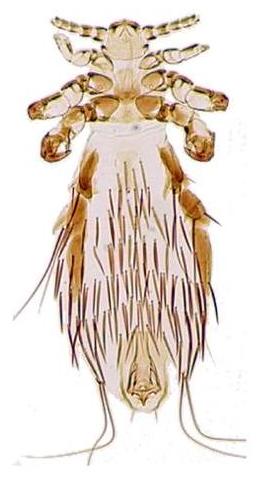
Louse is the common name for any member of the clade Phthiraptera, which contains nearly 5,000 species of wingless parasitic insects. Phthiraptera has variously been recognized as an order, infraorder, or a parvorder, as a result of developments in phylogenetic research.

Sea lions are pinnipeds characterized by external ear flaps, long foreflippers, the ability to walk on all fours, short and thick hair, and a big chest and belly. Together with the fur seals, they make up the family Otariidae, eared seals. The sea lions have six extant and one extinct species in five genera. Their range extends from the subarctic to tropical waters of the global ocean in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, with the notable exception of the northern Atlantic Ocean. They have an average lifespan of 20–30 years. A male California sea lion weighs on average about 300 kg (660 lb) and is about 2.4 m (8 ft) long, while the female sea lion weighs 100 kg (220 lb) and is 1.8 m (6 ft) long. The largest sea lions are Steller's sea lions, which can weigh 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) and grow to a length of 3.0 m (10 ft). Sea lions consume large quantities of food at a time and are known to eat about 5–8% of their body weight at a single feeding. Sea lions can move around 16 knots in water and at their fastest they can reach a speed of about 30 knots. Three species, the Australian sea lion, the Galápagos sea lion and the New Zealand sea lion, are listed as endangered.

Flea, the common name for the order Siphonaptera, includes 2,500 species of small flightless insects that live as external parasites of mammals and birds. Fleas live by ingesting the blood of their hosts. Adult fleas grow to about 3 millimetres long, are usually brown, and have bodies that are "flattened" sideways or narrow, enabling them to move through their hosts' fur or feathers. They lack wings; their hind legs are extremely well adapted for jumping. Their claws keep them from being dislodged, and their mouthparts are adapted for piercing skin and sucking blood. They can leap 50 times their body length, a feat second only to jumps made by another group of insects, the superfamily of froghoppers. Flea larvae are worm-like, with no limbs; they have chewing mouthparts and feed on organic debris left on their hosts' skin.

Trematoda is a class of flatworms known as flukes. They are obligate internal parasites with a complex life cycle requiring at least two hosts. The intermediate host, in which asexual reproduction occurs, is usually a snail. The definitive host, where the flukes sexually reproduce, is a vertebrate. Infection by trematodes can cause disease in all five traditional vertebrate classes: mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and fish.

Hector's beaked whale, is a small mesoplodont living in the Southern Hemisphere. This whale is named after Sir James Hector, a founder of the colonial museum in Wellington, New Zealand. The species has rarely been seen in the wild.

The South American sea lion, also called the southern sea lion and the Patagonian sea lion, is a sea lion found on the western and southeastern coasts of South America. It is the only member of the genus Otaria. The species is highly sexually dimorphic. Males have a large head and prominent mane. They mainly feed on fish and cephalopods and haul out on sand, gravel, rocky, or pebble beaches. In most populations, breeding males are both territorial and harem holding; they establish territories first and then try to herd females into them. The overall population of the species is considered stable, estimated at 265,000 animals.

Animal locomotion, in ethology, is any of a variety of methods that animals use to move from one place to another. Some modes of locomotion are (initially) self-propelled, e.g., running, swimming, jumping, flying, hopping, soaring and gliding. There are also many animal species that depend on their environment for transportation, a type of mobility called passive locomotion, e.g., sailing, kiting (spiders), rolling or riding other animals (phoresis).

Fasciola hepatica, also known as the common liver fluke or sheep liver fluke, is a parasitic trematode of the class Trematoda, phylum Platyhelminthes. It infects the livers of various mammals, including humans, and is transmitted by sheep and cattle to humans the world over. The disease caused by the fluke is called fasciolosis or fascioliasis, which is a type of helminthiasis and has been classified as a neglected tropical disease. Fasciolosis is currently classified as a plant/food-borne trematode infection, often acquired through eating the parasite's metacercariae encysted on plants. F. hepatica, which is distributed worldwide, has been known as an important parasite of sheep and cattle for decades and causes significant economic losses in these livestock species, up to £23 million in the UK alone. Because of its relatively large size and economic importance, it has been the subject of many scientific investigations and may be the best-known of any trematode species. F. hepatica's closest relative is Fasciola gigantica. These two flukes are sister species; they share many morphological features and can mate with each other.

Anisakis (a·nuh·saa·keez) is a genus of parasitic nematodes that have life cycles involving fish and marine mammals. They are infective to humans and cause anisakiasis. People who produce immunoglobulin E in response to this parasite may subsequently have an allergic reaction, including anaphylaxis, after eating fish infected with Anisakis species.

Metanephrops challengeri is a species of slim, pink lobster that lives around the coast of New Zealand. It is typically 13–18 cm (5–7 in) long and weighs around 100 g (3.5 oz). The carapace and abdomen are smooth, and adults are white with pink and brown markings and a conspicuous pair of long, slim claws. M. challengeri lives in burrows at depths of 140–640 m (460–2,100 ft) in a variety of sediments. Although individuals can live for up to 15 years, the species shows low fecundity, where small numbers of larvae hatch at an advanced stage.

X-ray microtomography, like tomography and X-ray computed tomography, uses X-rays to create cross-sections of a physical object that can be used to recreate a virtual model without destroying the original object. The prefix micro- is used to indicate that the pixel sizes of the cross-sections are in the micrometre range. These pixel sizes have also resulted in the terms high-resolution X-ray tomography, micro-computed tomography, and similar terms. Sometimes the terms high-resolution CT (HRCT) and micro-CT are differentiated, but in other cases the term high-resolution micro-CT is used. Virtually all tomography today is computed tomography.

Trichobilharzia regenti is a neuropathogenic parasitic flatworm of birds which also causes cercarial dermatitis in humans. The species was originally described in 1998 in the Czech Republic and afterwards it was detected also in other European countries, e.g. Denmark, Germany, France, Iceland, Poland, Switzerland, or Russia, and even in Iran. For its unique neurotropic behaviour in vertebrate hosts, the host-parasite interactions are extensively studied in terms of molecular biology, biochemistry and immunology.
Acanthocheilonema is a genus within the family Onchocercidae which comprises mainly tropical parasitic worms. Cobbold created the genus Acanthocheilonema with only one species, Acanthocheilonema dracunculoides, which was collected from aardwolf in the region of South Africa in the nineteenth century. These parasites have a wide range of mammalian species as hosts, including members of Carnivora, Macroscelidea, Rodentia, Pholidota, Edentata, and Marsupialia. Many species among several genera of filarioids exhibit a high degree of endemicity in studies done on mammalian species in Japan. However, no concrete evidence has confirmed any endemic species in the genus Acanthocheilonema.

Sea lice are copepods of the family Caligidae within the order Siphonostomatoida. They are marine ectoparasites that feed on the mucus, epidermal tissue, and blood of host fish. The roughly 559 species in 37 genera include around 162 Lepeophtheirus and 268 Caligus species.

The external morphology of Lepidoptera is the physiological structure of the bodies of insects belonging to the order Lepidoptera, also known as butterflies and moths. Lepidoptera are distinguished from other orders by the presence of scales on the external parts of the body and appendages, especially the wings. Butterflies and moths vary in size from microlepidoptera only a few millimetres long, to a wingspan of many inches such as the Atlas moth. Comprising over 160,000 described species, the Lepidoptera possess variations of the basic body structure which has evolved to gain advantages in adaptation and distribution.
Nicothoë astaci or the 'lobster louse' is an ectoparasitic copepod that parasitises the gills of the European lobster species Homarus gammarus. The lobster louse was first reported in 1826 by Audoin & Milne-Edwards. N. astaci has been found on lobsters inhabiting locations including Scotland, Lundy Island in the Bristol Channel and as far south as France and Portugal. The louse possesses a narrow suctorial mouthpart to feed on host haemolymph. Internally, In its adult form, Nicothoe is barely mobile and most likely remains in the same position for most of its life. The parasite occurs in groups, particularly near the base of the gills, and study has gone into its effects on the lobsters, which are considerably important, commercially. Not much is known about its life cycle, since there are significant gaps in knowledge of certain stages of its growth.

Gastrodiscoides is genus of zoonotic trematode under the class Trematoda. It has only one species, Gastrodiscoides hominis. It is a parasite of a variety of vertebrates, including humans. The first definitive specimen was described from a human subject in 1876. It is prevalent in Bangladesh, India, Burma, China, Kazakhstan, Philippines, Thailand, Vietnam, and the Volga Delta of Russia, with isolated cases from Africa, such as Nigeria. It is especially notable in the Assam, Bengal, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Orissa and Uttar Pradesh regions of India.

Argulus foliaceus, also known as the common fish louse, is a species of fish lice in the family Argulidae. It is "the most common and widespread native argulid in the Palaearctic" and "one of the most widespread crustacean ectoparasites of freshwater fish in the world", considering its distribution and range of hosts. It can cause the severe disease state argulosis in a wide variety of fish species. It is responsible for epizootic outbreaks that have led to the collapse of aquaculture operations. Fish lice are not related to lice, which are insects.

Echinophthiriidae is a family of lice in the suborder Anoplura, the sucking lice. This family of lice are parasites of seals and the river otter, and are the only insects that infest aquatic hosts.

The Uruguay - Buenos Aires Shelf marine ecoregion covers waters offshore of Uruguay, the mouth of the Rio de la Plata), and Buenos Aires Province of Argentina. It has an area of 258,490 square kilometres (99,800 sq mi) and a coastline of 1,300 kilometres (810 mi). Marine biodiversity is very high due to the mixing of currents, the mixing of fresh and salt water, the mixing of temperatures, and the broad, shallow continental shelf. Large amounts of nutrients arrive from the northwest flowing Malvinas Current and from the continental runoff of the Rio de la Plata. Aside from high populations of fish there are colonies of marine mammals, sea turtles, and seabirds.
















