| |
| Founded | 6 December 2008 |
|---|---|
| Type | Intermicronational organization |
| Purpose | Regulate micronational claims in Antarctica, caring for the natural environment |
| Leader | Yaroslav Mar |
| Staff | 9 member states (2025) |
| Website | amu |
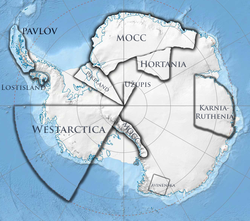
The Antarctic Micronational Union (AMU) is an intermicronational organization of self imaginative self proclaimed nations that aims to regulate micronational claims in Antarctica. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] The purpose of the AMU is to protect the claims of its members against other claimants. [6] [7] [8]