
Colocasia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae, native to southeastern Asia and the Indian subcontinent. Some species are widely cultivated and naturalized in other tropical and subtropical regions.

Manipur is a state in northeast India, with the city of Imphal as its capital. It is bounded by the Indian states of Nagaland to the north, Mizoram to the south and Assam to the west. It also borders two regions of Myanmar, Sagaing Region to the east and Chin State to the south. The state covers an area of 22,327 km2 (8,621 sq mi). The official and most widely spoken language is the Meitei language. Native to the Meitei people, it is also used as a lingua franca by smaller communities, who speak a variety of other Tibeto-Burman languages. Manipur has been at the crossroads of Asian economic and cultural exchange for more than 2,500 years. This exchange connects the Indian subcontinent and Central Asia to Southeast Asia, East Asia, Siberia, regions in the Arctic, Micronesia and Polynesia enabling migration of people, cultures and religions.

Northeast India, officially the North Eastern Region (NER), is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political administrative division of the country. It comprises eight states—Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura, and the "brother" state of Sikkim.

The Loktak Lake is a freshwater lake in Northeast India. It is the largest freshwater lake in India and possibly South Asia. It is a pulsating lake, with a surface area varying from 250 sq km to 500 sq km during the rainy season with a typical area of 287 sq km. The lake is located at Moirang in Manipur state, India. The etymology of Loktak is Lok = "stream" and tak = "the end" in Meitei language. It is famous for the phumdi floating over it. The largest of all the phumdis covers an area of 40 km2 (15 sq mi) and is situated on the southeastern shore of the lake. Located on this phumdi, Keibul Lamjao National Park is the only floating national park in the world. The park is the last natural refuge of the endangered Sangai, Rucervus eldii eldii or Manipur brow-antlered deer, one of three subspecies of Eld's deer.

The Keibul Lamjao National Park is a national park in the Bishnupur district of the state of Manipur in Northeast India. It is 40 km2 (15.4 sq mi) in area, the only floating national park in the world, and an integral part of Loktak Lake. It is currently under the tentative lists of the UNESCO World Heritage Sites, under the title "Keibul Lamjao Conservation Area (KLCA)", additionally covering the buffer of Loktak Lake and Pumlen Pat.

Ukhrul district is an administrative district of the state of Manipur in India with its headquarters at Ukhrul. The Ukhrul district has a long history dating back to the 1920s when it was created as the North-East Hill Sub-Division of the then princely state of Manipur. In 2016, the Kamjong subdivision of the Ukhrul district was spun out as a separate district, leading to the present configuration of the Ukhrul district.

Mount Harriet National Park, officially renamed as Mount Manipur National Park, is a national park located in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands union territory of India. The park, established in 1969, covers about 4.62 km2 (18.00 mi2). Mount Manipur, which is a part of the park, is the third-highest peak in the Andaman and Nicobar archipelago next to Saddle Peak in North Andaman and Mount Thullier in Great Nicobar.

Euryale ferox, commonly known as prickly waterlily, makhana or Gorgon plant, is a species of water lily found in southern and eastern Asia, and the only extant member of the genus Euryale. The edible seeds, called fox nuts or makhana when dried, are eaten in Asia.

The Barak River or Barbatro flows 900 kilometres (560 mi) through the states of Manipur, Mizoram and Assam in India. It flows into Bangladesh where it bifurcates into the Surma river and the Kushiyara river which converge again to become the Meghna river before forming the Ganges Delta. Of its total length, 524 km (326 mi) is in India, 31 km (19 mi) in Bangladesh. The upper part of its navigable part is in India — 121 km (75 mi) between Lakhipur and Bhanga, declared as National Waterway 6, (NW-6) since the year 2016. It drains a basin of 52,000 km2 (20,000 sq mi), of which 41,723 km2 (16,109 sq mi) lies in India, 1.38% (rounded) of the country. The water and banks host or are visited by a wide variety of flora and fauna.

Viviparidae, sometimes known as the river snails or mystery snails, are a family of large aquatic gastropod mollusks, being some of the most widely distributed operculate freshwater snails.

Psilorhynchus is a genus of fish in the family Psilorhynchidae native to South Asia. This genus is the only member of its family. The members of Psilorhynchus are small benthic fishes which occur in rivers and streams with fast to swift currents, hence they are often referred to a torrent minnows. They are distributed in southern Asia, in the Indo-Burma region and the Western Ghats.
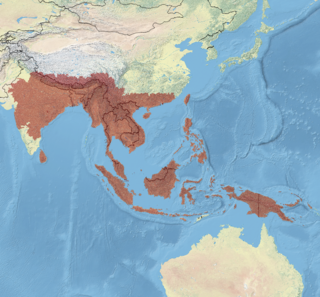
Intha umbilicalis is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod in the ram's horn snail family, Planorbidae.

Angulyagra polyzonata is a species of a freshwater snail with a gill and an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Viviparidae.
Bulinidae is a family of gastropods in the superfamily Lymnaeoidea.
Lourembam Bino Devi is a practitioner and a popularizer of the appliqué art of Manipur called Leeba in the Meitei language. The Leeba art is used in creating Monmai which is a decorative circular appliqué art piece used in covering both ends of the traditional Manipuri bolster pillow. In the olden days, Leeba was practiced at "Phiribi Loishang", which is a house for maintaining clothes worn by the deities and royals. The apparels used by the royals, including shoes, were mostly designed using the Leeba technique. Bino Devi has devoted her life to practice this art form and to revive it by trying to transmit her skills to younger generation of interested women. She has been providing this training in collaboration with the Heritage Foundation of Mankind, a Non-Governmantal Organization located in Imphal. She has also conducted several workshops at Imphal and at various other places in India.

Thangching or Thangjing is a primordial deity in Sanamahism, the indigenous religion of Manipur. He is the ruling deity of the Moirang dynasty. He rules supreme on the banks of the landlocked sea, Loktak lake. He is one of the four cardinal Umang Lais. The guardianship of the south western direction is alluded to Thangjing and the other directions to Koubru, Marjing and Wangbren.

Nymphaea manipurensis is a species of waterlily endemic to Assam, India.
















