Related Research Articles
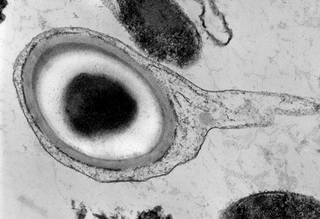
Carboxydothermus hydrogenoformans is an extremely thermophilic anaerobic Gram-positive bacterium that has the interesting property of producing hydrogen as a waste product while feeding on carbon monoxide and water. It also forms endospores.

Acidimicrobium ferrooxidans is a bacterium, the type species of its genus. It is a ferrous-iron-oxidizing, moderately thermophilic and acidophilic bacterium. A complete genome of one strain, DSM 10331 isolated in Iceland from hot spring runoff water, has been resolved.
Halomonas ventosae is a moderately halophilic, denitrifying, exopolysaccharide-producing bacterium. Its type strain is Al12T.
Thermosyntropha lipolytica is a lipolytic, anaerobic, alkalitolerant, thermophilic bacteria. It lives in syntrophic coculture with a methanogen. Its cells are non-motile, non-spore forming, straight or slightly curved rods. Its type strain is JW/VS-265T.
Clostridium paradoxum is a moderately thermophilic anaerobic alkaliphile bacteria. It is motile with 2-6 peritrichous flagella and forms round to slightly oval terminal spores. Its type strain is JW-YL-7.
Desulfotomaculum arcticum is a spore-forming, moderately thermophilic, sulfate-reducing bacterium. Its type strain is 15T.
Jeotgalibacillus alimentarius is a bacterium, the type species of its genus. It was first isolated from jeotgal, hence its name. It is a moderately halophilic, round-endospore-forming bacterium, with type strain YKJ-13T.
Bacillus fumarioli is a species of aerobic endospore-forming bacteria. It is moderately thermophilic and acidophilic, with type strain LMG 17489T.
Symbiobacterium thermophilum is a symbiotic thermophile that depends on co-culture with a Bacillus strain for growth. It is Gram-negative and tryptophanase-positive, with type strain T(T). It is the type species of its genus. Symbiobacterium is related to the Gram-positive Bacillota and Actinomycetota, but belongs to a lineage that is distinct from both.S. thermophilum has a bacillus shaped cell structure with no flagella. This bacterium is located throughout the environment in soils and fertilizers.
Thermoleophilum album is a bacterium obligate for thermophily and n-alkane substrates, the type species of its genus. It is Gram-negative, aerobic, small, and rod-shaped. It lacks pigmentation, motility, and the ability to form endospores, with type strain ATCC 35263.
Acetivibrio straminisolvens is a moderately thermophilic, aerotolerant and cellulolytic bacterium. It is non-motile, spore-forming, straight or slightly curved rod, with type strain CSK1T. Its genome has been sequenced.
Brevibacillus borstelensis is a Gram-positive, aerobic, rod-shaped, endospore-forming bacterium of the genus Brevibacillus. The genome of several B. borstelensis strains have been sequenced.
Geobacillus jurassicus is a thermophilic bacterium first isolated from a high-temperature petroleum reservoir. It is aerobic, gram-positive, rod-shaped, moderately thermophilic, chemoorganotrophic, and endospore-forming, with type species DS1T.
The genus Annwoodia was named in 2017 to circumscribe an organism previously described as a member of the genus Thiobacillus, Thiobacillus aquaesulis - the type and only species is Annwoodia aquaesulis, which was isolated from the geothermal waters of the Roman Baths in the city of Bath in the United Kingdom by Ann P. Wood and Donovan P. Kelly of the University of Warwick - the genus was subsequently named to honour Wood's contribution to microbiology. The genus falls within the family Thiobacillaceae along with Thiobacillus and Sulfuritortus, both of which comprise autotrophic organisms dependent on thiosulfate, other sulfur oxyanions and sulfide as electron donors for chemolithoheterotrophic growth. Whilst Annwoodia spp. and Sulfuritortus spp. are thermophilic, Thiobacillus spp. are mesophilic.
Moorella glycerini is a thermophilic, homoacetogenic, anaerobic and endospore-forming bacterium from the genus Moorella, which has been isolated from a hot spring from the Calcite Spring area from the Yellowstone National Park in the United States. This microorganism utilizes glycerol as a growth substrate and is considered Gram-positive type.
Flavobacterium anatoliense is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped and strictly aerobic bacterium from the genus of Flavobacterium which has been isolated from fresh water from Trabzon in Turkey.
Desulfurella amilsii is a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, obligately anaerobic sulfur-reducing, acidotolerant, moderately thermophilic and motile bacterium from the genus of Desulfurella which has been isolated from river sediments from the Tinto River in Spain. Desulfurella amilsii phenotypic characterization is also able to utilize thiosulfate as an electron acceptor and ferment pyruvate. In addition, it uses formate as an electron donor and can have a pH as low as 3.

Priestia flexa is an aerobic, Gram-variable, rod-shaped, endospore-forming, oxidase-positive bacterium. The endospores are ellipsoidal, located in central/paracentral, unswollen sporangia. In laboratory conditions, it produces opaque, creamish, raised-margin colonies at 30 ± 2°C when incubated for 24–72 hrs. on tryptic soy agar. This bacterial species may be isolated from feces (poultry) and soil.
Alicyclobacillus vulcanalis is a species of Gram positive, strictly aerobic, thermophilic bacterium. The bacteria are acidophilic and produce endospores. It was first isolated from water in a hot spring from Coso Hot Springs, California, United States. The species was first described in 2004, and the name refers to Vulcan, the Roman god of fire and metal working.
Parageobacillus caldoxylosilyticus is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, thermophilic and xylanolytic bacterium from the genus of Parageobacillus.
References
- ↑ Belduz, A. O. (2003). "Anoxybacillus gonensis sp. nov., a moderately thermophilic, xylose-utilizing, endospore-forming bacterium". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 53 (5): 1315–1320. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.02473-0 . ISSN 1466-5026. PMID 13130012.