
Ammonoids are extinct spiral shelled cephalopods comprising the subclass Ammonoidea. They are more closely related to living coleoids than they are to shelled nautiloids. The earliest ammonoids appeared during the Devonian, with the last species vanishing during or soon after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. They are often called ammonites, which is most frequently used for members of the order Ammonitida, the only remaining group of ammonoids from the Jurassic up until their extinction.

Redlichiida is an order of trilobites, a group of extinct marine arthropods. Species assigned to the order Redlichiida are among the first trilobites to appear in the fossil record, about halfway during the Lower Cambrian. Due to the difficulty to relate sediments in different areas, there remains some discussion, but among the earliest are Fallotaspis, and Lemdadella, both belonging to this order. The first representatives of the orders Corynexochida and Ptychopariida also appear very early on and may prove to be even earlier than any redlichiid species. In terms of anatomical comparison, the earliest redlichiid species are probably ancestral to all other trilobite orders and share many primitive characters. The last redlichiid trilobites died out before the end of the Middle Cambrian.
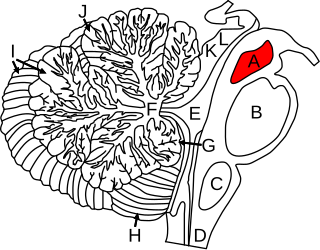
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
Astereognosis is the inability to identify an object by active touch of the hands without other sensory input, such as visual or sensory information. An individual with astereognosis is unable to identify objects by handling them, despite intact elementary tactile, proprioceptive, and thermal sensation. With the absence of vision, an individual with astereognosis is unable to identify what is placed in their hand based on cues such as texture, size, spatial properties, and temperature. As opposed to agnosia, when the object is observed visually, one should be able to successfully identify the object.

Adonis is a genus of about 20–30 species of flowering plants of the crowfoot family, Ranunculaceae, native to Europe and Asia.

Dalmanites is a genus of trilobite in the order Phacopida. They lived from the Late Ordovician to Middle Devonian.

The green lanternshark is a species of dogfish shark in the family Etmopteridae, found in the western central Atlantic Ocean. This species usually occurs on the upper continental slope below a depth of 350 m (1,150 ft). Reaching 26 cm (10 in) in length, the green lanternshark has a slender body with a long, thin tail and low, conical dermal denticles on its flanks. It is dark brown or gray with ventral black coloration, which contain light-emitting photophores that may serve a cryptic and/or social function. Green lanternsharks are thought to be gregarious and may attack their prey, squid and octopus often larger than themselves, in packs. Reproduction is aplacental viviparous, with females giving birth to litters of one to three young. This relatively common shark is an occasional, valueless bycatch of commercial fisheries; currently it does not appear to be significantly threatened by human activities.

The dwarf lanternshark is a species of dogfish shark in the family Etmopteridae and is the smallest shark in the world, reaching a maximum known length of 20 cm (8 in). It is known to be present only on the upper continental slopes off Colombia and Venezuela, at a depth of 283–439 m (928–1,440 ft). This species can be identified by its small size at maturity, long flattened head, and pattern of black ventral markings and a mid-dorsal line. Like other members of its genus, it is capable of producing light from a distinctive array of photophores. Reproduction is aplacental viviparous, with females gestating two or three young at a time. The dwarf lanternshark is not significant to commercial fisheries, but could be threatened by mortality from bycatch; the degree of impact from human activities on its population is unknown.
Dimorphoceratoidea is one of seventeen superfamilies included in the ammonoid suborder Goniatitina, a variety of shelled cephalopods that lived during the late Paleozoic.

Gastrioceratoidea is one of 17 superfamilies in the suborder Goniatitina, ammonoid cephalopods from the Late Paleozoic.
Thalassoceratoidea, formerly Thalassocerataceae, is a superfamily of Late Paleozoic ammonites characterized by their thick-discoidal to subglobular, involute shells with narrow or closed umbilici and biconvex growth striae with ventral sinuses. The ventral lobe of the suture, which straddles the outer rim, is wide, and bifid, with a tall median saddle.

Prolecanitida is an order of extinct ammonoid cephalopods, the major Late Paleozoic group of ammonoids alongside the order Goniatitida. Prolecanitids had narrow shells, discoidal (disc-shaped) to thinly lenticular (lens-shaped). They retained a retrochoanitic siphuncle, a simple form with septal necks extending backwards. As is typical for ammonoids, the siphuncle sits along the ventral margin of the shell.
The Centroceratidae is the ancestral family of the Trigonoceratoidea and of the equivalent Centroceratina; extinct shelled cephalopods belonging to the order Nautilida
The painted swellshark is a little-known species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae, found in eastern Indonesia. This species reaches a maximum known length of 72 cm (28 in), and has a thick body with a short, broad and flattened head. It is dark gray with a variegated pattern of irregular darker and lighter blotches above, and lighter below with gray blotches and speckling on the snout. Like other swellsharks, it can inflate itself as a defensive measure.
The flagtail swellshark is a little-known species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae, found at a depth of 480–700 m (1,570–2,300 ft) off northeastern Queensland, and possibly also nearby islands. This stout-bodied shark has a short, broad, and flattened head with a capacious mouth. Adults have a variegated brown coloration with 9–10 darker dorsal saddles and V-shaped blotch at the tip of the upper caudal fin lobe. Juveniles are yellow with narrow brown bars instead of saddles, and a distinctive marking between the spiracles shaped like two loops connected by a line. Like other swellsharks, this species can inflate its body when threatened.
The phallic catshark is a species of shark belonging to the family Pentanchidae, the deepwater catsharks. It is found on or near the ocean floor, in the deep waters off New Caledonia and Vanuatu. A slender species attaining a length of 46 cm (18 in), it is characterized by a long caudal fin bearing a crest of enlarged dermal denticles along the dorsal margin, and very long claspers in adult males. This shark is gray-colored, with four dark saddles along the back and tail.
Cravevoceras is an Upper Paleozoic ammonite in the goniatite family Cravenoceratidae, probably derived from Pachylyroceras and contemporary with other cravenoceratid genera like Caenolyroceras, Tympanoceras and later Alaoceras and Lyrogoniatites. It is also a member of the Neoglyphioceratoidea.
Sphegina uncinata is a species of hoverfly in the family Syrphidae found in Myanmar. It's easily identified by a straight dorsal line of frontal prominence that ends just before the ocellar triangle, a strongly projecting mouth edge, and a vibrissal angle more strongly protruding than the frontal prominence.
Sphegina (Asiosphegina) carinata is a species of hoverfly in the family Syrphidae found in Kambaiti Pass, Myanmar, a montane forest with swampy areas and streams located 2000 meters above sea level.
Sphegina kumaoniensis is a species of hoverfly in the family Syrphidae found in India, Thailand, and northeast Myanmar. It's characterized by a convex dorsal line of frontal prominence that ends clearly before the ocellar triangle as well as a mouthedge less strongly projecting, vibrissal angle less protruding or equal with the frontal prominence.








