
Gentianales is an order of flowering plants, included within the asterid clade of eudicots. It comprises more than 20,000 species in about 1,200 genera in 5 families. More than 80% of the species in this order belong to the family Rubiaceae.

Oleaceae, also known as the olive family, is a taxonomic family of flowering shrubs, trees, and a few lianas in the order Lamiales, It presently comprises 28 genera, one of which is recently extinct. The extant genera include Cartrema, which was resurrected in 2012. The number of species in the Oleaceae is variously estimated in a wide range around 700. The flowers are often numerous and highly odoriferous. The family has a subcosmopolitan distribution, ranging from the subarctic to the southernmost parts of Africa, Australia, and South America. Notable members include olive, ash, jasmine, and several popular ornamental plants including privet, forsythia, fringetrees, and lilac.

Loranthaceae, commonly known as the showy mistletoes, is a family of flowering plants. It consists of about 75 genera and 1,000 species of woody plants, many of them hemiparasites. The three terrestrial species are Nuytsia floribunda, Atkinsonia ligustrina, and Gaiadendron punctatum Loranthaceae are primarily xylem parasites, but their haustoria may sometimes tap the phloem, while Tristerix aphyllus is almost holoparasitic. For a more complete description of the Australian Loranthaceae, see Flora of Australia online., for the Malesian Loranthaceae see Flora of Malesia.

The gymnosperms are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae, the living members of which are also known as Acrogymnospermae. The term gymnosperm comes from the composite word in Greek: γυμνόσπερμος, literally meaning 'naked seeds'. The name is based on the unenclosed condition of their seeds. The non-encased condition of their seeds contrasts with the seeds and ovules of flowering plants (angiosperms), which are enclosed within an ovary. Gymnosperm seeds develop either on the surface of scales or leaves, which are often modified to form cones, or solitary as in yew, Torreya, Ginkgo. Gymnosperm lifecycles involve alternation of generations. They have a dominant diploid sporophyte phase and a reduced haploid gametophyte phase which is dependent on the sporophytic phase. The term "gymnosperm" is often used in paleobotany to refer to all non-angiosperm seed plants. In that case, to specify the modern monophyletic group of gymnosperms, the term Acrogymnospermae is sometimes used.

The Loganiaceae are a family of flowering plants classified in order Gentianales. The family includes up to 13 genera, distributed around the world's tropics. There are not any great morphological characteristics to distinguish these taxa from others in the order Gentianales.
In biology, gonochorism is a sexual system where there are only two sexes and each individual organism is either male or female. The term gonochorism is usually applied in animal species, the vast majority of which are gonochoric.

Griselinia is a genus of seven species of shrubs and trees, with a highly disjunct distribution native to New Zealand and South America. It is a classic example of the Antarctic flora. It is the sole genus in the family Griseliniaceae; in the past it was often placed in Cornaceae but differs from that in many features.

Male is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilization.
A kinin is any of various structurally related polypeptides, such as bradykinin and kallidin. They are members of the autacoid family. Kinins are peptides that are cleaved from kininogens by the process of kallikreins. Kallikreins activate kinins when stimulated.

A koilocyte is a squamous epithelial cell that has undergone a number of structural changes, which occur as a result of infection of the cell by human papillomavirus (HPV). Identification of these cells by pathologists can be useful in diagnosing various HPV-associated lesions.

Desfontainia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Columelliaceae, though it was placed formerly in Loganiaceae, Potaliaceae, or a family of its own, Desfontainiaceae.

Cannabigerol (CBG) is one of more than 120 identified cannabinoid compounds found in the plant genus Cannabis. Cannabigerol is the decarboxylated form of cannabigerolic acid, the parent molecule from which other cannabinoids are synthesized.
Cannabichromene (CBC), also called cannabichrome, cannanbichromene, pentylcannabichromene or cannabinochromene, is an anti-inflammatory which may contribute to the pain-killing effect of cannabis. It is one of the hundreds of cannabinoids found in the Cannabis plant, and is therefore a phytocannabinoid. It bears structural similarity to the other natural cannabinoids, including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), cannabidiol (CBD), and cannabinol (CBN), among others. CBC and its derivatives are as abundant as cannabinols in cannabis. It is not scheduled by the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. It is more common in tropical cannabis varieties.
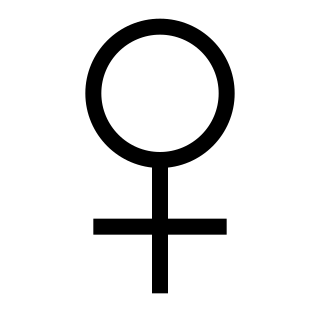
Female is the sex of an organism that produces the large non-motile ova, the type of gamete that fuses with the male gamete during sexual reproduction.

A diurnal cycle is any pattern that recurs every 24 hours as a result of one full rotation of the planet Earth around its axis. Earth's rotation causes surface temperature fluctuations throughout the day and night, as well as weather changes throughout the year. The diurnal cycle depends mainly on incoming solar radiation.

Buddleja nivea is a vigorous shrub endemic to western China, evergreen in the wild, but deciduous in cultivation in the UK. The plant was discovered by Wilson in the Yangtze basin at altitudes of 700 – 3,600 m. Introduced to cultivation in 1901, it was named by Duthie in 1905. Several plants similar to the species but originally treated as species and varieties in their own right have now been sunk as B. nivea.
Buddleja brachystachya is a small shrub endemic to the Yunnan, Szechuan and Kansu provinces of China, where it grows on open, rocky, often dry, places at altitudes of 2,000–2,400 m. It was first described and named by Diels in 1912.
Sanango is a genus of flowering plants containing a single species, Sanango racemosum. The genus was originally placed in family Loganiaceae but has since been variously placed in Scrophulariaceae, Gesneriaceae and Buddlejaceae. As of 2016 it is considered to be the sister genus to the family Gesneriaceae as previously defined, and the family was tentatively enlarged to include the genus, pending a revision of the families included in Lamiales. It has been placed as the only genus in the monotypic subfamily Sanangoideae.
Pieter Willem Leenhouts was a Dutch botanist. He worked at the Rijksherbarium from 1947 until his official retirement in 1991, and then was an honorary member of staff until 1999. He was editor of Blumea from 1973 to 1999.

Monoecy is a sexual system in seed plants where separate male and female cones or flowers are present on the same plant. It is a monomorphic sexual system alongside gynomonoecy, andromonoecy and trimonoecy.














