
Trilobites are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian stage of the Early Cambrian period and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic before slipping into a long decline, when, during the Devonian, all trilobite orders except the Proetida died out. The last trilobites disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian about 251.9 million years ago. Trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, existing in oceans for almost 270 million years, with over 22,000 species having been described.

Richard Alan Fortey is a British palaeontologist, natural historian, writer and television presenter, who served as president of the Geological Society of London for its bicentennial year of 2007.

Dalmanites is a genus of trilobite in the order Phacopida. They lived from the Late Ordovician to Middle Devonian.

Cloacaspis is an extinct genus of Olenid Ptychopariid trilobite. It lived during the early part of the Arenig stage of the Ordovician Period, a faunal stage which lasted from approximately 478 to 471 million years ago. Richard Fortey has proposed that these particular trilobites lived in anoxic regions of the ocean floor, and cultivated symbiotic, sulfur-metabolizing bacteria.

Globampyx is an extinct genus raphiophorid trilobites. It lived during the later part of the Arenig stage of the Ordovician Period, approximately 478 to 471 million years ago. Species of the genus are known from Canada, Norway (Svalbard) and Sweden.

Pytine is an extinct genus of asaphid trilobites. Species lived during the later part of the Arenig stage of the Ordovician Period, approximately 478 to 471 million years ago. Various species are found in the Svalbard, Valhallfonna Formation, Olenidsletta, Member, of Spitzbergen, Norway, the Megistaspis (Paramegistaspis) planilimbata Zone of the 'Shumardia Shale' of Sweden, Jujuy Province, Argentina, early Arenig-aged strata of Jiangxi province, China, and Darriwilian-aged strata in Western Hunan province, China. The type species, P. graia, has seven thorax segments, and lacks the rapier-like glabellar spine, that occurs in many other raphiophorids. The Chinese species, by contrast, have only six thoracic segments. So far, only the type species, and one of the Chinese species, P. laevigata, are known from complete specimens.

Cheirurus is a genus of phacopid trilobites that lived from the Ordovician to the Devonian. Its remains have been found in Africa, Asia, Australia, Europe, and North America. Cheirurus is the type genus of Cheiruridae.

Norasaphus monroeae is a species of asaphid trilobites named after Marilyn Monroe for its hourglass-like shaped glabellum. Its fossils are found in Arenig-aged marine strata from the Nora Formation, in the Georgina Basin, situated between the Northern Territory and Queensland, Australia.

The Fezouata Formation or Fezouata Shale is a geological formation in Morocco which dates to the Early Ordovician. It was deposited in a marine environment, and is known for its exceptionally preserved fossils, filling an important preservational window beyond the earlier and more common Cambrian Burgess shale-type deposits. The fauna of this geological unit is often described as the Fezouata biota, and the particular strata within the formation which exhibit exceptional preservation are generally termed the Fezouata Lagerstätte.

Illaenus is a genus of trilobites from Russia and Morocco, from the middle Ordovician.
Vietnamia is a genus of trilobites. A new species, V. yushanensis, was described from the late Ordovician of China by Dong-Chan Lee in 2011. It is also found in the U.A.E.

Trinodus is a very small to small blind trilobite, a well known group of extinct marine arthropods, which lived during the Ordovician, in what are now the Yukon Territories, Virginia, Italy, Czech Republic, Poland, Denmark, Sweden, Svalbard, Ireland, Scotland, Wales, Iran, Kazakhstan and China. It is one of the last of the Agnostida order to survive.
Prospectatrix is a genus of trilobites of average size, that lived in the Lower Ordovician and is probably ancestral to the other genera of the Cyclopygidae family. Its eyes are only moderately enlarged and it has six or seven thorax segments.
Sagavia is a genus of trilobites that lived during the Middle and Upper Ordovician in what are now Northwest and Southeast China, North Kazakhstan and Wales. It is a typical cyclopygid that can be distinguished by its large but separate eyes, elongated glabella, five thorax segments and a pygidium with clearly defined axis and border.
Carolinites is a genus of trilobite, assigned to the Telephinidae family, that occurs during the Lower and Middle Ordovician. Carolinites had a pantropical distribution, and there is evidence that it lived in upper parts of the water column. The free cheeks of Carolinites are largely covered by its huge eyes, except for the attachment of large genal spines that extend downward, backward and lateral and gradually curving further backward. The glabella is slightly bulbous, the occipital ring is well defined, but further transglabellar furrows are lacking. The thorax has 10 segments. The axis of the pygidium is highly vaulted, with a curved spine emerging almost perpendicular to the midline and ending parallel to it and a node on each of the other three segments. Carolinites is known from what are today Australia (Tasmania), Canada (Alberta), China, France, Spitsbergen, and the United States (Utah).

Raphiophoridae is a family of small to average-sized trilobites that first occurred at the start of the Ordovician and became extinct at the end of the Middle Silurian.
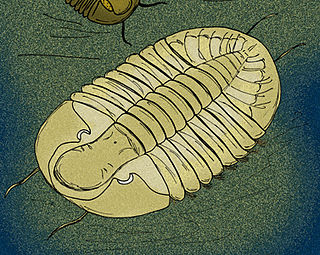
Gog is a genus of large, flattened asaphid trilobite from the Middle Arenig-aged Svalbard, Valhallfonna Formation, Olenidsletta, Member, of Spitzbergen, Norway, and the Upper Arenig-aged Dawan Formation in Hubei, China.

Paraceraurus is a genus of trilobites that lived in the Ordovician period. Its remains have been found in China, Estonia, Sweden and North America. These trilobites have a rounded and moderately convex cephalon. Glabella is convex or flattened, with a sub-rectangular outline. Thorax shows eleven segments.

Telephinidae is a family of pelagic trilobites with large wide-angle eyes, occupying most of the free cheeks, downward directed facial spines and 9-10 thorax segments. The family is known during the entire Ordovician and occurred in deep water around the globe.
Aponileus is an extinct genus of trilobites. Chung-Hung Hu circumscribed the genus in 1963. The genus was once considered a junior subjective synonym of the genus Psephosthenaspis but it is considered to be a distinct genus again. As of 2021, fossils have been found in Greenland, Texas, and Utah. They all date to the Upper Floian (Blackhillsian) within the Ordovician Period.













