
Volvox is a polyphyletic genus of chlorophyte green algae in the family Volvocaceae. Volvox species form spherical colonies of up to 50,000 cells, and for this reason they are sometimes called globe algae. They live in a variety of freshwater habitats, and were first reported by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1700. Volvox diverged from unicellular ancestors approximately 200 million years ago.

Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae consisting of about 150 species of unicellular flagellates, found in stagnant water and on damp soil, in freshwater, seawater, and even in snow as "snow algae". Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics. One of the many striking features of Chlamydomonas is that it contains ion channels (channelrhodopsins) that are directly activated by light. Some regulatory systems of Chlamydomonas are more complex than their homologs in Gymnosperms, with evolutionarily related regulatory proteins being larger and containing additional domains.

Botryococcus is a genus of green algae. The cells form an irregularly shaped aggregate. Thin filaments connect the cells. The cell body is ovoid, 6 to 10 μm long, and 3 to 6 μm wide. Fossils of the genus are known since Precambrian times, and form the single largest biological contributor to crude oil, and are a major component of oil shales.

Ankistrodesmus is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is one of the most common types of phytoplankton in freshwater habitats around the world.

Asterococcus is a genus of green algae in the order Chlamydomonadales. It is planktonic in freshwater ponds and lakes, or benthic within mires and swamps. It is a common and widespread genus, but is rarely abundant.
Characiochloris is a genus of green algae in the family Characiochloridaceae. Characiochloris is epiphytic on freshwater algae, or found in soil.

Characium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae. It is very commonly found in freshwater habitats, where it is attached to phytoplankton or zooplankton.

Chlamydocapsa is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae.

Chloromonas is a genus of green algae in the family Chlamydomonadaceae. It is closely related to the model green algae, Chlamydomonas, and traditionally has been distinguished mainly through the absence of a pyrenoid.
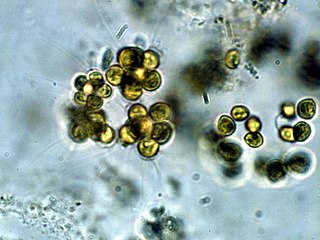
Micractinium is a genus of green algae in the family Chlorellaceae. Species of the genus Micractinium are common in freshwater habitats. A few species are found as endosymbionts of protozoa, such as Micractinium conductrix and Micractinium tetrahymenae.
Palmellopsis is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Palmellopsidaceae. They are either planktonic or attached to substrates in fresh water, or in aeroterrestrial habitats.

Paulschulzia is a genus of green algae, specifically of the family Tetrasporaceae.

Selenastrum is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is common in freshwater habitats around the world. Most species prefer temperate or warm-temperate waters.

Sorastrum is a genus of green algae in the family Hydrodictyaceae. It is a component of the phytoplankton of freshwater ponds, lakes, and ditches. Sorastrum is common in tropical to temperate regions of the world, but due to its small size it is often overlooked.
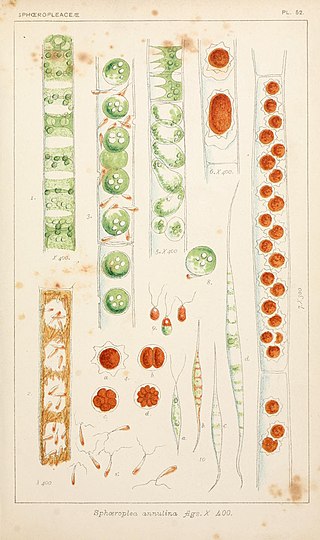
Sphaeroplea is a genus of green algae in the family Sphaeropleaceae. It was first circumscribed by the Swedish botanist Carl Adolph Agardh in 1824.

Stephanosphaera is a genus of green algae in the family Haematococcaceae, containing the single species Stephanosphaera pluvialis. It forms colonies of flagellated cells. Although it was once placed in the family Volvocaceae, it is not closely related to them; its sister is the unicellular genus Balticola.

Tetraspora is a genus of green algae in the family Tetrasporaceae of the order Chlamydomonadales, division Chlorophyta. Species of Tetraspora are unicellular green algae that exist in arrangements of four and consist of cells being packaged together in a gelatinous envelope that creates macroscopic colonies. These are primarily freshwater organisms, although there have been few cases where they have been found inhabiting marine environments and even contaminated water bodies. Tetraspora species can be found all around the globe, except in Antarctica. Despite the ubiquitous presence, the greatest growth of the genera's species is seen in the polar climatic zones.

Nephrocytium is a genus of green algae in the class Chlorophyceae. Formerly placed in the family Oocystaceae, it is currently placed in its own family, Nephrocytiaceae.

Aphanothece is a polyphyletic genus with 63 accepted species. The name is derived from the Greek words, ‘aphanes’ and ‘theke’ which mean “invisible" and “box or sheath” respectively. This genera is cosmopolitan, found in soils, thermal springs and other benthic, freshwater, marine, hypersaline, and moist terrestrial environments. Morphology can vary, with both microscopic and macroscopic colonies large enough to be collected and preserved in herbarium records.
Chlorolobion, sometimes spelled Chlorolobium, is a genus of algae belonging to the family Selenastraceae. The species of this genus are found in freshwater habitats in Europe and America.

















