
Ungulates are members of the diverse clade Euungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. Once part of the clade "Ungulata" along with the clade Paenungulata, "Ungulata" has since been determined to be a polyphyletic and thereby invalid clade based on molecular data. As a result, true ungulates had since been reclassified to the newer clade Euungulata in 2001 within the clade Laurasiatheria while Paenungulata has been reclassified to a distant clade Afrotheria. Living ungulates are divided into two orders: Perissodactyla including equines, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and Artiodactyla including cattle, antelope, pigs, giraffes, camels, sheep, deer, and hippopotamuses, among others. Cetaceans such as whales, dolphins, and porpoises are also classified as artiodactyls, although they do not have hooves. Most terrestrial ungulates use the hoofed tips of their toes to support their body weight while standing or moving. Two other orders of ungulates, Notoungulata and Litopterna, both native to South America, became extinct at the end of the Pleistocene, around 12,000 years ago.

Artiodactyls are mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla. Typically, they are ungulates which bear weight equally on two of their five toes: the third and fourth, often in the form of a hoof. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, most perissodactyls bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two is that many artiodactyls digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine as perissodactyls do. The advent of molecular biology, along with new fossil discoveries, found that cetaceans fall within this taxonomic branch, being most closely related to hippopotamuses. Some modern taxonomists thus apply the name Cetartiodactyla to this group, while others opt to include cetaceans within the existing name of Artiodactyla. Some researchers use "even-toed ungulates" to exclude cetaceans and only include terrestrial artiodactyls, making the term paraphyletic in nature.

Hippopotamidae is a family of stout, naked-skinned, and semiaquatic artiodactyl mammals, possessing three-chambered stomachs and walking on four toes on each foot. While they resemble pigs physiologically, their closest living relatives are the cetaceans. They are sometimes referred to as hippopotamids.

Anthracotherium is an extinct genus of artiodactyls characterized by having 44 teeth, with five semi-crescentic cusps on the crowns of the upper molars. The genus ranged from the middle Eocene period until the early Miocene, having a distribution throughout Eurasia. Material subjectively assigned to Anthracotherium from Pakistan suggests the last species died out soon after the start of the Miocene.

Elomeryx is an extinct genus of artiodactyl ungulate, and is among the earliest known anthracotheres. The genus was extremely widespread, first being found in Asia in the middle Eocene, in Europe during the latest Eocene, and having spread to North America by the early Oligocene. The closest living relatives of the Elomeryx are bovids, suids, and cetaceans.
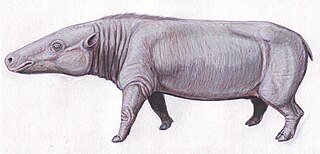
Anthracotheriidae is a paraphyletic family of extinct, hippopotamus-like artiodactyl ungulates related to hippopotamuses and whales. The oldest genus, Elomeryx, first appeared during the middle Eocene in Asia. They thrived in Africa and Eurasia, with a few species ultimately entering North America during the Oligocene. They died out in Europe and Africa during the Miocene, possibly due to a combination of climatic changes and competition with other artiodactyls, including pigs and true hippopotamuses. The youngest genus, Merycopotamus, died out in Asia during the late Pliocene, possibly for the same reasons. The family is named after the first genus discovered, Anthracotherium, which means "coal beast", as the first fossils of it were found in Paleogene-aged coal beds in France. Fossil remains of the anthracothere genus were discovered by the Harvard University and Geological Survey of Pakistan joint research project (Y-GSP) in the well-dated middle and late Miocene deposits of the Pothohar Plateau in northern Pakistan.
Kenyapotamus is a possible ancestor of living hippopotamuses that lived roughly 16 million to 8 million years ago during the Miocene epoch. Its name reflects that its fossils were first found in modern-day Kenya.

Merycopotamus is an extinct genus of Asian anthracothere that appeared during the Middle Miocene, and died out in the Late Pliocene. At the height of the genus' influence, species ranged throughout southern Asia. With the extinction of the last species, M. dissimilis, the lineage of anthracotheres came to an end. Merycopotamus was closely related to the anthracothere genus Libycosaurus, which, unlike the former, never left Africa. In fact, some African fossils originally placed in Merycopotamus, but are now referred to Libycosaurus.
Anthracothema was a genus of extinct artiodactyl ungulate mammals that lived in Myanmar during the late Eocene.

Anthracokeryx is a genus of extinct artiodactyl ungulate mammal belonging to Anthracotheriidae that lived in Asia during the middle to late Eocene.
Anthracohyus was a genus of extinct artiodactyl ungulate mammal belonging to Anthracotheriidae that lived in Asia during the middle to late Eocene.

Microbunodon was a genus of extinct artiodactyl mammals in the family Anthracotheriidae. It lived between the upper Eocene and the lower Pliocene. Its fossil remains have been found in Europe and Asia.
Paenanthracotherium was a genus of anthracothere that lived in Europe and Asia during the Oligocene.

Brachyodus was a genus of anthracothere that lived in Europe during the Early Miocene.

Helohyidae were a group of artiodactyl mammals. They were most prominent in the mid-to-upper Eocene.

The bothriodontines are a paraphyletic assemblage of anthracotheres that originated from Eurasia in the late middle Eocene (Bartonian). The group can be distinguished from other anthracothere lineages by their upper molars with the mesostyle that is occupied by the transverse valley, selenodont cusps, ventrally concave symphysis, elongated muzzles, with presence of a diastema between the canine and first premolar. The size range of the group ranged from small, basal forms to larger and more derived forms. During their evolution, the bothriodontines undergone a trend from evolving from small basal forms such as Qatraniodon into larger taxa such as Libycosaurus and Merycopotamus. Some genera the snouts became even more elongated and teeth specialized in a folivorous diet, while others like Merycopotamus became wide, heavy and shallow muzzles with teeth more adapted for grazing.

The microbunodontines were an extinct subfamily of anthracotheres that were predominately a Paleogene group of Eurasian artiodactyls. The group died out at the end of the Late Miocene. It comprised the genera Anthracokeryx, Geniokeryx, Microbunodon, and possibly Etruscotherium. They are different from the other anthracothere lineages by their smaller size, slenderer limbs and male specimens having laterally compressed, longer canines. They were originally classified as members of the other subfamily of anthracotheres, Anthracotheriinae but recent phylogenetic studies have found them to be their own clade sister to Bothriodontinae.

Ancodonta is an infraorder of semiaquatic artiodactyl ungulates including modern hippopotamus and all mammals closer to hippos than to cetaceans (whales). Ancodonts first appeared in the Middle Eocene, with some of the earliest representatives found in fossil deposits in Southeast Asia. Throughout their evolutionary history they have occupied different browsing and grazing niches in North America, Eurasia and Africa. The last continent is notable as they were among the first laurasiatherian mammals to have migrated to Africa from Europe, where they competed with the native afrothere herbivores for the same niches. Of the nearly 50 genera that have existed, only two of them are extant – Choeropsis and Hippopotamus. The interrelationships within the ancodonts has been contended. The traditional notion is that there at minimum two families Anthracotheriidae and Hippopotamidae and were merely sister taxa. However many detailed research of the dentition among ancodonts, as well as how some anthracotheres were similar to hippos in appearance, lead the current consensus where Anthracotheriidae is paraphyletic to Hippopotamidae. Among the anthracotheres members of Bothriodontinae are among the closest to the ancestry of hippos, with the Oligocene aged Epirigenys from Lokon, Turkana, Kenya being the sister taxon to hippos. In response of this many similar clade names have been used for this clade.
Heptacodon is an extinct genus of anthracothere endemic to North America during the Paleogene. They were medium to large-sized anthracotheres with a distinct facial features such short heavy rostrums and robust but simple molars. Heptacodon is a member of the anthracothere subfamily Anthracotheriinae, whose distribution as a whole are in North America and Eurasia. However Heptacodon has only been found in North America, with the species H. yeguaensis from Texas representing the oldest known anthracotheres to be found in North America dating to the middle Eocene. Fossils of this genus have been found in the states of North Dakota, Oregon, South Dakota, Texas, and Utah.
Ephelcomenus is an extinct genus of Paleogene artiodactyls endemic to western Europe. It contains one species E. filholi, which was first described by Richard Lydekker in 1889 but eventually classified to its own genus by the Swiss palaeontologist Johannes Hürzeler in 1938. It has an uncertain stratigraphic range, but some sources suggest that it was present in the Oligocene after the Grande Coupure turnover event of western Europe.














