
The Power Macintosh, later Power Mac, is a family of personal computers designed, manufactured, and sold by Apple Computer, Inc as the core of the Macintosh brand from March 1994 until August 2006.

Digital Visual Interface (DVI) is a video display interface developed by the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG). The digital interface is used to connect a video source, such as a video display controller, to a display device, such as a computer monitor. It was developed with the intention of creating an industry standard for the transfer of uncompressed digital video content.

A graphics card is a computer expansion card that generates a feed of graphics output to a display device such as a monitor. Graphics cards are sometimes called discrete or dedicated graphics cards to emphasize their distinction to an integrated graphics processor on the motherboard or the central processing unit (CPU). A graphics processing unit (GPU) that performs the necessary computations is the main component in a graphics card, but the acronym "GPU" is sometimes also used to erroneously refer to the graphics card as a whole.
Display Data Channel (DDC) is a collection of protocols for digital communication between a computer display and a graphics adapter that enable the display to communicate its supported display modes to the adapter and that enable the computer host to adjust monitor parameters, such as brightness and contrast.
Apple Inc. has sold a variety of LCD and CRT computer displays since introducing their first display in 1980. Apple paused production of their own standalone displays in 2016 and partnered with LG to design displays for Macs. In June 2019, the Pro Display XDR was introduced, however it was expensive and targeted for professionals. In March 2022, the Studio Display was launched as a consumer-targeted counterpart. These are currently the only Apple-branded displays available.

High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed video data and compressed or uncompressed digital audio data from an HDMI-compliant source device, such as a display controller, to a compatible computer monitor, video projector, digital television, or digital audio device. HDMI is a digital replacement for analog video standards.

The Video Graphics Array (VGA) connector is a standard connector used for computer video output. Originating with the 1987 IBM PS/2 and its VGA graphics system, the 15-pin connector went on to become ubiquitous on PCs, as well as many monitors, projectors and HD television sets.

Mini-VGA connectors are proprietary and non-standard alternative video connectors that were used on some laptops and other computer systems in place of a standard VGA connector. Apple, HP, and Asus each introduced separate connectors using the same moniker of "mini-VGA", but which are otherwise physically incompatible with each other.
An output device is any piece of computer hardware that converts information or data into a human-perceptible form or, historically, into a physical machine-readable form for use with other non-computerized equipment. It can be text, graphics, tactile, audio, or video. Examples include monitors, printers, speakers, headphones, projectors, GPS devices, optical mark readers, and braille readers.

The Apple Cinema Display is a line of flat-panel computer monitors developed and sold by Apple Inc. between 1999 and 2011. It was initially sold alongside the older line of Studio Displays, but eventually replaced them. Apple offered 20, 22, 23, 24, 27, and 30-inch sizes, with the last model being a 27-inch size with LED backlighting.

DB13W3 (13W3) is a style of D-subminiature connector used for analog video interfaces. The 13 refers to the total number of pins, the W refers to workstation and the 3 refers to the number of high-frequency pins. The connector was something of a pseudo-standard for high-end graphical workstations from the early 1990s to the early 2000s.
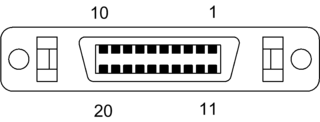
The VESA Digital Flat Panel (DFP) interface standard specifies a video connector and digital TMDS signaling for flat-panel displays. It features 20 pins and uses the PanelLink protocol; the standard is based on the preceding VESA Plug and Display (P&D) standard, ratified in 1997. Unlike the later, electrically-compatible Digital Visual Interface, DFP never achieved widespread implementation.

DisplayPort (DP) is a proprietary digital display interface developed by a consortium of PC and chip manufacturers and standardized by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA). It is primarily used to connect a video source to a display device such as a computer monitor. It can also carry audio, USB, and other forms of data.

VESA Plug and Display is a video connector that carries digital signals for monitors, such as flat panel displays and video projectors, ratified by Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) in 1997. Introduced around the same time as the competing connectors for the Digital Visual Interface and VESA's own Digital Flat Panel, it was marketed as a replacement for the VESA Enhanced Video Connector. Unlike DVI, it never achieved widespread implementation.

The Mini-DVI connector is used on certain Apple computers as a digital alternative to the Mini-VGA connector. Its size is between the full-sized DVI and the tiny Micro-DVI. It is found on the 12-inch PowerBook G4, the Intel-based iMac, the MacBook Intel-based laptop, the Intel-based Xserve, the 2009 Mac mini, and some late model eMacs.

Target Disk Mode is a boot mode unique to Macintosh computers.

The Mini DisplayPort is a miniaturized version of the DisplayPort audio-visual digital interface.
Audio connectors and video connectors are electrical or optical connectors for carrying audio or video signals. Audio interfaces or video interfaces define physical parameters and interpretation of signals. For digital audio and digital video, this can be thought of as defining the physical layer, data link layer, and most or all of the application layer. For analog audio and analog video these functions are all represented in a single signal specification like NTSC or the direct speaker-driving signal of analog audio.

The Apple Studio Display is a series of non-widescreen LCD and CRT displays manufactured and sold by Apple Computer, Inc. and introduced in 1998. After the 1999 introduction of the widescreen Apple Cinema Display, the Apple Studio Display line ran concurrently until it was discontinued in 2004. With the exception of the last model, the 5:4 17" Apple Studio Display, all Apple Studio Displays had an aspect ratio of 4:3.

USB-C, or USB Type-C, is a 24-pin connector that supersedes previous USB connectors and can carry audio, video, and other data, to connect to monitors or external drives. It can also provide and receive power, to power, e.g., a laptop or a mobile phone. It is used not only by USB technology, but also by other protocols, including Thunderbolt, PCIe, HDMI, DisplayPort, and others. It is extensible to support future protocols.

















