Related Research Articles
Methylotrophs are a diverse group of microorganisms that can use reduced one-carbon compounds, such as methanol or methane, as the carbon source for their growth; and multi-carbon compounds that contain no carbon-carbon bonds, such as dimethyl ether and dimethylamine. This group of microorganisms also includes those capable of assimilating reduced one-carbon compounds by way of carbon dioxide using the ribulose bisphosphate pathway. These organisms should not be confused with methanogens which on the contrary produce methane as a by-product from various one-carbon compounds such as carbon dioxide. Some methylotrophs can degrade the greenhouse gas methane, and in this case they are called methanotrophs. The abundance, purity, and low price of methanol compared to commonly used sugars make methylotrophs competent organisms for production of amino acids, vitamins, recombinant proteins, single-cell proteins, co-enzymes and cytochromes.
A halohydrin dehalogenase is an enzyme involved in the bacterial degradation of vicinal halohydrins. In several species of bacteria, it catalyses the dehalogenation of halohydrins to produce the corresponding epoxides. Different isoforms of the enzyme fall into one of three groups, A, B or C. Halogenases of the same class are genetically similar, but differ greatly from halogenases from a different group. Currently the most well-studied isoform is HheC which is purified from the bacterial species Agrobacterium radiobacter. The ability to dehalogenate organic compounds as well as form enantiomeric selective epoxides have generated interest in the potential of this enzyme in the biochemical field.
2-Chloroethanol (also called ethylene chlorohydrin or glycol chlorohydrin) is an organic chemical compound with the chemical formula HOCH2CH2Cl and the simplest beta-halohydrin (chlorohydrin). This colorless liquid has a pleasant ether-like odor. It is miscible with water. The molecule is bifunctional, consisting of both an alkyl chloride and an alcohol functional group.
Organohalide respiration (OHR) (previously named halorespiration or dehalorespiration) is the use of halogenated compounds as terminal electron acceptors in anaerobic respiration. Organohalide respiration can play a part in microbial biodegradation. The most common substrates are chlorinated aliphatics (PCE, TCE, chloroform) and chlorinated phenols. Organohalide-respiring bacteria are highly diverse. This trait is found in some Campylobacterota, Thermodesulfobacteriota, Chloroflexota (green nonsulfur bacteria), low G+C gram positive Clostridia, and ultramicrobacteria.

Oxatomide, sold under the brand name Tinset among others, is a antihistamine of the diphenylmethylpiperazine family which is marketed in Europe, Japan, and a number of other countries. It was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1975. Oxatomide lacks any anticholinergic effects. In addition to its H1 receptor antagonism, it also possesses antiserotonergic activity similarly to hydroxyzine.
Dehalococcoides is a genus of bacteria within class Dehalococcoidia that obtain energy via the oxidation of hydrogen and subsequent reductive dehalogenation of halogenated organic compounds in a mode of anaerobic respiration called organohalide respiration. They are well known for their great potential to remediate halogenated ethenes and aromatics. They are the only bacteria known to transform highly chlorinated dioxins, PCBs. In addition, they are the only known bacteria to transform tetrachloroethene to ethene.
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxyacetophenone monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.84) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
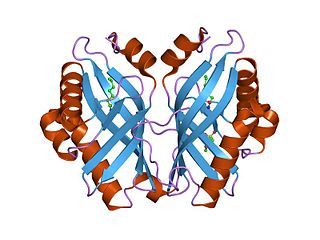
In enzymology, a limonene-1,2-epoxide hydrolase (EC 3.3.2.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
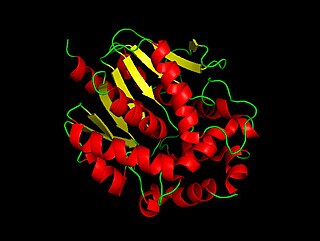
In enzymology, a haloalkane dehalogenase (EC 3.8.1.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Cupriavidus metallidurans is a non-spore-forming, Gram-negative bacterium which is adapted to survive several forms of heavy metal stress.

Chloroacetaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula ClCH2CHO. Like some related compounds, it is highly electrophilic reagent and a potentially dangerous alkylating agent. The compound is not normally encountered in the anhydrous form, but rather as the hemiacetal (ClCH2CH(OH))2O.
Desulfitobacterium dehalogenans is a species of bacteria. They are facultative organohalide respiring bacteria capable of reductively dechlorinating chlorophenolic compounds and tetrachloroethene. They are anaerobic, motile, Gram-positive and rod-shaped bacteria capable of utilizing a wide range of electron donors and acceptors. The type strain JW/IU-DCT, DSM 9161, NCBi taxonomy ID 756499.

3-Methylcatechol is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H3(OH)2 A white solid, it is one of the isomers of methylbenzenediol. Being structurally related to lignans, it is contributes to the aerosol generate by combustion of wood.
Desulfitobacterium hafniense is a species of gram positive bacteria, its type strain is DCB-2T..
Dehalogenimonas lykanthroporepellens is an anaerobic, Gram-negative bacteria in the phylum Chloroflexota isolated from a Superfund site in Baton Rouge, Louisiana. It is useful in bioremediation for its ability to reductively dehalogenate chlorinated alkanes.
Starkeya novella is a chemolithoautotrophic and methylotrophic bacteria from the family Xanthobacteraceae which has been isolated from soil. Starkeya novella has the ability to oxidise thiosulfate. The complete genome of Starkeya novella is sequenced.
Xanthobacter autotrophicus is a Gram-negative, aerobic, pleomorphic and nitrogen-fixing bacterium from the family of Xanthobacteraceae which has been isolated from black pool sludge in Germany. Xanthobacter autotrophicus can utilize 1,2-dichloroethane, methanol and propane.
Ann Patricia Wood is a retired British biochemist and bacteriologist who specialized in the ecology, taxonomy and physiology of sulfur-oxidizing chemolithoautotrophic bacteria and how methylotrophic bacteria play a role in the degradation of odour causing compounds in the human mouth, vagina and skin. The bacterial genus Annwoodia was named to honor her contributions to microbial research in 2017.
Cytophagales is an order of non-spore forming, rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacteria that move through a gliding or flexing motion. These chemoorganotrophs are important remineralizers of organic materials into micronutrients. They are widely dispersed in the environment, found in ecosystems including soil, freshwater, seawater and sea ice. Cytophagales is included in the Bacteroidota phylum.

Jan Rudolph Deiman or Johann Rudolf Deimann was a German-Dutch physician and chemist who was among the first to examine electrolysis of water, and examine the application of electricity for medical uses along with Adriaan Paets van Troostwijk. In 1791, they founded the De Bataafsche Societeit which later became the Gezelschap der Hollandsche Scheikundigen.
References
- 1 2 LPSN lpsn.dsmz.de
- ↑ "Straininfo of Ancylobacter aquaticus". Archived from the original on 2016-06-25. Retrieved 2016-02-14.
- ↑ Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen
- ↑ UniProt
- ↑ van den Wijngaard, AJ; van der Kamp, KW; van der Ploeg, J; Pries, F; Kazemier, B; Janssen, DB (March 1992). "Degradation of 1,2-dichloroethane by Ancylobacter aquaticus and other facultative methylotrophs". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 58 (3): 976–83. Bibcode:1992ApEnM..58..976V. doi:10.1128/AEM.58.3.976-983.1992. PMC 195365 . PMID 1575500.
- ↑ Neilson, with contributions by A.-S. Allard ... Vol. ed.: Alasdair H. (2003). Organic bromine and iodine compounds. Berlin [u.a.]: Springer. ISBN 3-540-02777-7.