus.

Ananteris bernabei is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae. It was first described in a 2009 paper along with the species Ananteris chagasi and Ananteris kuryi. It is endemic to Espírito Santo, Brazil.

Ananteris chagasi is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae. It was first described in a 2009 paper along with the species Ananteris kuryi and Ananteris bernabei. It is endemic to Minas Gerais, Brazil.

Ananteris kuryi is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae. It was first described in a 2009 paper along with the species Ananteris chagasi and Ananteris bernabei. It is endemic to Bahia, Brazil.














